+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3780 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Molecular basis of human kinesin-8 function and inhibition | |||||||||
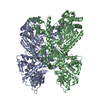
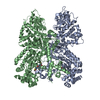
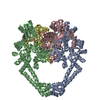
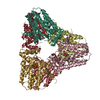
 Map data Map data | Asymmetric unit extracted from the full MT-bound Kif18A motor domain AMPPNP-bound reconstruction | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtubulin-dependent ATPase activity / mitotic spindle astral microtubule / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane /  Cilium Assembly / Cilium Assembly /  Intraflagellar transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase ...tubulin-dependent ATPase activity / mitotic spindle astral microtubule / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Intraflagellar transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase ...tubulin-dependent ATPase activity / mitotic spindle astral microtubule / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane /  Cilium Assembly / Cilium Assembly /  Intraflagellar transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / MHC class II antigen presentation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / mitotic spindle midzone / Aggrephagy / kinetochore microtubule / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / male meiotic nuclear division / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Intraflagellar transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Kinesins / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / MHC class II antigen presentation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / mitotic spindle midzone / Aggrephagy / kinetochore microtubule / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / male meiotic nuclear division / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes /  Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Hedgehog 'off' state / microtubule plus-end binding / Kinesins / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule depolymerization / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Hedgehog 'off' state / microtubule plus-end binding / Kinesins / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule depolymerization /  kinesin complex / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / microtubule-based movement / seminiferous tubule development / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / cytoplasmic microtubule / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / ruffle / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / MHC class II antigen presentation / cellular response to interleukin-4 / cellular response to estradiol stimulus / kinesin complex / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / microtubule-based movement / seminiferous tubule development / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / cytoplasmic microtubule / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / ruffle / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / MHC class II antigen presentation / cellular response to interleukin-4 / cellular response to estradiol stimulus /  caveola / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / caveola / RHO GTPases Activate Formins /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization /  kinetochore / Separation of Sister Chromatids / microtubule cytoskeleton / kinetochore / Separation of Sister Chromatids / microtubule cytoskeleton /  protein transport / protein transport /  double-stranded RNA binding / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / mitotic cell cycle /  actin binding / actin binding /  microtubule binding / microtubule binding /  microtubule / microtubule /  hydrolase activity / hydrolase activity /  GTPase activity / GTPase activity /  centrosome / centrosome /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Bos taurus (cattle) / Bos taurus (cattle) /   Sus scrofa (pig) / Sus scrofa (pig) /   Bovine (cattle) / Bovine (cattle) /   Pig (pig) Pig (pig) | |||||||||
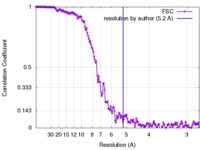
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Locke J / Joseph AP / Topf M / Moores CA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017Title: Structural basis of human kinesin-8 function and inhibition. Authors: Julia Locke / Agnel Praveen Joseph / Alejandro Peña / Martin M Möckel / Thomas U Mayer / Maya Topf / Carolyn A Moores /   Abstract: Kinesin motors play diverse roles in mitosis and are targets for antimitotic drugs. The clinical significance of these motors emphasizes the importance of understanding the molecular basis of their ...Kinesin motors play diverse roles in mitosis and are targets for antimitotic drugs. The clinical significance of these motors emphasizes the importance of understanding the molecular basis of their function. Equally important, investigations into the modes of inhibition of these motors provide crucial information about their molecular mechanisms. Kif18A regulates spindle microtubules through its dual functionality, with microtubule-based stepping and regulation of microtubule dynamics. We investigated the mechanism of Kif18A and its inhibition by the small molecule BTB-1. The Kif18A motor domain drives ATP-dependent plus-end microtubule gliding, and undergoes conformational changes consistent with canonical mechanisms of plus-end-directed motility. The Kif18A motor domain also depolymerizes microtubule plus and minus ends. BTB-1 inhibits both of these microtubule-based Kif18A activities. A reconstruction of BTB-1-bound, microtubule-bound Kif18A, in combination with computational modeling, identified an allosteric BTB-1-binding site near loop5, where it blocks the ATP-dependent conformational changes that we characterized. Strikingly, BTB-1 binding is close to that of well-characterized Kif11 inhibitors that block tight microtubule binding, whereas BTB-1 traps Kif18A on the microtubule. Our work highlights a general mechanism of kinesin inhibition in which small-molecule binding near loop5 prevents a range of conformational changes, blocking motor function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3780.map.gz emd_3780.map.gz | 646.8 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3780-v30.xml emd-3780-v30.xml emd-3780.xml emd-3780.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3780_fsc.xml emd_3780_fsc.xml | 17.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3780.png emd_3780.png | 64.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3780 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3780 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3780 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3780 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5ocuMC 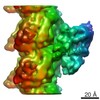 3778C 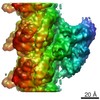 3803C  5oamC  5ogcC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3780.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3780.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Asymmetric unit extracted from the full MT-bound Kif18A motor domain AMPPNP-bound reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.39 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 13-Protofilament microtuble-bound human Kinesin-8 motor domain ne...
+Supramolecule #1: 13-Protofilament microtuble-bound human Kinesin-8 motor domain ne...
+Supramolecule #2: Kinesin-8 motor domain neck-linker
+Supramolecule #3: Tubulin, alpha
+Supramolecule #4: Tubulin, beta
+Macromolecule #1: Kinesin-like protein KIF18A
+Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha chain
+Macromolecule #3: Tubulin beta chain
+Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
+Macromolecule #6: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #7: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #8: GUANOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #9: TAXOL
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 3.5 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.3 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.3 mm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Details | FEI Polara |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3840 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3712 pixel / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 5.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5ocu: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller