[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6pwb: Rigid body fitting of flagellin FlaB, and flagellar coiling prote... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6pwb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
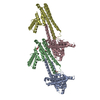
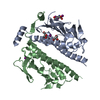
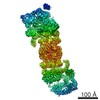
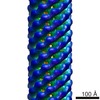
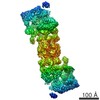
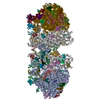
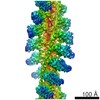
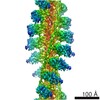
| Title | Rigid body fitting of flagellin FlaB, and flagellar coiling proteins, FcpA and FcpB, into a 10 Angstrom structure of the asymmetric flagellar filament purified from Leptospira biflexa Patoc WT cells resolved via subtomogram averaging | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  bacterial flagella / FcpA / FcpB / FlaA / FlaB / bacterial flagella / FcpA / FcpB / FlaA / FlaB /  Leptospira Leptospira | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationperiplasmic flagellum / bacterial-type flagellum filament / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / structural molecule activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (bacteria) Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9.83 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9.83 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gibson, K.H. / Sindelar, C.V. / Trajtenberg, F. / Buschiazzo, A. / San Martin, F. / Mechaly, A. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, Uruguay, 10items United States, Uruguay, 10items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: An asymmetric sheath controls flagellar supercoiling and motility in the leptospira spirochete. Authors: Kimberley H Gibson / Felipe Trajtenberg / Elsio A Wunder / Megan R Brady / Fabiana San Martin / Ariel Mechaly / Zhiguo Shang / Jun Liu / Mathieu Picardeau / Albert Ko / Alejandro Buschiazzo ...Authors: Kimberley H Gibson / Felipe Trajtenberg / Elsio A Wunder / Megan R Brady / Fabiana San Martin / Ariel Mechaly / Zhiguo Shang / Jun Liu / Mathieu Picardeau / Albert Ko / Alejandro Buschiazzo / Charles Vaughn Sindelar /    Abstract: Spirochete bacteria, including important pathogens, exhibit a distinctive means of swimming via undulations of the entire cell. Motility is powered by the rotation of supercoiled 'endoflagella' that ...Spirochete bacteria, including important pathogens, exhibit a distinctive means of swimming via undulations of the entire cell. Motility is powered by the rotation of supercoiled 'endoflagella' that wrap around the cell body, confined within the periplasmic space. To investigate the structural basis of flagellar supercoiling, which is critical for motility, we determined the structure of native flagellar filaments from the spirochete by integrating high-resolution cryo-electron tomography and X-ray crystallography. We show that these filaments are coated by a highly asymmetric, multi-component sheath layer, contrasting with flagellin-only homopolymers previously observed in exoflagellated bacteria. Distinct sheath proteins localize to the filament inner and outer curvatures to define the supercoiling geometry, explaining a key functional attribute of this spirochete flagellum. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun / Year: 2017 Title: Crystallization of FcpA from Leptospira, a novel flagellar protein that is essential for pathogenesis. Authors: Fabiana San Martin / Ariel E Mechaly / Nicole Larrieux / Elsio A Wunder / Albert I Ko / Mathieu Picardeau / Felipe Trajtenberg / Alejandro Buschiazzo /   Abstract: The protein FcpA is a unique component of the flagellar filament of spirochete bacteria belonging to the genus Leptospira. Although it plays an essential role in translational motility and ...The protein FcpA is a unique component of the flagellar filament of spirochete bacteria belonging to the genus Leptospira. Although it plays an essential role in translational motility and pathogenicity, no structures of FcpA homologues are currently available in the PDB. Its three-dimensional structure will unveil the novel motility mechanisms that render pathogenic Leptospira particularly efficient at invading and disseminating within their hosts, causing leptospirosis in humans and animals. FcpA from L. interrogans was purified and crystallized, but despite laborious attempts no useful X ray diffraction data could be obtained. This challenge was solved by expressing a close orthologue from the related saprophytic species L. biflexa. Three different crystal forms were obtained: a primitive and a centred monoclinic form, as well as a hexagonal variant. All forms diffracted X-rays to suitable resolutions for crystallographic analyses, with the hexagonal type typically reaching the highest limits of 2.0 Å and better. A variation of the quick-soaking procedure resulted in an iodide derivative that was instrumental for single-wavelength anomalous diffraction methods. #2: Journal: Mol Microbiol / Year: 2016 Title: A novel flagellar sheath protein, FcpA, determines filament coiling, translational motility and virulence for the Leptospira spirochete. Authors: Elsio A Wunder / Cláudio P Figueira / Nadia Benaroudj / Bo Hu / Brian A Tong / Felipe Trajtenberg / Jun Liu / Mitermayer G Reis / Nyles W Charon / Alejandro Buschiazzo / Mathieu Picardeau / Albert I Ko /    Abstract: Leptospira are unique among bacteria based on their helical cell morphology with hook-shaped ends and the presence of periplasmic flagella (PF) with pronounced spontaneous supercoiling. The factors ...Leptospira are unique among bacteria based on their helical cell morphology with hook-shaped ends and the presence of periplasmic flagella (PF) with pronounced spontaneous supercoiling. The factors that provoke such supercoiling, as well as the role that PF coiling plays in generating the characteristic hook-end cell morphology and motility, have not been elucidated. We have now identified an abundant protein from the pathogen L. interrogans, exposed on the PF surface, and named it Flagellar-coiling protein A (FcpA). The gene encoding FcpA is highly conserved among Leptospira and was not found in other bacteria. fcpA(-) mutants, obtained from clinical isolates or by allelic exchange, had relatively straight, smaller-diameter PF, and were not able to produce translational motility. These mutants lost their ability to cause disease in the standard hamster model of leptospirosis. Complementation of fcpA restored the wild-type morphology, motility and virulence phenotypes. In summary, we identified a novel Leptospira 36-kDa protein, the main component of the spirochete's PF sheath, and a key determinant of the flagella's coiled structure. FcpA is essential for bacterial translational motility and to enable the spirochete to penetrate the host, traverse tissue barriers, disseminate to cause systemic infection and reach target organs. #3: Journal: Front Cell Infect Microbiol / Year: 2018 Title: FcpB Is a Surface Filament Protein of the Endoflagellum Required for the Motility of the Spirochete . Authors: Elsio A Wunder / Leyla Slamti / David N Suwondo / Kimberley H Gibson / Zhiguo Shang / Charles V Sindelar / Felipe Trajtenberg / Alejandro Buschiazzo / Albert I Ko / Mathieu Picardeau /    Abstract: The spirochete endoflagellum is a unique motility apparatus among bacteria. Despite its critical importance for pathogenesis, the full composition of the flagellum remains to be determined. We have ...The spirochete endoflagellum is a unique motility apparatus among bacteria. Despite its critical importance for pathogenesis, the full composition of the flagellum remains to be determined. We have recently reported that FcpA is a novel flagellar protein and a major component of the sheath of the filament of the spirochete . By screening a library of random transposon mutants in the spirochete , we found a motility-deficient mutant harboring a disruption in a hypothetical gene of unknown function. Here, we show that this gene encodes a surface component of the endoflagellar filament and is required for typical hook- and spiral-shaped ends of the cell body, coiled structure of the endoflagella, and high velocity phenotype. We therefore named the gene for flagellar-coiling protein B. is conserved in all members of the genus, but not present in other organisms including other spirochetes. Complementation of the mutant restored the wild-type morphology and motility phenotypes. Immunoblotting with anti-FcpA and anti-FcpB antisera and cryo-electron microscopy of the filament indicated that FcpB assembled onto the surface of the sheath of the filament and mostly located on the outer (convex) side of the coiled filament. We provide evidence that FcpB, together with FcpA, are -specific novel components of the sheath of the filament, key determinants of the coiled and asymmetric structure of the endoflagella and are essential for high velocity. Defining the components of the endoflagella and their functions in these atypical bacteria should greatly enhance our understanding of the mechanisms by which these bacteria produce motility. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6pwb.cif.gz 6pwb.cif.gz | 4.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6pwb.ent.gz pdb6pwb.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6pwb.json.gz 6pwb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pw/6pwb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pw/6pwb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pw/6pwb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pw/6pwb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20504MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29467.033 Da / Num. of mol.: 84 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria) Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria)Cell: bacteria / Strain: Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris / References: UniProt: B0SSZ5 #2: Protein | Mass: 28931.002 Da / Num. of mol.: 47 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria) Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria)Cell: bacteria / Strain: Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris / References: UniProt: B0STJ8 #3: Protein | Mass: 25539.666 Da / Num. of mol.: 32 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria) Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (strain Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris) (bacteria)Cell: bacteria / Strain: Patoc 1 / ATCC 23582 / Paris / References: UniProt: B0SR03 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Flagellar filament purified from the periplasm of the Spirochete bacterium, Leptospira biflexa Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT Details: Filaments were purified from Leptospira biflexa wild type cells. Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain 'Patoc 1 (Paris)' (bacteria) Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain 'Patoc 1 (Paris)' (bacteria)Cellular location: periplasm / Organelle  : flagellar filament : flagellar filament |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.8 / Details: Tris-HCl or ddH20, pH6.8 with <1% sodium azide as a preservative. FIDUCIAL MARKERS: Prior to vitrification, 1 uL of 6x concentrated Gold Tracer beads (10 nm colloidal gold) were mixed with 2 uL of purified flagella. To each grid, 3 uL of this mixture were applied. |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain Patoc I wild type, fcpA, and fcpB mutant cells cultured in Ellinghausen-McCullough-Johnson-Harris liquid medium until they reached logarithmic phase ...Details: Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc strain Patoc I wild type, fcpA, and fcpB mutant cells cultured in Ellinghausen-McCullough-Johnson-Harris liquid medium until they reached logarithmic phase at 30C. The cells were pelleted and the periplasmic flagellar filaments were purified as described in Wunder et al., 2016; Wunder et al., 2018. |
| Specimen support | Details: Model 950 Solarus Advanced Plasma System manufactured by GATAN. Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K Details: 2 minute incubation time; blot time of 6-7.5 seconds; and blot offset of -2 mm |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 15000 X / Calibrated magnification: 19230 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 3000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 15000 X / Calibrated magnification: 19230 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 3000 nm / Cs : 2 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.2 sec. / Electron dose: 1.7 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 Details: Tilt series acquisition. A total of ~35 tilt angles per tilt stack were acquired. The total dose was ~ 60 e/Angstrom2. |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 3710 / Height: 3838 / Movie frames/image: 12 / Used frames/image: 1-12 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: Motion correction was performed on movie stacks acquired at each angle in each tilt series using IMOD alignframes. Tilt series were aligned in IMOD eTomo usinf 10 nm fiducial gold markers. ...Details: Motion correction was performed on movie stacks acquired at each angle in each tilt series using IMOD alignframes. Tilt series were aligned in IMOD eTomo usinf 10 nm fiducial gold markers. CTF estimation with phase flipping was carried out, along with gold bead subtraction in IMOD eTomo. Tilt series were reconstructed using Weighted Back Projection in Tomo3D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: CTF estimation was initially done in IMOD. / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 9.83 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 10581 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION Details: emClarity: The two half-dataset volumes were combined with a B-170 factor of 0, and the Gold standard FSC at 0.143 was calculated to be 9.83 A with anisotropic resolutions ranging from 8.89-16.17 Angstrom. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Method: Manual selection Details: Using IMOD 3dmod, filament trajectories were traced by selecting particle points along a single filament. Each continuous filament was a single contour (3dmod). Using the addModPts program ...Details: Using IMOD 3dmod, filament trajectories were traced by selecting particle points along a single filament. Each continuous filament was a single contour (3dmod). Using the addModPts program in PEET, particle gaps along each filament trajectory contour were filled in with additional points according to a repeat spacing of 52 angstroms. The x,y,z coordinates were then imported into RELION using a modified version of the RELION preprocessing.py python script described in Bharat et. al. (2015). The script was modified to ensure that particles in one filament would be sorted into the same ODD or EVEN grouping to prevent over-estimation of FSC due to inclusion of the 2 or more overlapping particles in a filament in both half-datasets. Num. of tomograms: 62 / Num. of volumes extracted: 15000 / Reference model: de novo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: RECIPROCAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient Details: Eliminate minor clashes between FlaB1, FcpA, and FcpB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj