[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
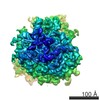
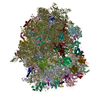
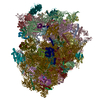
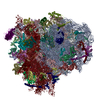
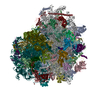
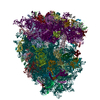
Yorodumi- PDB-6r6p: Structure of XBP1u-paused ribosome nascent chain complex (rotated... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6r6p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
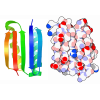
| Title | Structure of XBP1u-paused ribosome nascent chain complex (rotated state) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  RIBOSOME / translational pausing / RIBOSOME / translational pausing /  XBP1 / UPR XBP1 / UPR | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATF6-mediated unfolded protein response / positive regulation of protein acetylation / response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of vascular wound healing / organelle organization / positive regulation of plasma cell differentiation / positive regulation of lactation / IRE1alpha activates chaperones / sterol homeostasis / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes ...ATF6-mediated unfolded protein response / positive regulation of protein acetylation / response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of vascular wound healing / organelle organization / positive regulation of plasma cell differentiation / positive regulation of lactation / IRE1alpha activates chaperones / sterol homeostasis / ATF6 (ATF6-alpha) activates chaperone genes / positive regulation of ERAD pathway / : / positive regulation of phospholipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of myotube differentiation / intracellular triglyceride homeostasis / cellular response to fructose stimulus / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / cellular response to laminar fluid shear stress / cellular response to nutrient / cellular response to fluid shear stress / positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process / positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / endothelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation / muscle organ development / ERAD pathway / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus / positive regulation of B cell differentiation / IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / positive regulation of immunoglobulin production / neuron development / positive regulation of TOR signaling / positive regulation of fat cell differentiation / fatty acid homeostasis / cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus / cellular response to glucose starvation / adipose tissue development /  rough endoplasmic reticulum / cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of autophagy / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / cellular response to interleukin-4 / rough endoplasmic reticulum / cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of autophagy / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / cellular response to interleukin-4 /  DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / cytosolic ribosome / cholesterol homeostasis / liver development / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / cytosolic ribosome / cholesterol homeostasis / liver development / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / nuclear estrogen receptor binding /  regulation of cell growth / cellular response to glucose stimulus / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / protein destabilization / regulation of cell growth / cellular response to glucose stimulus / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / protein destabilization /  regulation of protein stability / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / chromatin DNA binding / regulation of protein stability / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / chromatin DNA binding /  autophagy / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / cellular response to insulin stimulus / fatty acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation of angiogenesis / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / autophagy / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / cellular response to insulin stimulus / fatty acid biosynthetic process / positive regulation of angiogenesis / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding /  protein transport / protein transport /  ribosome biogenesis / cellular response to oxidative stress / ribosome biogenesis / cellular response to oxidative stress /  5S rRNA binding / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / 5S rRNA binding / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process /  angiogenesis / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / angiogenesis / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide /  protease binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / protease binding / transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific /  ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / positive regulation of cell migration / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / positive regulation of cell migration /  immune response / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / immune response / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation /  translation / translation /  ribonucleoprotein complex / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein heterodimerization activity / apoptotic process / ribonucleoprotein complex / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein heterodimerization activity / apoptotic process /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / endoplasmic reticulum membrane /  nucleolus nucleolusSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)  Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Shanmuganathan, V. / Cheng, J. / Berninghausen, O. / Beckmann, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2019 Journal: Elife / Year: 2019Title: Structural and mutational analysis of the ribosome-arresting human XBP1u. Authors: Vivekanandan Shanmuganathan / Nina Schiller / Anastasia Magoulopoulou / Jingdong Cheng / Katharina Braunger / Florian Cymer / Otto Berninghausen / Birgitta Beatrix / Kenji Kohno / Gunnar von ...Authors: Vivekanandan Shanmuganathan / Nina Schiller / Anastasia Magoulopoulou / Jingdong Cheng / Katharina Braunger / Florian Cymer / Otto Berninghausen / Birgitta Beatrix / Kenji Kohno / Gunnar von Heijne / Roland Beckmann /    Abstract: XBP1u, a central component of the unfolded protein response (UPR), is a mammalian protein containing a functionally critical translational arrest peptide (AP). Here, we present a 3 Å cryo-EM ...XBP1u, a central component of the unfolded protein response (UPR), is a mammalian protein containing a functionally critical translational arrest peptide (AP). Here, we present a 3 Å cryo-EM structure of the stalled human XBP1u AP. It forms a unique turn in the ribosomal exit tunnel proximal to the peptidyl transferase center where it causes a subtle distortion, thereby explaining the temporary translational arrest induced by XBP1u. During ribosomal pausing the hydrophobic region 2 (HR2) of XBP1u is recognized by SRP, but fails to efficiently gate the Sec61 translocon. An exhaustive mutagenesis scan of the XBP1u AP revealed that only 8 out of 20 mutagenized positions are optimal; in the remaining 12 positions, we identify 55 different mutations increase the level of translational arrest. Thus, the wildtype XBP1u AP induces only an intermediate level of translational arrest, allowing efficient targeting by SRP without activating the Sec61 channel. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6r6p.cif.gz 6r6p.cif.gz | 4.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6r6p.ent.gz pdb6r6p.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6r6p.json.gz 6r6p.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r6/6r6p https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r6/6r6p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r6/6r6p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r6/6r6p | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4737MC  4729C  4735C  4745C  6r5qC  6r6gC  6r7qC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 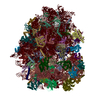
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 7 types, 7 molecules 57823K4
| #1: RNA chain |  Mass: 1186579.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain |  Mass: 38691.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| #3: RNA chain |  Mass: 50143.648 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| #49: RNA chain | Mass: 24414.496 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| #50: RNA chain | Mass: 24148.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| #51: RNA chain |  18S ribosomal RNA 18S ribosomal RNAMass: 548024.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| #85: RNA chain |  Messenger RNA Messenger RNAMass: 3145.932 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
+Protein , 41 types, 41 molecules ABCFGHJOPQRSTVXacdefghkmorsqvMM...
-60S ribosomal protein ... , 7 types, 7 molecules DELZbin
| #7: Protein |  Mass: 34006.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SYJ6 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SYJ6 |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein |  Mass: 28529.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TG04 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TG04 |
| #14: Protein |  Mass: 24216.525 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TPV0 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TPV0 |
| #28: Protein |  Mass: 15704.635 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TXF6 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TXF6 |
| #30: Protein |  Mass: 8706.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TN82 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TN82 |
| #37: Protein |  Mass: 11888.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TTQ5 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TTQ5 |
| #42: Protein/peptide |  Mass: 3213.075 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: A0A087WNH4 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: A0A087WNH4 |
+Ribosomal protein ... , 21 types, 21 molecules IMNUWYjlptXXEEQQUUTTVVDDBBOOFF6
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules 1
| #48: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2895.380 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XBP1, TREB5, XBP2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XBP1, TREB5, XBP2 / Production host:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P17861 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P17861 |
|---|
-40S ribosomal protein ... , 8 types, 8 molecules uxzyCCJJAARR
| #53: Protein |  Mass: 24759.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SS70 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SS70 |
|---|---|
| #55: Protein |  Mass: 29523.674 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TK17 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TK17 |
| #56: Protein |  Mass: 27471.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TM55 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TM55 |
| #57: Protein |  Mass: 21629.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SVB0 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SVB0 |
| #58: Protein |  Mass: 24003.012 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TJW1 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TJW1 |
| #70: Protein |  Mass: 9348.990 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TZ76 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1TZ76 |
| #71: Protein |  Mass: 6317.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1T8A2 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1T8A2 |
| #75: Protein |  Mass: 13048.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SFR8 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: G1SFR8 |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 164 molecules 


| #86: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #87: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 28 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 94923 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj