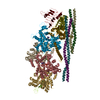
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3672 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Open protomer of human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Open protomer of human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of DNA catabolic process / establishment of RNA localization to telomere / positive regulation of telomerase catalytic core complex assembly / cellular response to nitrosative stress / negative regulation of telomere capping / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / establishment of protein-containing complex localization to telomere / regulation of microglial cell activation / Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening ...positive regulation of DNA catabolic process / establishment of RNA localization to telomere / positive regulation of telomerase catalytic core complex assembly / cellular response to nitrosative stress / negative regulation of telomere capping / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / establishment of protein-containing complex localization to telomere / regulation of microglial cell activation / Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / meiotic telomere clustering / lipoprotein catabolic process / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / male meiotic nuclear division / histone mRNA catabolic process / female meiotic nuclear division / regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / pexophagy / cellular response to X-ray / peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation /  V(D)J recombination / oocyte development / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / reciprocal meiotic recombination / V(D)J recombination / oocyte development / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / reciprocal meiotic recombination /  DNA repair complex / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity / response to ionizing radiation / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / negative regulation of B cell proliferation / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / peroxisomal matrix / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / DNA repair complex / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity / response to ionizing radiation / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / negative regulation of B cell proliferation / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / peroxisomal matrix / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release /  replicative senescence / positive regulation of cell adhesion / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / replicative senescence / positive regulation of cell adhesion / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response /  somitogenesis / regulation of cellular response to heat / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest / cellular response to retinoic acid / somitogenesis / regulation of cellular response to heat / DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest / cellular response to retinoic acid /  signal transduction in response to DNA damage / ovarian follicle development / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / Pexophagy / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / ovarian follicle development / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / Pexophagy /  telomere maintenance / post-embryonic development / thymus development / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance / post-embryonic development / thymus development / regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / DNA damage checkpoint signaling /  regulation of autophagy / determination of adult lifespan / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Stabilization of p53 / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of autophagy / determination of adult lifespan / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Stabilization of p53 / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination /  brain development / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / multicellular organism growth / cellular response to gamma radiation / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / spindle / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Methylation / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / brain development / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / multicellular organism growth / cellular response to gamma radiation / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / spindle / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Methylation / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence /  Meiotic recombination / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / double-strand break repair / Meiotic recombination / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / double-strand break repair /  cellular senescence / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / cellular senescence / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks /  heart development / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / cytoplasmic vesicle / neuron apoptotic process / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / regulation of apoptotic process / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / protein autophosphorylation / response to hypoxia / heart development / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / cytoplasmic vesicle / neuron apoptotic process / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / regulation of apoptotic process / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / protein autophosphorylation / response to hypoxia /  regulation of cell cycle / regulation of cell cycle /  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of apoptotic process / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of apoptotic process /  protein phosphorylation / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle protein phosphorylation / intracellular membrane-bounded organelleSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Baretic D / Pollard HK / Fisher DI / Johnson CM / Santhanam B / Truman CM / Kouba T / Fersht AR / Phillips C / Williams RL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2017 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2017Title: Structures of closed and open conformations of dimeric human ATM. Authors: Domagoj Baretić / Hannah K Pollard / David I Fisher / Christopher M Johnson / Balaji Santhanam / Caroline M Truman / Tomas Kouba / Alan R Fersht / Christopher Phillips / Roger L Williams /  Abstract: ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) is a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase (PIKK) best known for its role in DNA damage response. ATM also functions in oxidative stress response, ...ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) is a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase (PIKK) best known for its role in DNA damage response. ATM also functions in oxidative stress response, insulin signaling, and neurogenesis. Our electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) suggests that human ATM is in a dynamic equilibrium between closed and open dimers. In the closed state, the PIKK regulatory domain blocks the peptide substrate-binding site, suggesting that this conformation may represent an inactive or basally active enzyme. The active site is held in this closed conformation by interaction with a long helical hairpin in the TRD3 (tetratricopeptide repeats domain 3) domain of the symmetry-related molecule. The open dimer has two protomers with only a limited contact interface, and it lacks the intermolecular interactions that block the peptide-binding site in the closed dimer. This suggests that the open conformation may be more active. The ATM structure shows the detailed topology of the regulator-interacting N-terminal helical solenoid. The ATM conformational dynamics shown by the structures represent an important step in understanding the enzyme regulation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3672.map.gz emd_3672.map.gz | 94.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3672-v30.xml emd-3672-v30.xml emd-3672.xml emd-3672.xml | 18.7 KB 18.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3672_fsc.xml emd_3672_fsc.xml | 10.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3672.png emd_3672.png | 141.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3672 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3672 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3672 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3672 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5np1MC  3668C  3669C  3670C  3671C  3673C  5np0C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3672.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3672.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Open protomer of human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.43 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dimeric human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) kinase
| Entire | Name: Dimeric human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) kinase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dimeric human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) kinase
| Supramolecule | Name: Dimeric human ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) kinase type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 705 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293 / Recombinant plasmid: pDEST12.2-OriP Homo sapiens (human) / Recombinant cell: HEK293 / Recombinant plasmid: pDEST12.2-OriP |
-Macromolecule #1: Serine-protein kinase ATM
| Macromolecule | Name: Serine-protein kinase ATM / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 352.393969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDYKDDDDKH MSLVLNDLLI CCRQLEHDRA TERKKEVEKF KRLIRDPETI KHLDRHSDSK QGKYLNWDAV FRFLQKYIQK ETECLRIAK PNVSASTQAS RQKKMQEISS LVKYFIKCAN RRAPRLKCQE LLNYIMDTVK DSSNGAIYGA DCSNILLKDI L SVRKYWCE ...String: MDYKDDDDKH MSLVLNDLLI CCRQLEHDRA TERKKEVEKF KRLIRDPETI KHLDRHSDSK QGKYLNWDAV FRFLQKYIQK ETECLRIAK PNVSASTQAS RQKKMQEISS LVKYFIKCAN RRAPRLKCQE LLNYIMDTVK DSSNGAIYGA DCSNILLKDI L SVRKYWCE ISQQQWLELF SVYFRLYLKP SQDVHRVLVA RIIHAVTKGC CSQTDGLNSK FLDFFSKAIQ CARQEKSSSG LN HILAALT IFLKTLAVNF RIRVCELGDE ILPTLLYIWT QHRLNDSLKE VIIELFQLQI YIHHPKGAKT QEKGAYESTK WRS ILYNLY DLLVNEISHI GSRGKYSSGF RNIAVKENLI ELMADICHQV FNEDTRSLEI SQSYTTTQRE SSDYSVPCKR KKIE LGWEV IKDHLQKSQN DFDLVPWLQI ATQLISKYPA SLPNCELSPL LMILSQLLPQ QRHGERTPYV LRCLTEVALC QDKRS NLES SQKSDLLKLW NKIWCITFRG ISSEQIQAEN FGLLGAIIQG SLVEVDREFW KLFTGSACRP SCPAVCCLTL ALTTSI VPG TVKMGIEQNM CEVNRSFSLK ESIMKWLLFY QLEGDLENST EVPPILHSNF PHLVLEKILV SLTMKNCKAA MNFFQSV PE CEHHQKDKEE LSFSEVEELF LQTTFDKMDF LTIVRECGIE KHQSSIGFSV HQNLKESLDR CLLGLSEQLL NNYSSEIT N SETLVRCSRL LVGVLGCYCY MGVIAEEEAY KSELFQKAKS LMQCAGESIT LFKNKTNEEF RIGSLRNMMQ LCTRCLSNC TKKSPNKIAS GFFLRLLTSK LMNDIADICK SLASFIKKPF DRGEVESMED DTNGNLMEVE DQSSMNLFND YPDSSVSDAN EPGESQSTI GAINPLAEEY LSKQDLLFLD MLKFLCLCVT TAQTNTVSFR AADIRRKLLM LIDSSTLEPT KSLHLHMYLM L LKELPGEE YPLPMEDVLE LLKPLSNVCS LYRRDQDVCK TILNHVLHVV KNLGQSNMDS ENTRDAQGQF LTVIGAFWHL TK ERKYIFS VRMALVNCLK TLLEADPYSK WAILNVMGKD FPVNEVFTQF LADNHHQVRM LAAESINRLF QDTKGDSSRL LKA LPLKLQ QTAFENAYLK AQEGMREMSH SAENPETLDE IYNRKSVLLT LIAVVLSCSP ICEKQALFAL CKSVKENGLE PHLV KKVLE KVSETFGYRR LEDFMASHLD YLVLEWLNLQ DTEYNLSSFP FILLNYTNIE DFYRSCYKVL IPHLVIRSHF DEVKS IANQ IQEDWKSLLT DCFPKILVNI LPYFAYEGTR DSGMAQQRET ATKVYDMLKS ENLLGKQIDH LFISNLPEIV VELLMT LHE PANSSASQST DLCDFSGDLD PAPNPPHFPS HVIKATFAYI SNCHKTKLKS ILEILSKSPD SYQKILLAIC EQAAETN NV YKKHRILKIY HLFVSLLLKD IKSGLGGAWA FVLRDVIYTL IHYINQRPSC IMDVSLRSFS LCCDLLSQVC QTAVTYCK D ALENHLHVIV GTLIPLVYEQ VEVQKQVLDL LKYLVIDNKD NENLYITIKL LDPFPDHVVF KDLRITQQKI KYSRGPFSL LEEINHFLSV SVYDALPLTR LEGLKDLRRQ LELHKDQMVD IMRASQDNPQ DGIMVKLVVN LLQLSKMAIN HTGEKEVLEA VGSCLGEVG PIDFSTIAIQ HSKDASYTKA LKLFEDKELQ WTFIMLTYLN NTLVEDCVKV RSAAVTCLKN ILATKTGHSF W EIYKMTTD PMLAYLQPFR TSRKKFLEVP RFDKENPFEG LDDINLWIPL SENHDIWIKT LTCAFLDSGG TKCEILQLLK PM CEVKTDF CQTVLPYLIH DILLQDTNES WRNLLSTHVQ GFFTSCLRHF SQTSRSTTPA NLDSESEHFF RCCLDKKSQR TML AVVDYM RRQKRPSSGT IFNDAFWLDL NYLEVAKVAQ SCAAHFTALL YAEIYADKKS MDDQEKRSLA FEEGSQSTTI SSLS EKSKE ETGISLQDLL LEIYRSIGEP DSLYGCGGGK MLQPITRLRT YEHEAMWGKA LVTYDLETAI PSSTRQAGII QALQN LGLC HILSVYLKGL DYENKDWCPE LEELHYQAAW RNMQWDHCTS VSKEVEGTSY HESLYNALQS LRDREFSTFY ESLKYA RVK EVEEMCKRSL ESVYSLYPTL SRLQAIGELE SIGELFSRSV THRQLSEVYI KWQKHSQLLK DSDFSFQEPI MALRTVI LE ILMEKEMDNS QRECIKDILT KHLVELSILA RTFKNTQLPE RAIFQIKQYN SVSCGVSEWQ LEEAQVFWAK KEQSLALS I LKQMIKKLDA SCAANNPSLK LTYTECLRVC GNWLAETCLE NPAVIMQTYL EKAVEVAGNY DGESSDELRN GKMKAFLSL ARFSDTQYQR IENYMKSSEF ENKQALLKRA KEEVGLLREH KIQTNRYTVK VQRELELDEL ALRALKEDRK RFLCKAVENY INCLLSGEE HDMWVFRLCS LWLENSGVSE VNGMMKRDGM KIPTYKFLPL MYQLAARMGT KMMGGLGFHE VLNNLISRIS M DHPHHTLF IILALANANR DEFLTKPEVA RRSRITKNVP KQSSQLDEDR TEAANRIICT IRSRRPQMVR SVEALCDAYI IL ANLDATQ WKTQRKGINI PADQPITKLK NLEDVVVPTM EIKVDHTGEY GNLVTIQSFK AEFRLAGGVN LPKIIDCVGS DGK ERRQLV KGRDDLRQDA VMQQVFQMCN TLLQRNTETR KRKLTICTYK VVPLSQRSGV LEWCTGTVPI GEFLVNNEDG AHKR YRPND FSAFQCQKKM MEVQKKSFEE KYEVFMDVCQ NFQPVFRYFC MEKFLDPAIW FEKRLAYTRS VATSSIVGYI LGLGD RHVQ NILINEQSAE LVHIDLGVAF EQGKILPTPE TVPFRLTRDI VDGMGITGVE GVFRRCCEKT MEVMRNSQET LLTIVE VLL YDPLFDWTMN PLKALYLQQR PEDETELHPT LNADDQECKR NLSDIDQSFN KVAERVLMRL QEKLKGVEEG TVLSVGG QV NLLIQQAIDP KNLSRLFPGW KAWV |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.6 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil, UltrAuFoil, R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: 3 uL sample/grid blotted for 12 s before plunge-freezing. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | The sample was purified by anti-FLAG affinity chromatography followed by overnight dialysis and a final gel-filtration. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 35714 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 97902 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 97902 |
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF / Energy filter - Lower energy threshold: 0 eV / Energy filter - Upper energy threshold: 20 eV |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Temperature | Min: 80.15 K |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-20 / Number grids imaged: 4 / Number real images: 2720 / Average exposure time: 0.8 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.1 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5np1: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller