+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of hexameric yeast Lon protease (PIM1) highlights the importance of conserved structural elements. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | J Biol Chem, Vol. 298, Issue 3, Page 101694, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Feb 7, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Jie Yang / Albert S Song / R Luke Wiseman / Gabriel C Lander /  |
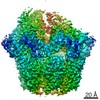
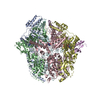
| PubMed Abstract | Lon protease is a conserved ATP-dependent serine protease composed of an AAA+ domain that mechanically unfolds substrates and a serine protease domain that degrades these unfolded substrates. In ...Lon protease is a conserved ATP-dependent serine protease composed of an AAA+ domain that mechanically unfolds substrates and a serine protease domain that degrades these unfolded substrates. In yeast, dysregulation of Lon protease (PIM1) attenuates lifespan and leads to gross mitochondrial morphological perturbations. Although structures of the bacterial and human Lon protease reveal a hexameric assembly, yeast PIM1 was speculated to form a heptameric assembly and is uniquely characterized by a ∼50-residue insertion between the ATPase and protease domains. To further understand the yeast-specific properties of PIM1, we determined a high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of PIM1 in a substrate-translocating state. Here, we reveal that PIM1 forms a hexamer, conserved with that of bacterial and human Lon proteases, wherein the ATPase domains form a canonical closed spiral that enables pore loop residues to translocate substrates to the protease chamber. In the substrate-translocating state, PIM1 protease domains form a planar protease chamber in an active conformation and are uniquely characterized by a ∼15-residue C-terminal extension. These additional C-terminal residues form an α-helix located along the base of the protease domain. Finally, we did not observe density for the yeast-specific insertion between the ATPase and protease domains, likely due to high conformational flexibility. Biochemical studies to investigate the insertion using constructs that truncated or replaced the insertion with a glycine-serine linker suggest that the yeast-specific insertion is dispensable for PIM1's enzymatic function. Altogether, our structural and biochemical studies highlight unique components of PIM1 machinery and demonstrate evolutionary conservation of Lon protease function. |
 External links External links |  J Biol Chem / J Biol Chem /  PubMed:35143841 / PubMed:35143841 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.3 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-25502, PDB-7sxo: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE /  Protease / AAA+ ATPase Protease / AAA+ ATPase |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers