[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
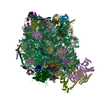
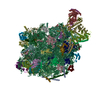
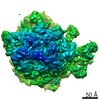
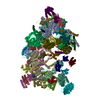
Yorodumi- PDB-4v6m: Structure of the ribosome-SecYE complex in the membrane environment -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4v6m | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the ribosome-SecYE complex in the membrane environment | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME/RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN / RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN / RIBONUCLEOPROTEIN / NUCLEOTIDE-BINDING / PROTEIN BIOSYNTHESIS / TRANSLATION / ZINC-FINGER / 70S RIBOSOME / RIBOSOME / TRANSLOCON / SECYEG / NANODISC / RIBOSOME-RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell septum assembly / Defective ABCA1 causes TGD / high-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / peptidyl-methionine modification / HDL clearance / spherical high-density lipoprotein particle / Scavenging by Class B Receptors / negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / protein oxidation / regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption ...cell septum assembly / Defective ABCA1 causes TGD / high-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / peptidyl-methionine modification / HDL clearance / spherical high-density lipoprotein particle / Scavenging by Class B Receptors / negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / protein oxidation / regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption / vitamin transport / blood vessel endothelial cell migration / cholesterol import / negative regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / high-density lipoprotein particle binding / ABC transporters in lipid homeostasis / apolipoprotein A-I receptor binding / apolipoprotein receptor binding / negative regulation of cell adhesion molecule production / protein transport by the Sec complex / negative regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response / intracellular protein transmembrane transport / HDL assembly / negative regulation of very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling / phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process / glucocorticoid metabolic process / protein-transporting ATPase activity / acylglycerol homeostasis / phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activator activity / positive regulation of phospholipid efflux / Chylomicron remodeling / cellular response to lipoprotein particle stimulus / Chylomicron assembly / high-density lipoprotein particle clearance / phospholipid efflux / chylomicron / high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling / positive regulation of cholesterol metabolic process / reverse cholesterol transport / lipid storage / phospholipid homeostasis / high-density lipoprotein particle assembly / chemorepellent activity / low-density lipoprotein particle / lipoprotein biosynthetic process / cholesterol transfer activity / cholesterol transport / high-density lipoprotein particle / very-low-density lipoprotein particle / FtsZ-dependent cytokinesis / endothelial cell proliferation / regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction / HDL remodeling / cholesterol efflux / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / triglyceride homeostasis / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / negative chemotaxis / cholesterol binding / cell division site / cholesterol biosynthetic process / amyloid-beta formation / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / stringent response / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / protein secretion / misfolded RNA binding / endocytic vesicle / Group I intron splicing / protein transmembrane transporter activity / RNA folding / positive regulation of cholesterol efflux / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / membrane => GO:0016020 / transcriptional attenuation / Scavenging of heme from plasma / protein targeting / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / cholesterol metabolic process / Retinoid metabolism and transport / translational termination / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / four-way junction DNA binding / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / DnaA-L2 complex / heat shock protein binding / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of translational initiation / regulation of mRNA stability / endocytic vesicle lumen / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of phagocytosis / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cholesterol homeostasis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |       Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Frauenfeld, J. / Gumbart, J. / van der Sluis, E.O. / Funes, S. / Gartmann, M. / Beatrix, B. / Mielke, T. / Berninghausen, O. / Becker, T. / Schulten, K. / Beckmann, R. | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2011 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2011Title: Cryo-EM structure of the ribosome-SecYE complex in the membrane environment. Authors: Jens Frauenfeld / James Gumbart / Eli O van der Sluis / Soledad Funes / Marco Gartmann / Birgitta Beatrix / Thorsten Mielke / Otto Berninghausen / Thomas Becker / Klaus Schulten / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: The ubiquitous SecY-Sec61 complex translocates nascent secretory proteins across cellular membranes and integrates membrane proteins into lipid bilayers. Several structures of mostly detergent- ...The ubiquitous SecY-Sec61 complex translocates nascent secretory proteins across cellular membranes and integrates membrane proteins into lipid bilayers. Several structures of mostly detergent-solubilized Sec complexes have been reported. Here we present a single-particle cryo-EM structure of the SecYEG complex in a membrane environment, bound to a translating ribosome, at subnanometer resolution. Using the SecYEG complex reconstituted in a so-called Nanodisc, we could trace the nascent polypeptide chain from the peptidyltransferase center into the membrane. The reconstruction allowed for the identification of ribosome-lipid interactions. The rRNA helix 59 (H59) directly contacts the lipid surface and appears to modulate the membrane in immediate vicinity to the proposed lateral gate of the protein-conducting channel (PCC). On the basis of our map and molecular dynamics simulations, we present a model of a signal anchor-gated PCC in the membrane. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4v6m.cif.gz 4v6m.cif.gz | 3.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4v6m.ent.gz pdb4v6m.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4v6m.json.gz 4v6m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  4v6m_validation.pdf.gz 4v6m_validation.pdf.gz | 3.8 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  4v6m_full_validation.pdf.gz 4v6m_full_validation.pdf.gz | 5.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  4v6m_validation.xml.gz 4v6m_validation.xml.gz | 356.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  4v6m_validation.cif.gz 4v6m_validation.cif.gz | 580.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v6/4v6m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v6/4v6m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v6/4v6m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/v6/4v6m | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1858MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules AAAXAVB7B8
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 499690.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 3442.106 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 24876.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #26: RNA chain | Mass: 38790.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #27: RNA chain | Mass: 941612.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 2 types, 3 molecules AZA0A1
| #4: Protein | Mass: 11085.822 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 23309.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Details: nanodiscs derived from human Apo-A1 / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P02647 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P02647 |
-30S ribosomal protein ... , 20 types, 20 molecules ABACADAEAFAGAHAIAJAKALAMANAOAPAQARASATAU
| #6: Protein | Mass: 26650.475 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 25900.117 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 23383.002 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 17498.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 15727.512 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 19923.959 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 14015.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 14755.074 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 11755.597 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 13739.778 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #16: Protein | Mass: 13636.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 12997.271 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #18: Protein | Mass: 11475.364 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 10188.687 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #20: Protein | Mass: 9207.572 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #21: Protein | Mass: 9593.296 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #22: Protein | Mass: 8874.276 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #23: Protein | Mass: 10324.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #24: Protein | Mass: 9577.268 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #25: Protein | Mass: 8392.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Preprotein translocase ... , 2 types, 2 molecules BABB
| #28: Protein | Mass: 47669.277 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #29: Protein | Mass: 12623.296 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 30 types, 30 molecules B5B6BDBEBFBGBHBIBJBKBLBMBNBOBPBQBRBSBTBUBVBWBXBYBZB0B1B2B3B4
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 133 molecules 
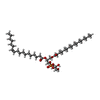

| #60: Chemical | ChemComp-PEV / ( #61: Chemical | ChemComp-PGV / ( |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: An active E. coli SecYEG complex embedded in a lipid bilayer (Nanodisc), bound to a translating E. coli ribosome Type: RIBOSOME Details: The heterotrimeric SecYEG complex was embedded in a lipid bilayer (nascent HDL, Nanodisc) |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.2), 100 mM KOAc, 10 mM Mg(OAc)2, 1 mM DTT, 250 microg/ml chloramphenicol pH: 7.2 Details: 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.2), 100 mM KOAc, 10 mM Mg(OAc)2, 1 mM DTT, 250 microg/ml chloramphenicol |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: liquid ethane was used as a cryogen |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 39000 X / Calibrated magnification: 38000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.26 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 22 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: DEFOCUS GROUP VOLUMES | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.1 Å / Num. of particles: 85664 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--flexible fitting | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj