+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5wk5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
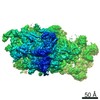
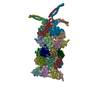
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of P. aeruginosa flagellar filaments A443V | ||||||
 Components Components | B-type flagellin | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / bacteria flagella / helical polymers /  cryo-EM cryo-EM | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / structural molecule activity / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Pseudomonas aeruginosa (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  negative staining / negative staining /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, F. / Postel, S. / Sundberg, E.J. / Egelman, E.H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2017Title: A structural model of flagellar filament switching across multiple bacterial species. Authors: Fengbin Wang / Andrew M Burrage / Sandra Postel / Reece E Clark / Albina Orlova / Eric J Sundberg / Daniel B Kearns / Edward H Egelman /  Abstract: The bacterial flagellar filament has long been studied to understand how a polymer composed of a single protein can switch between different supercoiled states with high cooperativity. Here we ...The bacterial flagellar filament has long been studied to understand how a polymer composed of a single protein can switch between different supercoiled states with high cooperativity. Here we present near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structures for flagellar filaments from both Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis and Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Seven mutant flagellar filaments in B. subtilis and two in P. aeruginosa capture two different states of the filament. These reliable atomic models of both states reveal conserved molecular interactions in the interior of the filament among B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa and Salmonella enterica. Using the detailed information about the molecular interactions in two filament states, we successfully predict point mutations that shift the equilibrium between those two states. Further, we observe the dimerization of P. aeruginosa outer domains without any perturbation of the conserved interior of the filament. Our results give new insights into how the flagellin sequence has been "tuned" over evolution.Bacterial flagellar filaments are composed almost entirely of a single protein-flagellin-which can switch between different supercoiled states in a highly cooperative manner. Here the authors present near-atomic resolution cryo-EM structures of nine flagellar filaments, and begin to shed light on the molecular basis of filament switching. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5wk5.cif.gz 5wk5.cif.gz | 3.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5wk5.ent.gz pdb5wk5.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5wk5.json.gz 5wk5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wk/5wk5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wk/5wk5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wk/5wk5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wk/5wk5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8855MC  8847C  8848C  8849C  8850C  8851C  8852C  8853C  8856C  5wjtC  5wjuC  5wjvC  5wjwC  5wjxC  5wjyC  5wjzC  5wk6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 20 / Rise per n subunits: 4.61 Å / Rotation per n subunits: 65.75 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49302.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 41 / Mutation: A443V Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: fliC, PA1092 / Production host:   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P72151 Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P72151 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella filament / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: PBS |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : YES / Vitrification applied : YES / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| EM staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: negative stain |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) Details: Images were stored containing seven parts, where each part represented a set of frames corresponding to a dose of ~20 electrons per Angstrom^2. The full dose image stack was used for the ...Details: Images were stored containing seven parts, where each part represented a set of frames corresponding to a dose of ~20 electrons per Angstrom^2. The full dose image stack was used for the estimation of the CTF as well as for boxing filaments. Only the first two parts were used for the reconstruction (~5 electrons per Angstrom^2). |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 7 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_2471: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 65.75 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 4.61 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Num. of particles: 102119 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Details: model-map FSC 0.38 cut-off / Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj