[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
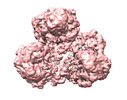
Yorodumi- EMDB-32779: Cryo-EM structure of human pyruvate carboxylase with acetyl-CoA i... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
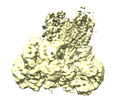
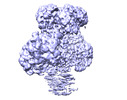
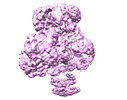
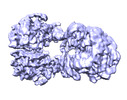
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human pyruvate carboxylase with acetyl-CoA in the intermediate state 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / Biotin transport and metabolism /  pyruvate carboxylase / pyruvate carboxylase /  pyruvate carboxylase activity / viral RNA genome packaging / NADP metabolic process / positive regulation by host of viral process / pyruvate metabolic process / NADH metabolic process / pyruvate carboxylase activity / viral RNA genome packaging / NADP metabolic process / positive regulation by host of viral process / pyruvate metabolic process / NADH metabolic process /  Gluconeogenesis ...Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / Biotin transport and metabolism / Gluconeogenesis ...Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / Biotin transport and metabolism /  pyruvate carboxylase / pyruvate carboxylase /  pyruvate carboxylase activity / viral RNA genome packaging / NADP metabolic process / positive regulation by host of viral process / pyruvate metabolic process / NADH metabolic process / pyruvate carboxylase activity / viral RNA genome packaging / NADP metabolic process / positive regulation by host of viral process / pyruvate metabolic process / NADH metabolic process /  Gluconeogenesis / Gluconeogenesis /  biotin binding / viral release from host cell / biotin binding / viral release from host cell /  gluconeogenesis / lipid metabolic process / gluconeogenesis / lipid metabolic process /  mitochondrial matrix / negative regulation of gene expression / mitochondrial matrix / negative regulation of gene expression /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   human (human) human (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chai P / Lan P / Wu J / Lei M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Mechanistic insight into allosteric activation of human pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl-CoA. Authors: Peiwei Chai / Pengfei Lan / Shaobai Li / Deqiang Yao / Chenchen Chang / Mi Cao / Yafeng Shen / Shengfang Ge / Jian Wu / Ming Lei / Xianqun Fan /  Abstract: Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes the two-step carboxylation of pyruvate to produce oxaloacetate, playing a key role in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis in cells. Given its involvement in ...Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes the two-step carboxylation of pyruvate to produce oxaloacetate, playing a key role in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis in cells. Given its involvement in multiple diseases, PC has been regarded as a potential therapeutic target for obesity, diabetes, and cancer. Albeit acetyl-CoA has been recognized as the allosteric regulator of PC for over 60 years, the underlying mechanism of how acetyl-CoA induces PC activation remains enigmatic. Herein, by using time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy, we have captured the snapshots of PC transitional states during its catalytic cycle. These structures and the biochemical studies reveal that acetyl-CoA stabilizes PC in a catalytically competent conformation, which triggers a cascade of events, including ATP hydrolysis and the long-distance communication between the two reactive centers. These findings provide an integrated picture for PC catalysis and unveil the unique allosteric mechanism of acetyl-CoA in an essential biochemical reaction in all kingdoms of life. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32779.map.gz emd_32779.map.gz | 105.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32779-v30.xml emd-32779-v30.xml emd-32779.xml emd-32779.xml | 13.1 KB 13.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_32779.png emd_32779.png | 118.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_32779_additional_1.map.gz emd_32779_additional_1.map.gz | 4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32779 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32779 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32779 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32779 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7wtdMC  7wtaC  7wtbC  7wtcC  7wteC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32779.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 115.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32779.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 115.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_32779_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PC
| Entire | Name: PC |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: PC
| Supramolecule | Name: PC / type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial
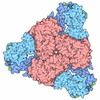
| Macromolecule | Name: Pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  pyruvate carboxylase pyruvate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   human (human) human (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 129.799359 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MLKFRTVHGG LRLLGIRRTS TAPAASPNVR RLEYKPIKKV MVANRGEIAI RVFRACTELG IRTVAIYSEQ DTGQMHRQKA DEAYLIGRG LAPVQAYLHI PDIIKVAKEN NVDAVHPGYG FLSERADFAQ ACQDAGVRFI GPSPEVVRKM GDKVEARAIA I AAGVPVVP ...String: MLKFRTVHGG LRLLGIRRTS TAPAASPNVR RLEYKPIKKV MVANRGEIAI RVFRACTELG IRTVAIYSEQ DTGQMHRQKA DEAYLIGRG LAPVQAYLHI PDIIKVAKEN NVDAVHPGYG FLSERADFAQ ACQDAGVRFI GPSPEVVRKM GDKVEARAIA I AAGVPVVP GTDAPITSLH EAHEFSNTYG FPIIFKAAYG GGGRGMRVVH SYEELEENYT RAYSEALAAF GNGALFVEKF IE KPRHIEV QILGDQYGNI LHLYERDCSI QRRHQKVVEI APAAHLDPQL RTRLTSDSVK LAKQVGYENA GTVEFLVDRH GKH YFIEVN SRLQVEHTVT EEITDVDLVH AQIHVAEGRS LPDLGLRQEN IRINGCAIQC RVTTEDPARS FQPDTGRIEV FRSG EGMGI RLDNASAFQG AVISPHYDSL LVKVIAHGKD HPTAATKMSR ALAEFRVRGV KTNIAFLQNV LNNQQFLAGT VDTQF IDEN PELFQLRPAQ NRAQKLLHYL GHVMVNGPTT PIPVKASPSP TDPVVPAVPI GPPPAGFRDI LLREGPEGFA RAVRNH PGL LLMDTTFRDA HQSLLATRVR THDLKKIAPY VAHNFSKLFS MENWGGATFD VAMRFLYECP WRRLQELREL IPNIPFQ ML LRGANAVGYT NYPDNVVFKF CEVAKENGMD VFRVFDSLNY LPNMLLGMEA AGSAGGVVEA AISYTGDVAD PSRTKYSL Q YYMGLAEELV RAGTHILCIK DMAGLLKPTA CTMLVSSLRD RFPDLPLHIH THDTSGAGVA AMLACAQAGA DVVDVAADS MSGMTSQPSM GALVACTRGT PLDTEVPMER VFDYSEYWEG ARGLYAAFDC TATMKSGNSD VYENEIPGGQ YTNLHFQAHS MGLGSKFKE VKKAYVEANQ MLGDLIKVTP SSKIVGDLAQ FMVQNGLSRA EAEAQAEELS FPRSVVEFLQ GYIGVPHGGF P EPFRSKVL KDLPRVEGRP GASLPPLDLQ ALEKELVDRH GEEVTPEDVL SAAMYPDVFA HFKDFTATFG PLDSLNTRLF LQ GPKIAEE FEVELERGKT LHIKALAVSD LNRAGQRQVF FELNGQLRSI LVKDTQAMKE MHFHPKALKD VKGQIGAPMP GKV IDIKVV AGAKVAKGQP LCVLSAMKME TVVTSPMEGT VRKVHVTKDM TLEGDDLILE IE |
-Macromolecule #2: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #3: COENZYME A
| Macromolecule | Name: COENZYME A / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: COA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 767.534 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-COA: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 79353 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z
Z Y
Y X
X