+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3897 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA | |||||||||
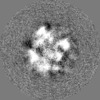
 Map data Map data | Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstress response to cadmium ion / stress response to copper ion / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity /  peptidase activity / peptidase activity /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  proteolysis / proteolysis /  ATP binding ATP bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) / Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) /   Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 11.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 11.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Carroni M / Mogk A / Bukau B / Franke K | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Regulatory coiled-coil domains promote head-to-head assemblies of AAA+ chaperones essential for tunable activity control. Authors: Marta Carroni / Kamila B Franke / Michael Maurer / Jasmin Jäger / Ingo Hantke / Felix Gloge / Daniela Linder / Sebastian Gremer / Kürşad Turgay / Bernd Bukau / Axel Mogk /   Abstract: Ring-forming AAA+ chaperones exert ATP-fueled substrate unfolding by threading through a central pore. This activity is potentially harmful requiring mechanisms for tight repression and substrate- ...Ring-forming AAA+ chaperones exert ATP-fueled substrate unfolding by threading through a central pore. This activity is potentially harmful requiring mechanisms for tight repression and substrate-specific activation. The AAA+ chaperone ClpC with the peptidase ClpP forms a bacterial protease essential to virulence and stress resistance. The adaptor MecA activates ClpC by targeting substrates and stimulating ClpC ATPase activity. We show how ClpC is repressed in its ground state by determining ClpC cryo-EM structures with and without MecA. ClpC forms large two-helical assemblies that associate via head-to-head contacts between coiled-coil middle domains (MDs). MecA converts this resting state to an active planar ring structure by binding to MD interaction sites. Loss of ClpC repression in MD mutants causes constitutive activation and severe cellular toxicity. These findings unravel an unexpected regulatory concept executed by coiled-coil MDs to tightly control AAA+ chaperone activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3897.map.gz emd_3897.map.gz | 5.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3897-v30.xml emd-3897-v30.xml emd-3897.xml emd-3897.xml | 22.6 KB 22.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3897_fsc.xml emd_3897_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3897.png emd_3897.png | 118.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_3897_msk_1.map emd_3897_msk_1.map | 67 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_3897_half_map_1.map.gz emd_3897_half_map_1.map.gz emd_3897_half_map_2.map.gz emd_3897_half_map_2.map.gz | 52.1 MB 52.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3897 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3897 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3897 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3897 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6emwMC  3894C  3895C  6em8C  6em9C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3897.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3897.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 67 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.36 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_3897_msk_1.map emd_3897_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA, half mapA
| File | emd_3897_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA, half mapA | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA, half mapB
| File | emd_3897_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Low-resolution map of S.aureus ClpC in complex with MecA, half mapB | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ClpC in complex with MecA from S. aureus
| Entire | Name: ClpC in complex with MecA from S. aureus List of electric distribution utilities in the Philippines List of electric distribution utilities in the Philippines |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ClpC in complex with MecA from S. aureus
| Supramolecule | Name: ClpC in complex with MecA from S. aureus / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.325732 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: KLTKEELKEI VTMMVNKLTN RLSEQNINII VTDKAKDKIA EEGYDPEYGA RPLIRAIQKT IEDNLSELIL DGNQIEGKKV TV |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.18359 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: LTKINETESE KLLSLEDTLH ERVIGQKDAV NSISKAVRRA RAGLKDPKRP IGSFIFLGPT GVGKTELARA LAESMFGDDD AMIRVDMSE FMEKHAVSRL VGAPPGYVGH DDGGQLTEKV RRKPYSVILF DEIEKAHPDV FNILLQVLDD GHLTDTKGRT V DFRNTIII ...String: LTKINETESE KLLSLEDTLH ERVIGQKDAV NSISKAVRRA RAGLKDPKRP IGSFIFLGPT GVGKTELARA LAESMFGDDD AMIRVDMSE FMEKHAVSRL VGAPPGYVGH DDGGQLTEKV RRKPYSVILF DEIEKAHPDV FNILLQVLDD GHLTDTKGRT V DFRNTIII MTSNVGAQEL QDQRFAGFGG SSDGQDYETI RKTMLKELKN SFRPEFLNRV DDIIVFH |
-Macromolecule #3: Class III stress response-related ATPase, AAA+ superfamily
| Macromolecule | Name: Class III stress response-related ATPase, AAA+ superfamily type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 6.539123 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: NNLKEIEQEI EKVKNEKDAA VHAQEFENAA NLRDKQTKLE KQYEEAKNEW KNAQN |
-Macromolecule #4: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.42625 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: SVVDTVAILK GLRDRYEAHH RINISDEAIE AAVKLSNRYV SDRFLPDKAI DLIDEASSKV RLKSHTTPNN LKEIEQEIEK VKNEKDAAV HAQEFENAAN LRDKQTKLEK QYEEAKNEWK NAQNGMSTSL SEEDIAEVIA GWTGIP |
-Macromolecule #5: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria)Strain: bovine RF122 / ET3-1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.699514 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: TLDSLARDLT VIAKDGTLDP VIGRDKEITR VIEVLSRRTK NNPVLIGEPG VGKTAIAEGL AQAIVNNEVP ETLKDKRVMS LDMGTVVAG TKYRGEFEER LKKVMEEIQQ AGNVILFIDE LHTLVGAGGA EGAIDASNIL KPALARGELQ CIGATTLDEY R KNIEKDAA LERRFQPVQV DEP |
-Macromolecule #6: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain bovine RF122 / ET3-1) (bacteria)Strain: bovine RF122 / ET3-1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 17.446889 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: RLTERAQRVL AHAQEEAIRL NHSNIGTEHL LLGLMKEPEG IAAKVLESFN ITEDKVIEEV EKLIGHGQDH VGTLHYTPRA KKVIELSMD EARKLHHNFV GTEHILLGLI RENEGVAARV FANLDLNITK ARAQVVKALG NPEMSNKNAQ ASKSNNTP |
-Macromolecule #7: Adapter protein MecA
| Macromolecule | Name: Adapter protein MecA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.758939 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MRIERVDDTT VKLFITYSDI EARGFSREDL WTNRKRGEEF FWSMMDEINE EEDFVVEGPL WIQVHAFEKG VEVTISKSKN EDMMNMSDD D |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Lower energy threshold: 0 eV / Energy filter - Upper energy threshold: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 1.25 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6emw: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z
Z Y
Y X
X