[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
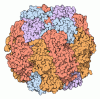
Yorodumi- PDB-5nv3: Structure of Rubisco from Rhodobacter sphaeroides in complex with CABP -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5nv3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of Rubisco from Rhodobacter sphaeroides in complex with CABP | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  LYASE / LYASE /  beta barrel beta barrel | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase /  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle /  monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.39 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.39 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bracher, A. / Milicic, G. / Ciniawsky, S. / Wendler, P. / Hayer-Hartl, M. / Hartl, F.U. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2017Title: Mechanism of Enzyme Repair by the AAA Chaperone Rubisco Activase. Authors: Javaid Y Bhat / Goran Miličić / Gabriel Thieulin-Pardo / Andreas Bracher / Andrew Maxwell / Susanne Ciniawsky / Oliver Mueller-Cajar / John R Engen / F Ulrich Hartl / Petra Wendler / Manajit Hayer-Hartl /   Abstract: How AAA+ chaperones conformationally remodel specific target proteins in an ATP-dependent manner is not well understood. Here, we investigated the mechanism of the AAA+ protein Rubisco activase (Rca) ...How AAA+ chaperones conformationally remodel specific target proteins in an ATP-dependent manner is not well understood. Here, we investigated the mechanism of the AAA+ protein Rubisco activase (Rca) in metabolic repair of the photosynthetic enzyme Rubisco, a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits containing eight catalytic sites. Rubisco is prone to inhibition by tight-binding sugar phosphates, whose removal is catalyzed by Rca. We engineered a stable Rca hexamer ring and analyzed its functional interaction with Rubisco. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange and chemical crosslinking showed that Rca structurally destabilizes elements of the Rubisco active site with remarkable selectivity. Cryo-electron microscopy revealed that Rca docks onto Rubisco over one active site at a time, positioning the C-terminal strand of RbcL, which stabilizes the catalytic center, for access to the Rca hexamer pore. The pulling force of Rca is fine-tuned to avoid global destabilization and allow for precise enzyme repair. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5nv3.cif.gz 5nv3.cif.gz | 906.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5nv3.ent.gz pdb5nv3.ent.gz | 775.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5nv3.json.gz 5nv3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nv/5nv3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nv/5nv3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nv/5nv3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nv/5nv3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3699MC  3700C  3701C  3702C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 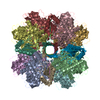
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 51768.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Fragment: RbcL Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) / Gene: cbbL, cbbL1, rbcL / Production host: Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) / Gene: cbbL, cbbL1, rbcL / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria)References: UniProt: P27997,  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase#2: Protein | Mass: 15183.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) / Gene: cbbS, rbcS / Production host: Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) / Gene: cbbS, rbcS / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria)References: UniProt: P27998,  ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase#3: Sugar | ChemComp-CAP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rubisco / Type: COMPLEX / Details: Rubisco was treated with the inhibitor CABP. / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT / Type: COMPLEX / Details: Rubisco was treated with the inhibitor CABP. / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) Rhodobacter sphaeroides (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: RcaCC hexamers (20 micromolar monomer) were mixed with E.C.M-CABP octamers (10 micromolar monomer) in a reaction containing 20 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM ATP and 1mM ...Details: RcaCC hexamers (20 micromolar monomer) were mixed with E.C.M-CABP octamers (10 micromolar monomer) in a reaction containing 20 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM ATP and 1mM RuBP, for 1 min at 25oC prior to addition of 0.125 % of glutaraldehyde (GA). After 10 min the reaction was quenched by addition of 0.1M Tris HCl pH 8 followed by gel filtration on a Superdex 200 PC 3.2/30 column (GE Healthcare).The fractions were eluted in buffer A and analyzed on a 6 % native gel. Fraction 13 containing HMW complexes with the least amount of free Rubisco were chosen for cryo-EM. The crosslinked E.C.M.-CABP-RcaCC complexes were diluted to 0.0030-0.0035 g ml-1 in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM ATP, 1 mM ATP-gammaS and 1 mM RuBP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: Cs corrected Krios 1 at NeCEN (June 2016) |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.25 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 22 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral : D4 (2x4 fold dihedral ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.39 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 333122 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL / Target criteria: Maximum likelihood |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj