[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6alf: CryoEM structure of crosslinked E.coli RNA polymerase elongation ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6alf | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
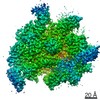
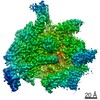
| Title | CryoEM structure of crosslinked E.coli RNA polymerase elongation complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | transcription/dna/rna /  DNA-dependent RNA polymerase / DNA-dependent RNA polymerase /  TRANSCRIPTION / transcription-dna-rna complex TRANSCRIPTION / transcription-dna-rna complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / transcription elongation factor complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation ... RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / transcription elongation factor complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation ... RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / transcription elongation factor complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / transcription elongation factor complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination /  cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation /  ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis /  protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / magnesium ion binding / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / magnesium ion binding /  DNA binding / zinc ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding /  membrane / membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)   Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kang, J.Y. / Darst, S.A. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Structural basis of transcription arrest by coliphage HK022 Nun in an RNA polymerase elongation complex. Authors: Jin Young Kang / Paul Dominic B Olinares / James Chen / Elizabeth A Campbell / Arkady Mustaev / Brian T Chait / Max E Gottesman / Seth A Darst /  Abstract: Coliphage HK022 Nun blocks superinfection by coliphage λ by stalling RNA polymerase (RNAP) translocation specifically on λ DNA. To provide a structural framework to understand how Nun blocks RNAP ...Coliphage HK022 Nun blocks superinfection by coliphage λ by stalling RNA polymerase (RNAP) translocation specifically on λ DNA. To provide a structural framework to understand how Nun blocks RNAP translocation, we determined structures of RNAP ternary elongation complexes (TECs) with and without Nun by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Nun fits tightly into the TEC by taking advantage of gaps between the RNAP and the nucleic acids. The C-terminal segment of Nun interacts with the RNAP β and β' subunits inside the RNAP active site cleft as well as with nearly every element of the nucleic acid scaffold, essentially crosslinking the RNAP and the nucleic acids to prevent translocation, a mechanism supported by the effects of Nun amino acid substitutions. The nature of Nun interactions inside the RNAP active site cleft suggests that RNAP clamp opening is required for Nun to establish its interactions, explaining why Nun acts on paused TECs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6alf.cif.gz 6alf.cif.gz | 593.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6alf.ent.gz pdb6alf.ent.gz | 472.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6alf.json.gz 6alf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/al/6alf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/al/6alf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/al/6alf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/al/6alf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 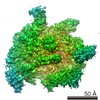 8585MC  8584C 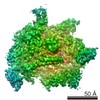 8586C  6algC  6alhC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: DNA chain | Mass: 8840.689 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)    Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) |
|---|---|
| #2: DNA chain | Mass: 8813.646 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)    Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules R
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 6509.968 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)    Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T7 (virus) |
|---|
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules GHIJK
| #4: Protein |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit alpha / RNA polymerase subunit alpha / Transcriptase subunit alpha Polymerase / RNAP subunit alpha / RNA polymerase subunit alpha / Transcriptase subunit alphaMass: 26459.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria) Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria)Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoA, pez, phs, sez, b3295, JW3257 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A7Z4, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A7Z4,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#5: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta / RNA polymerase subunit beta / Transcriptase subunit beta Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta / RNA polymerase subunit beta / Transcriptase subunit betaMass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria) Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria)Strain: K12 Gene: rpoB, groN, nitB, rif, ron, stl, stv, tabD, b3987, JW3950 Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A8V2, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A8V2,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#6: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta' / RNA polymerase subunit beta' / Transcriptase subunit beta' Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta' / RNA polymerase subunit beta' / Transcriptase subunit beta'Mass: 155366.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria) Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria)Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoC, tabB, b3988, JW3951 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A8T7, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A8T7,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#7: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP omega subunit / RNA polymerase omega subunit / Transcriptase subunit omega Polymerase / RNAP omega subunit / RNA polymerase omega subunit / Transcriptase subunit omegaMass: 9094.239 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria) Escherichia coli (strain K12) (bacteria)Strain: K12 / Gene: rpoZ, b3649, JW3624 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A800, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0A800,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #9: Chemical |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: crosslinked E.coli RNA polymerase elongation complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.393 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20 mM Tris pH8.0, 150 mM KCl, 5mM MgCl2, 5mM DTT |
| Specimen | Conc.: 3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat CF-1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 71 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: Used CTFFIND4 / Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 84000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj

































































