Yorodumi
Yorodumi+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3445 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
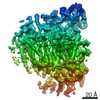
| Title | cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of microtubule-bound S.pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-electron microscopy of microtubule-bound S. pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmitotic spindle formation (spindle phase one) / mitotic spindle elongation (spindle phase three) / Kinesins / initial mitotic spindle pole body separation / microtubule plus-end directed mitotic chromosome migration / meiotic spindle pole /  meiotic spindle assembly / mitotic spindle pole body / mitotic spindle midzone assembly / mitotic spindle midzone ...mitotic spindle formation (spindle phase one) / mitotic spindle elongation (spindle phase three) / Kinesins / initial mitotic spindle pole body separation / microtubule plus-end directed mitotic chromosome migration / meiotic spindle pole / meiotic spindle assembly / mitotic spindle pole body / mitotic spindle midzone assembly / mitotic spindle midzone ...mitotic spindle formation (spindle phase one) / mitotic spindle elongation (spindle phase three) / Kinesins / initial mitotic spindle pole body separation / microtubule plus-end directed mitotic chromosome migration / meiotic spindle pole /  meiotic spindle assembly / mitotic spindle pole body / mitotic spindle midzone assembly / mitotic spindle midzone / spindle elongation / polar microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / meiotic spindle assembly / mitotic spindle pole body / mitotic spindle midzone assembly / mitotic spindle midzone / spindle elongation / polar microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  meiotic spindle / positive regulation of axon guidance / microtubule associated complex / meiotic spindle / positive regulation of axon guidance / microtubule associated complex /  microtubule motor activity / microtubule motor activity /  mitotic spindle assembly / microtubule-based process / spindle microtubule / mitotic spindle assembly / microtubule-based process / spindle microtubule /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton /  mitotic spindle / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / mitotic spindle / microtubule cytoskeleton organization /  kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton / mitotic cell cycle / kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton / mitotic cell cycle /  nervous system development / nervous system development /  microtubule binding / microtubule binding /  microtubule / microtubule /  hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity /  cell division / cell division /  GTPase activity / GTP binding / GTPase activity / GTP binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Bovine (cattle) / Bovine (cattle) /   Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (yeast) Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (yeast) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 9.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 9.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Goulet A / Moores CA / Cross RA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016Title: Schizosaccharomyces pombe kinesin-5 switches direction using a steric blocking mechanism. Authors: Mishan Britto / Adeline Goulet / Syeda Rizvi / Ottilie von Loeffelholz / Carolyn A Moores / Robert A Cross /  Abstract: Cut7, the sole kinesin-5 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, is essential for mitosis. Like other yeast kinesin-5 motors, Cut7 can reverse its stepping direction, by mechanisms that are currently unclear. ...Cut7, the sole kinesin-5 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, is essential for mitosis. Like other yeast kinesin-5 motors, Cut7 can reverse its stepping direction, by mechanisms that are currently unclear. Here we show that for full-length Cut7, the key determinant of stepping direction is the degree of motor crowding on the microtubule lattice, with greater crowding converting the motor from minus end-directed to plus end-directed stepping. To explain how high Cut7 occupancy causes this reversal, we postulate a simple proximity sensing mechanism that operates via steric blocking. We propose that the minus end-directed stepping action of Cut7 is selectively inhibited by collisions with neighbors under crowded conditions, whereas its plus end-directed action, being less space-hungry, is not. In support of this idea, we show that the direction of Cut7-driven microtubule sliding can be reversed by crowding it with non-Cut7 proteins. Thus, crowding by either dynein microtubule binding domain or Klp2, a kinesin-14, converts Cut7 from net minus end-directed to net plus end-directed stepping. Biochemical assays confirm that the Cut7 N terminus increases Cut7 occupancy by binding directly to microtubules. Direct observation by cryoEM reveals that this occupancy-enhancing N-terminal domain is partially ordered. Overall, our data point to a steric blocking mechanism for directional reversal through which collisions of Cut7 motor domains with their neighbors inhibit their minus end-directed stepping action, but not their plus end-directed stepping action. Our model can potentially reconcile a number of previous, apparently conflicting, observations and proposals for the reversal mechanism of yeast kinesins-5. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3445.map.gz emd_3445.map.gz | 201.1 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3445-v30.xml emd-3445-v30.xml emd-3445.xml emd-3445.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3445.png emd_3445.png | 192.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3445 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3445 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3445 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3445 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5m5iMC  5m5lMC  5m5mMC  5m5nMC  5m5oMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3445.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 489.3 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3445.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 489.3 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-electron microscopy of microtubule-bound S. pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : microtubule-bound S.pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state
| Entire | Name: microtubule-bound S.pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: microtubule-bound S.pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state
| Supramolecule | Name: microtubule-bound S.pombe kinesin-5 motor domain in the AMPPNP state type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 140 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin alpha-1D chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1D chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bovine (cattle) Bovine (cattle) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.107238 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFSVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFSVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLIGQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRGHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRTIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YEPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GVDSVEGEGE EEGEEY |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin beta-2B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta-2B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Bovine (cattle) Bovine (cattle) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 49.90777 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGSYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEAAGNKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKESESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMSAT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QDATADEQGE FEEEEGEDEA |
-Macromolecule #3: Kinesin-like protein cut7
| Macromolecule | Name: Kinesin-like protein cut7 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (yeast) Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972 / ATCC 24843) (yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.737527 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: ALHDENETNI NVVVRVRGRT DQEVRDNSSL AVSTSGAMGA ELAIQSDPSS MLVTKTYAFD KVFGPEADQL MLFENSVAPM LEQVLNGYN CTIFAYGQTG TGKTYTMSGD LSDSDGILSE GAGLIPRALY QLFSSLDNSN QEYAVKCSYY ELYNEEIRDL L VSEELRKP ...String: ALHDENETNI NVVVRVRGRT DQEVRDNSSL AVSTSGAMGA ELAIQSDPSS MLVTKTYAFD KVFGPEADQL MLFENSVAPM LEQVLNGYN CTIFAYGQTG TGKTYTMSGD LSDSDGILSE GAGLIPRALY QLFSSLDNSN QEYAVKCSYY ELYNEEIRDL L VSEELRKP ARVFEDTSRR GNVVITGIEE SYIKNAGDGL RLLREGSHRR QVAATKCNDL SSRSHSIFTI TLHRKVSSGM TD ETNSLTI NNNSDDLLRA SKLHMVDLAG SENIGRSGAE NKRARETGMI NQSLLTLGRV INALVEKAHH IPYRESKLTR LLQ DSLGGK TKTSMIVTVS STNTNLEETI STLEYAARAK SIRNKPQNNQ LVF |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Macromolecule #6: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: GDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 443.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GDP: |
-Macromolecule #7: TAXOL
| Macromolecule | Name: TAXOL / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: TA1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 853.906 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-TA1: |
-Macromolecule #8: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ANP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 506.196 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ANP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 297 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 68000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN CT3500 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Software: (Name: CTFFIND (ver. 3), FREALIGN) |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: SPIDER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: FREALIGN |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: FREALIGN / Number images used: 144300 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | An initial homology model of S. pombe cut7 kinesin-5 motor domain based on human kinesin-5 structure (PDB 3HQD) was prepared using Modeller. The coordinates of motor bound to an alpha-beta tubulin dimer (PDB 1JFF) were rigidly fitted into the cryo-EM map using Chimera and refined by flexible fitting using Flex-EM. Structural models of loop5 and loop10 were generated using Modeller. The conformation of the neck-linker and the N-terminus were calculated using a conjugate-gradient energy minimization approach. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
| Output model |  PDB-5m5i:  PDB-5m5l:  PDB-5m5m:  PDB-5m5n:  PDB-5m5o: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller