[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-1ry1: Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1ry1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSLATION / TRANSLATION /  signal recognition particle / signal recognition particle /  RNA binding RNA binding | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information signal recognition particle receptor complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition / endoplasmic reticulum signal peptide binding / signal recognition particle receptor complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition / endoplasmic reticulum signal peptide binding /  signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting / signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting /  signal recognition particle binding / granulocyte differentiation / absorption of visible light / negative regulation of translational elongation / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity ... signal recognition particle binding / granulocyte differentiation / absorption of visible light / negative regulation of translational elongation / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity ... signal recognition particle receptor complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition / endoplasmic reticulum signal peptide binding / signal recognition particle receptor complex / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition / endoplasmic reticulum signal peptide binding /  signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting / signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting /  signal recognition particle binding / granulocyte differentiation / absorption of visible light / negative regulation of translational elongation / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity / signal recognition particle binding / granulocyte differentiation / absorption of visible light / negative regulation of translational elongation / G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity /  signal recognition particle / photoreceptor inner segment membrane / rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway / signal recognition particle / photoreceptor inner segment membrane / rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway /  11-cis retinal binding / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / 11-cis retinal binding / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane /  signal-recognition-particle GTPase / protein targeting to ER / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / 7S RNA binding / exocrine pancreas development / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / protein targeting to ER / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / 7S RNA binding / exocrine pancreas development / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / photoreceptor outer segment membrane / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / ribonucleoprotein complex binding /  visual perception / visual perception /  neutrophil chemotaxis / photoreceptor disc membrane / GDP binding / secretory granule lumen / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / neutrophil chemotaxis / photoreceptor disc membrane / GDP binding / secretory granule lumen / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen /  nuclear body / nuclear speck / nuclear body / nuclear speck /  GTPase activity / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding / GTPase activity / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding /  nucleolus / nucleolus /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  RNA binding / extracellular region / RNA binding / extracellular region /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog)  Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 12 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 12 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Halic, M. / Becker, T. / Pool, M.R. / Spahn, C.M. / Grassucci, R.A. / Frank, J. / Beckmann, R. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2004 Journal: Nature / Year: 2004Title: Structure of the signal recognition particle interacting with the elongation-arrested ribosome. Authors: Mario Halic / Thomas Becker / Martin R Pool / Christian M T Spahn / Robert A Grassucci / Joachim Frank / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: Cotranslational translocation of proteins across or into membranes is a vital process in all kingdoms of life. It requires that the translating ribosome be targeted to the membrane by the signal ...Cotranslational translocation of proteins across or into membranes is a vital process in all kingdoms of life. It requires that the translating ribosome be targeted to the membrane by the signal recognition particle (SRP), an evolutionarily conserved ribonucleoprotein particle. SRP recognizes signal sequences of nascent protein chains emerging from the ribosome. Subsequent binding of SRP leads to a pause in peptide elongation and to the ribosome docking to the membrane-bound SRP receptor. Here we present the structure of a targeting complex consisting of mammalian SRP bound to an active 80S ribosome carrying a signal sequence. This structure, solved to 12 A by cryo-electron microscopy, enables us to generate a molecular model of SRP in its functional conformation. The model shows how the S domain of SRP contacts the large ribosomal subunit at the nascent chain exit site to bind the signal sequence, and that the Alu domain reaches into the elongation-factor-binding site of the ribosome, explaining its elongation arrest activity. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1ry1.cif.gz 1ry1.cif.gz | 310 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1ry1.ent.gz pdb1ry1.ent.gz | 231.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1ry1.json.gz 1ry1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ry/1ry1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ry/1ry1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ry/1ry1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ry/1ry1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 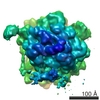 1063MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 8 types, 8 molecules EAMNOPQR
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 16277.622 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 41566.715 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #3: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 8784.278 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #4: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 9807.837 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #5: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 7695.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #6: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 6325.847 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #7: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 3844.320 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
| #8: RNA chain |  Signal recognition particle RNA Signal recognition particle RNAMass: 3804.296 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) Canis lupus familiaris (dog) |
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules CDBUW
| #9: Protein |  Signal recognition particle 9 Signal recognition particle 9Mass: 9996.567 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo / References: UniProt: P49458*PLUS / References: UniProt: P49458*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #10: Protein | Mass: 12114.235 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo / References: UniProt: P37108 / References: UniProt: P37108 |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 12561.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Homo / References: UniProt: P09132*PLUS / References: UniProt: P09132*PLUS |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 32472.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Thermus Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Thermus / References: UniProt: O07347*PLUS / References: UniProt: O07347*PLUS |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 12473.440 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Mus / References: UniProt: P14576*PLUS Canis lupus familiaris (dog) / Genus: Mus / References: UniProt: P14576*PLUS |
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules S
| #14: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2121.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) / References: UniProt: O62798*PLUS Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) / References: UniProt: O62798*PLUS |
|---|
-Details
| Sequence details | This structure has been modeled using polymer sequences from other organisms, including Homo ...This structure has been modeled using polymer sequences from other organisms, including Homo sapiens (chains C,D,E), Thermus aquaticus (chain U), Mus musculus (chain W), and Tursiops truncatus (chain S). |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: PLUNGED INTO ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Jan 1, 2000 Details: SAMPLES WERE MAINTAINED AT LIQUID NITROGEN TEMPERATURES IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 160 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 160 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 51000 X / Calibrated magnification: 52000 X / Nominal defocus max: 45000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 10000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 51000 X / Calibrated magnification: 52000 X / Nominal defocus max: 45000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 10000 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 95 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 10 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 75 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 12 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF Details: The chains M, N, O, P, Q and R are fragments of a double helical strand of RNA. The author maintains that some of the residues could not be modeled correctly due to limited resolution in this region. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 12 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 12 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj







































