[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
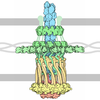
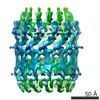
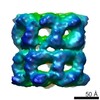
Yorodumi- PDB-5wln: Cryo-EM structure of the T2SS secretin XcpQ from Pseudomonas aeru... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5wln | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the T2SS secretin XcpQ from Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |||||||||
 Components Components | Type II secretion system protein D Type II secretion system Type II secretion system | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  T2SS / T2SS /  Secretin / Secretin /  Type 2 secretion system / Pentadecamer / GspD / XcpQ Type 2 secretion system / Pentadecamer / GspD / XcpQ | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information protein secretion by the type II secretion system / protein secretion by the type II secretion system /  type II protein secretion system complex / type II protein secretion system complex /  protein secretion / cell outer membrane / identical protein binding protein secretion / cell outer membrane / identical protein bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Pseudomonas aeruginosa (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.57 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.57 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hay, I.D. / Belousoff, M.J. / Lithgow, T.J. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 2items Australia, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2017 Journal: mBio / Year: 2017Title: Structural Basis of Type 2 Secretion System Engagement between the Inner and Outer Bacterial Membranes. Authors: Iain D Hay / Matthew J Belousoff / Trevor Lithgow /  Abstract: Sophisticated nanomachines are used by bacteria for protein secretion. In Gram-negative bacteria, the type 2 secretion system (T2SS) is composed of a pseudopilus assembly platform in the inner ...Sophisticated nanomachines are used by bacteria for protein secretion. In Gram-negative bacteria, the type 2 secretion system (T2SS) is composed of a pseudopilus assembly platform in the inner membrane and a secretin complex in the outer membrane. The engagement of these two megadalton-sized complexes is required in order to secrete toxins, effectors, and hydrolytic enzymes. has at least two T2SSs, with the ancestral nanomachine having a secretin complex composed of XcpQ. Until now, no high-resolution structural information was available to distinguish the features of this -type secretin, which varies greatly in sequence from the well-characterized -type and -type secretins. We have purified the ~1-MDa secretin complex and analyzed it by cryo-electron microscopy. Structural comparisons with the -type secretin complex revealed a striking structural homology despite the differences in their sequence characteristics. At 3.6-Å resolution, the secretin complex was found to have 15-fold symmetry throughout the membrane-embedded region and through most of the domains in the periplasm. However, the N1 domain and N0 domain were not well ordered into this 15-fold symmetry. We suggest a model wherein this disordering of the subunit symmetry for the periplasmic N domains provides a means to engage with the 6-fold symmetry in the inner membrane platform, with a metastable engagement that can be disrupted by substrate proteins binding to the region between XcpP, in the assembly platform, and the XcpQ secretin. How the outer membrane and inner membrane components of the T2SS engage each other and yet can allow for substrate uptake into the secretin chamber has challenged the protein transport field for some time. This vexing question is of significance because the T2SS collects folded protein substrates in the periplasm for transport out of the bacterium and yet must discriminate these few substrate proteins from all the other hundred or so folded proteins in the periplasm. The structural analysis here supports a model wherein substrates must compete against a metastable interaction between XcpP in the assembly platform and the XcpQ secretin, wherein only structurally encoded features in the T2SS substrates compete well enough to disrupt XcpQ-XcpP for entry into the XcpQ chamber, for secretion across the outer membrane. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5wln.cif.gz 5wln.cif.gz | 978.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5wln.ent.gz pdb5wln.ent.gz | 810.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5wln.json.gz 5wln.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/5wln https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/5wln ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/5wln ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/5wln | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8860MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Type II secretion system / T2SS protein D / General secretion pathway protein D Type II secretion system / T2SS protein D / General secretion pathway protein DMass: 66485.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 15 / Fragment: UNP residues 35-658 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (strain ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 15692 / DSM 22644 / CIP 104116 / JCM 14847 / LMG 12228 / 1C / PRS 101 / PAO1 Gene: xcpQ, PA3105 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): C43 / References: UniProt: P35818 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): C43 / References: UniProt: P35818 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Type 2 secretion system outer membrane secretin XcpQ Type II secretion system Type II secretion systemType: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1 MDa | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: C43 / Plasmid Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: C43 / Plasmid : pET20b : pET20b | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 130000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 600 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 130000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 600 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2500 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF : GIF |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.12_2829: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: MotionCorr 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND4 / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 18005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C15 (15 fold cyclic : C15 (15 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.57 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 18005 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj