[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
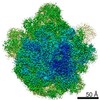
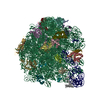
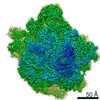
Yorodumi- PDB-6ddd: Structure of the 50S ribosomal subunit from Methicillin Resistant... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ddd | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the 50S ribosomal subunit from Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in complex with the oxazolidinone antibiotic LZD-5 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome/Antibiotic /  antibiotic complex / antibiotic complex /  linezolid / linezolid /  oxazolidinone / 50S / oxazolidinone / 50S /  ribosome / Ribosome-Antibiotic complex ribosome / Ribosome-Antibiotic complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlarge ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit /  5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / 5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit /  transferase activity / negative regulation of translation / transferase activity / negative regulation of translation /  tRNA binding / tRNA binding /  rRNA binding / rRNA binding /  ribosome ...large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome ...large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit /  5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / 5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit /  transferase activity / negative regulation of translation / transferase activity / negative regulation of translation /  tRNA binding / tRNA binding /  rRNA binding / rRNA binding /  ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome /  translation / translation /  ribonucleoprotein complex / ribonucleoprotein complex /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Belousoff, M.J. / Venugopal, H. / Bamert, R.S. / Lithgow, T. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ChemMedChem / Year: 2019 Journal: ChemMedChem / Year: 2019Title: cryoEM-Guided Development of Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Authors: Matthew J Belousoff / Hari Venugopal / Alexander Wright / Samuel Seoner / Isabella Stuart / Chris Stubenrauch / Rebecca S Bamert / David W Lupton / Trevor Lithgow /  Abstract: While the ribosome is a common target for antibiotics, challenges with crystallography can impede the development of new bioactives using structure-based drug design approaches. In this study we ...While the ribosome is a common target for antibiotics, challenges with crystallography can impede the development of new bioactives using structure-based drug design approaches. In this study we exploit common structural features present in linezolid-resistant forms of both methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) to redesign the antibiotic. Enabled by rapid and facile cryoEM structures, this process has identified (S)-2,2-dichloro-N-((3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-5-yl)methyl)acetamide (LZD-5) and (S)-2-chloro-N-((3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-5-yl)methyl) acetamide (LZD-6), which inhibit the ribosomal function and growth of linezolid-resistant MRSA and VRE. The strategy discussed highlights the potential for cryoEM to facilitate the development of novel bioactive materials. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ddd.cif.gz 6ddd.cif.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ddd.ent.gz pdb6ddd.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ddd.json.gz 6ddd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dd/6ddd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dd/6ddd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dd/6ddd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dd/6ddd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 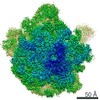 7867MC 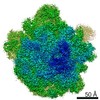 7870C  6ddgC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 25 types, 25 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSVWXYZa
-RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules 12
| #26: RNA chain |  23S ribosomal RNA 23S ribosomal RNAMass: 946696.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) / References: Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) / References:  GenBank: 1269117575 GenBank: 1269117575 |
|---|---|
| #27: RNA chain |  5S ribosomal RNA 5S ribosomal RNAMass: 36974.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) / References: Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) / References:  GenBank: 1333434557 GenBank: 1333434557 |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 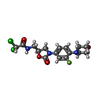
| #28: Chemical | ChemComp-G6V / |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 50S Ribosomal subunit from MRSA in complex with oxazolidinone LZD-5 Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#27 / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 35 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 49223 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj






























