[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-26738: Integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain in complex with adenylate cyclas... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
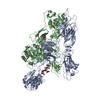
| Title | Integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain in complex with adenylate cyclase toxin RTX751 and M1F5 Fab | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map of global and local sharpened maps | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular extravasation / ectodermal cell differentiation / integrin alphaM-beta2 complex / positive regulation of prostaglandin-E synthase activity / response to curcumin / positive regulation of neutrophil degranulation / response to Gram-positive bacterium / positive regulation of microglial cell mediated cytotoxicity / complement component C3b binding / vertebrate eye-specific patterning ...cellular extravasation / ectodermal cell differentiation / integrin alphaM-beta2 complex / positive regulation of prostaglandin-E synthase activity / response to curcumin / positive regulation of neutrophil degranulation / response to Gram-positive bacterium / positive regulation of microglial cell mediated cytotoxicity / complement component C3b binding / vertebrate eye-specific patterning /  cytolysis / complement-mediated synapse pruning / Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade / leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process / cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / cytolysis / complement-mediated synapse pruning / Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade / leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process / cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules / complement receptor mediated signaling pathway / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion /  integrin complex / cargo receptor activity / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / integrin complex / cargo receptor activity / cell adhesion mediated by integrin /  phagocytosis, engulfment / leukocyte cell-cell adhesion / amyloid-beta clearance / plasma membrane raft / tertiary granule membrane / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / endothelial cell migration / Integrin cell surface interactions / specific granule membrane / phagocytosis, engulfment / leukocyte cell-cell adhesion / amyloid-beta clearance / plasma membrane raft / tertiary granule membrane / positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane / endothelial cell migration / Integrin cell surface interactions / specific granule membrane /  phagocytosis / response to mechanical stimulus / forebrain development / phagocytosis / response to mechanical stimulus / forebrain development /  heat shock protein binding / heat shock protein binding /  cell adhesion molecule binding / cell adhesion molecule binding /  receptor-mediated endocytosis / cell-matrix adhesion / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / response to ischemia / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / microglial cell activation / receptor-mediated endocytosis / cell-matrix adhesion / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / response to ischemia / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / microglial cell activation /  cell-cell adhesion / positive regulation of angiogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / cell-cell adhesion / positive regulation of angiogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process /  integrin binding / response to estradiol / integrin binding / response to estradiol /  amyloid-beta binding / amyloid-beta binding /  toxin activity / Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling / toxin activity / Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling /  cell adhesion / cell adhesion /  membrane raft / external side of plasma membrane / membrane raft / external side of plasma membrane /  innate immune response / innate immune response /  calcium ion binding / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding / calcium ion binding / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding /  cell surface / cell surface /  extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Bordetella pertussis (bacteria) Bordetella pertussis (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Goldsmith JA / McLellan JS | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for non-canonical integrin engagement by Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin. Authors: Jory A Goldsmith / Andrea M DiVenere / Jennifer A Maynard / Jason S McLellan /  Abstract: Integrins are ubiquitous cell-surface heterodimers that are exploited by pathogens and toxins, including leukotoxins that target β integrins on phagocytes. The Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin ...Integrins are ubiquitous cell-surface heterodimers that are exploited by pathogens and toxins, including leukotoxins that target β integrins on phagocytes. The Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin (ACT) uses the αβ integrin as a receptor, but the structural basis for integrin binding and neutralization by antibodies is poorly understood. Here, we use cryoelectron microscopy to determine a 2.7 Å resolution structure of an ACT fragment bound to αβ. This structure reveals that ACT interacts with the headpiece and calf-2 of the α subunit in a non-canonical manner specific to bent, inactive αβ. Neutralizing antibody epitopes map to ACT residues involved in α binding, providing the basis for antibody-mediated attachment inhibition. Furthermore, binding to αβ positions the essential ACT acylation sites, which are conserved among toxins exported by type I secretion systems, at the cell membrane. These findings reveal a structural mechanism for integrin-mediated attachment and explain antibody-mediated neutralization of ACT intoxication. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_26738.map.gz emd_26738.map.gz | 109 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-26738-v30.xml emd-26738-v30.xml emd-26738.xml emd-26738.xml | 17 KB 17 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_26738.png emd_26738.png | 58.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26738 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26738 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26738 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7uslMC  7usmC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_26738.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 147.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_26738.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 147.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map of global and local sharpened maps | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.073 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain with adenylat...
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain with adenylate cyclase toxin RTX domain and M1F5 Fab |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain with adenylat...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of integrin alphaM/beta2 ectodomain with adenylate cyclase toxin RTX domain and M1F5 Fab type: complex / Chimera: Yes / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Integrin alpha-M
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin alpha-M / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 128.455289 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: FNLDTENAMT FQENARGFGQ SVVQLQGSRV VVGAPQEIVA ANQRGSLYQC DYSTGSCEPI RLQVPVEAVN MSLGLSLAAT TSPPQLLAC GPTVHQTCSE NTYVKGLCFL FGSNLRQQPQ KFPEALRGCP QEDSDIAFLI DGSGSIIPHD FRRMKEFVST V MEQLKKSK ...String: FNLDTENAMT FQENARGFGQ SVVQLQGSRV VVGAPQEIVA ANQRGSLYQC DYSTGSCEPI RLQVPVEAVN MSLGLSLAAT TSPPQLLAC GPTVHQTCSE NTYVKGLCFL FGSNLRQQPQ KFPEALRGCP QEDSDIAFLI DGSGSIIPHD FRRMKEFVST V MEQLKKSK TLFSLMQYSE EFRIHFTFKE FQNNPNPRSL VKPITQLLGR THTATGIRKV VRELFNITNG ARKNAFKILV VI TDGEKFG DPLGYEDVIP EADREGVIRY VIGVGDAFRS EKSRQELNTI ASKPPRDHVF QVNNFEALKT IQNQLREKIF AIE GTQTGS SSSFEHEMSQ EGFSAAITSN GPLLSTVGSY DWAGGVFLYT SKEKSTFINM TRVDSDMNDA YLGYAAAIIL RNRV QSLVL GAPRYQHIGL VAMFRQNTGM WESNANVKGT QIGAYFGASL CSVDVDSNGS TDLVLIGAPH YYEQTRGGQV SVCPL PRGR ARWQCDAVLY GEQGQPWGRF GAALTVLGDV NGDKLTDVAI GAPGEEDNRG AVYLFHGTSG SGISPSHSQR IAGSKL SPR LQYFGQSLSG GQDLTMDGLV DLTVGAQGHV LLLRSQPVLR VKAIMEFNPR EVARNVFECN DQVVKGKEAG EVRVCLH VQ KSTRDRLREG QIQSVVTYDL ALDSGRPHSR AVFNETKNST RRQTQVLGLT QTCETLKLQL PNCIEDPVSP IVLRLNFS L VGTPLSAFGN LRPVLAEDAQ RLFTALFPFE KNCGNDNICQ DDLSITFSFM SLDCLVVGGP REFNVTVTVR NDGEDSYRT QVTFFFPLDL SYRKVSTLQN QRSQRSWRLA CESASSTEVS GALKSTSCSI NHPIFPENSE VTFNITFDVD SKASLGNKLL LKANVTSEN NMPRTNKTEF QLELPVKYAV YMVVTSHGVS TKYLNFTASE NTSRVMQHQY QVSNLGQRSL PISLVFLVPV R LNQTVIWD RPQVTFSENL SSTCHTKERL PSHSDFLAEL RKAPVVNCSI AVCQRIQCDI PFFGIQEEFN ATLKGNLSFD WY IKTSHNH LLIVSTAEIL FNDSVFTLLP GQGAFVRSQT ETKVEPFEVP NGCGGLEVLF QGPGENAQCE KELQALEKEN AQL EWELQA LEKELAQWSH PQFEKGGGSG GGGSGGSAWS HPQFEK |
-Macromolecule #2: Integrin beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80.784938 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QECTKFKVSS CRECIESGPG CTWCQKLNFT GPGDPDSIRC DTRPQLLMRG CAADDIMDPT SLAETQEDHN GGQKQLSPQK VTLYLRPGQ AAAFNVTFRR AKGYPIDLYY LMDLSYSMLD DLRNVKKLGG DLLRALNEIT ESGRIGFGSF VDKTVLPFVN T HPDKLRNP ...String: QECTKFKVSS CRECIESGPG CTWCQKLNFT GPGDPDSIRC DTRPQLLMRG CAADDIMDPT SLAETQEDHN GGQKQLSPQK VTLYLRPGQ AAAFNVTFRR AKGYPIDLYY LMDLSYSMLD DLRNVKKLGG DLLRALNEIT ESGRIGFGSF VDKTVLPFVN T HPDKLRNP CPNKEKECQP PFAFRHVLKL TNNSNQFQTE VGKQLISGNL DAPEGGLDAM MQVAACPEEI GWRNVTRLLV FA TDDGFHF AGDGKLGAIL TPNDGRCHLE DNLYKRSNEF DYPSVGQLAH KLAENNIQPI FAVTSRMVKT YEKLTEIIPK SAV GELSED SSNVVHLIKN AYNKLSSRVF LDHNALPDTL KVTYDSFCSN GVTHRNQPRG DCDGVQINVP ITFQVKVTAT ECIQ EQSFV IRALGFTDIV TVQVLPQCEC RCRDQSRDRS LCHGKGFLEC GICRCDTGYI GKNCECQTQG RSSQELEGSC RKDNN SIIC SGLGDCVCGQ CLCHTSDVPG KLIYGQYCEC DTINCERYNG QVCGGPGRGL CFCGKCRCHP GFEGSACQCE RTTEGC LNP RRVECSGRGR CRCNVCECHS GYQLPLCQEC PGCPSPCGKY ISCAECLKFE KGPFGKNCSA ACPGLQLSNN PVKGRTC KE RDSEGCWVAY TLEQQDGMDR YLIYVDESRE CVAGPDGCGL EVLFQGPGKN AQCKKKLQAL KKKNAQLKWK LQALKKKL A QGGHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #3: Bifunctional hemolysin-adenylate cyclase
| Macromolecule | Name: Bifunctional hemolysin-adenylate cyclase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bordetella pertussis (bacteria) Bordetella pertussis (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 100.286688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: GPGSANSDGL RKMLADLQAG WNASSVIGVQ TTEISKSALE LAAITGNADN LKSVDVFVDR FVQGERVAGQ PVVLDVAAGG IDIASRKGE RPALTFITPL AAPGEEQRRR TKTGKSEFTT FVEIVGKQDR WRIRDGAADT TIDLAKVVSQ LVDANGVLKH S IKLDVIGG ...String: GPGSANSDGL RKMLADLQAG WNASSVIGVQ TTEISKSALE LAAITGNADN LKSVDVFVDR FVQGERVAGQ PVVLDVAAGG IDIASRKGE RPALTFITPL AAPGEEQRRR TKTGKSEFTT FVEIVGKQDR WRIRDGAADT TIDLAKVVSQ LVDANGVLKH S IKLDVIGG DGDDVVLANA SRIHYDGGAG TNTVSYAALG RQDSITVSAD GERFNVRKQL NNANVYREGV ATQTTAYGKR TE NVQYRHV ELARVGQLVE VDTLEHVQHI IGGAGNDSIT GNAHDNFLAG GSGDDRLDGG AGNDTLVGGE GQNTVIGGAG DDV FLQDLG VWSNQLDGGA GVDTVKYNVH QPSEERLERM GDTGIHADLQ KGTVEKWPAL NLFSVDHVKN IENLHGSRLN DRIA GDDQD NELWGHDGND TIRGRGGDDI LRGGLGLDTL YGEDGNDIFL QDDETVSDDI DGGAGLDTVD YSAMIHPGRI VAPHE YGFG IEADLSREWV RKASALGVDY YDNVRNVENV IGTSMKDVLI GDAQANTLMG QGGDDTVRGG DGDDLLFGGD GNDMLY GDA GNDTLYGGLG DDTLEGGAGN DWFGQTQARE HDVLRGGDGV DTVDYSQTGA HAGIAAGRIG LGILADLGAG RVDKLGE AG SSAYDTVSGI ENVVGTELAD RITGDAQANV LRGAGGADVL AGGEGDDVLL GGDGDDQLSG DAGRDRLYGE AGDDWFFQ D AANAGNLLDG GDGRDTVDFS GPGRGLDAGA KGVFLSLGKG FASLMDEPET SNVLRNIENA VGSARDDVLI GDAGANVLN GLAGNDVLSG GAGDDVLLGD EGSDLLSGDA GNDDLFGGQG DDTYLFGVGY GHDTIYESGG GHDTIRINAG ADQLWFARQG NDLEIRILG TDDALTVHDW YRDADHRVEI IHAANQAVDQ AGIEKLVEAM AQYPDPGAAA AAPPAARVPD TLMQSLAVNW R |
-Macromolecule #4: M1F5 fab heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: M1F5 fab heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.665729 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QVQLKQSGPE LVKPGASVRM SCKGSGYSFT FHNIHWVKQR PGQGLEWIGW IYPGDGNTKY NEKFKGKTTL TVDKSSNTAY MLLSSLTSE DSAIYFCAYG NYYFDQWGQG TTLTVSSRST KGPSVFPLAP SSKSTSGGTA ALGCLVKDYF PEPVTVSWNS G ALTSGVHT ...String: QVQLKQSGPE LVKPGASVRM SCKGSGYSFT FHNIHWVKQR PGQGLEWIGW IYPGDGNTKY NEKFKGKTTL TVDKSSNTAY MLLSSLTSE DSAIYFCAYG NYYFDQWGQG TTLTVSSRST KGPSVFPLAP SSKSTSGGTA ALGCLVKDYF PEPVTVSWNS G ALTSGVHT FPAVLQSSGL YSLSSVVTVP SSSLGTQTYI CNVNHKPSNT KVDKKVEPKS CDKGLEVLFQ |
-Macromolecule #5: M1F5 fab light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: M1F5 fab light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.360854 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: IQMMQSTSSL SASLGDRVTI SCSASQGITN YLNWYQQKPD GTVKLLIYYT SSLHSGVPSR FSGSGSGTDY SLTISNLEPE DIATYYCQQ YSNLPWTFGG GTKLEIKRTV AAPSVFIFPP SDEQLKSGTA SVVCLLNNFY PREAKVQWKV DNALQSGNSQ E SVTEQDSK ...String: IQMMQSTSSL SASLGDRVTI SCSASQGITN YLNWYQQKPD GTVKLLIYYT SSLHSGVPSR FSGSGSGTDY SLTISNLEPE DIATYYCQQ YSNLPWTFGG GTKLEIKRTV AAPSVFIFPP SDEQLKSGTA SVVCLLNNFY PREAKVQWKV DNALQSGNSQ E SVTEQDSK DSTYSLSSTL TLSKADYEKH KVYACEVTHQ GLSSPVTKSF NRGEC |
-Macromolecule #8: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 33 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #9: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 11 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 80.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 347508 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller