+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5o9g | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
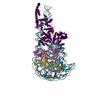
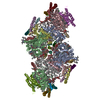
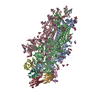
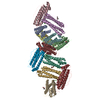
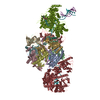
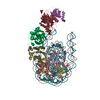
| Title | Structure of nucleosome-Chd1 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN /  ATPase / ATPase /  Complex / Complex /  Nucleosome / Nucleosome /  DNA / DNA /  Chromatin Remodeling Chromatin Remodeling | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization /  rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion ...nucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion ...nucleolar chromatin / regulation of transcriptional start site selection at RNA polymerase II promoter / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome organization /  rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / methylated histone binding / rDNA binding / SLIK (SAGA-like) complex / SAGA complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / sister chromatid cohesion / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / methylated histone binding /  helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / chromatin DNA binding / structural constituent of chromatin / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / chromatin DNA binding / structural constituent of chromatin /  nucleosome / nucleosome /  histone binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / histone binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding /  chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  nucleus nucleusSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog)  Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (yeast)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Farnung, L. / Vos, S.M. / Wigge, C. / Cramer, P. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2017 Journal: Nature / Year: 2017Title: Nucleosome-Chd1 structure and implications for chromatin remodelling. Authors: Lucas Farnung / Seychelle M Vos / Christoph Wigge / Patrick Cramer /  Abstract: Chromatin-remodelling factors change nucleosome positioning and facilitate DNA transcription, replication, and repair. The conserved remodelling factor chromodomain-helicase-DNA binding protein ...Chromatin-remodelling factors change nucleosome positioning and facilitate DNA transcription, replication, and repair. The conserved remodelling factor chromodomain-helicase-DNA binding protein 1(Chd1) can shift nucleosomes and induce regular nucleosome spacing. Chd1 is required for the passage of RNA polymerase IIthrough nucleosomes and for cellular pluripotency. Chd1 contains the DNA-binding domains SANT and SLIDE, a bilobal motor domain that hydrolyses ATP, and a regulatory double chromodomain. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of Chd1 from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae bound to a nucleosome at a resolution of 4.8 Å. Chd1 detaches two turns of DNA from the histone octamer and binds between the two DNA gyres in a state poised for catalysis. The SANT and SLIDE domains contact detached DNA around superhelical location (SHL) -7 of the first DNA gyre. The ATPase motor binds the second DNA gyre at SHL +2 and is anchored to the N-terminal tail of histone H4, as seen in a recent nucleosome-Snf2 ATPase structure. Comparisons with published results reveal that the double chromodomain swings towards nucleosomal DNA at SHL +1, resulting in ATPase closure. The ATPase can then promote translocation of DNA towards the nucleosome dyad, thereby loosening the first DNA gyre and remodelling the nucleosome. Translocation may involve ratcheting of the two lobes of the ATPase, which is trapped in a pre- or post-translocation state in the absence or presence, respectively, of transition state-mimicking compounds. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5o9g.cif.gz 5o9g.cif.gz | 490.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5o9g.ent.gz pdb5o9g.ent.gz | 377.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5o9g.json.gz 5o9g.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/5o9g https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/5o9g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/5o9g ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/5o9g | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 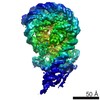 3765MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 7 molecules AEBFCGW
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15435.126 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233#2: Protein |  Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799#3: Protein |  Mass: 14109.436 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Gene: hist1h2aj, LOC494591 / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Gene: hist1h2aj, LOC494591 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q6AZJ8, UniProt: P06897*PLUS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q6AZJ8, UniProt: P06897*PLUS#8: Protein | | Mass: 168496.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (yeast) / Gene: CHD1, YER164W, SYGP-ORF4 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (yeast) / Gene: CHD1, YER164W, SYGP-ORF4 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P32657,  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|
-Histone H2B 1. ... , 2 types, 2 molecules DH
| #4: Protein | Mass: 13655.948 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281 |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 13526.769 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 64143.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 64293.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 


| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP /  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate |
|---|---|
| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-BEF / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1250 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1250 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 150 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 150 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 3 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 3802 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Quantum : GIF Quantum |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 990000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 67032 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj








































