[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
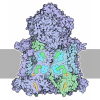
Yorodumi- EMDB-4343: Filament of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT domains of BRCA1 (ACC... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4343 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
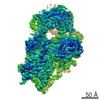
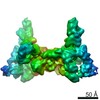
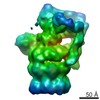
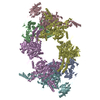
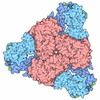
| Title | Filament of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT domains of BRCA1 (ACC-BRCT) core at 4.6 A resolution | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Filament / Helical / Multienzyme / Ligase / Biotin-dependent carboxylase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationfatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / acetyl-CoA carboxylase / Biotin transport and metabolism / Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis / acetyl-CoA metabolic process / malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process / ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression / acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity / tissue homeostasis ...fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / acetyl-CoA carboxylase / Biotin transport and metabolism / Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis / acetyl-CoA metabolic process / malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process / ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression / acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity / tissue homeostasis / Carnitine metabolism / protein metabolic process / lipid homeostasis / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / fibrillar center / fatty acid biosynthetic process / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / actin cytoskeleton / protein homotetramerization / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / metal ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hunkeler M / Hagmann A | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3 items Switzerland, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Structural basis for regulation of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Authors: Moritz Hunkeler / Anna Hagmann / Edward Stuttfeld / Mohamed Chami / Yakir Guri / Henning Stahlberg / Timm Maier /   Abstract: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, a rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis. Eukaryotic acetyl-CoA carboxylases are large, homodimeric multienzymes. ...Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, a rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis. Eukaryotic acetyl-CoA carboxylases are large, homodimeric multienzymes. Human acetyl-CoA carboxylase occurs in two isoforms: the metabolic, cytosolic ACC1, and ACC2, which is anchored to the outer mitochondrial membrane and controls fatty acid β-oxidation. ACC1 is regulated by a complex interplay of phosphorylation, binding of allosteric regulators and protein-protein interactions, which is further linked to filament formation. These filaments were discovered in vitro and in vivo 50 years ago, but the structural basis of ACC1 polymerization and regulation remains unknown. Here, we identify distinct activated and inhibited ACC1 filament forms. We obtained cryo-electron microscopy structures of an activated filament that is allosterically induced by citrate (ACC-citrate), and an inactivated filament form that results from binding of the BRCT domains of the breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1). While non-polymeric ACC1 is highly dynamic, filament formation locks ACC1 into different catalytically competent or incompetent conformational states. This unique mechanism of enzyme regulation via large-scale conformational changes observed in ACC1 has potential uses in engineering of switchable biosynthetic systems. Dissecting the regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase opens new paths towards counteracting upregulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in disease. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4343.map.gz emd_4343.map.gz | 14.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4343-v30.xml emd-4343-v30.xml emd-4343.xml emd-4343.xml | 12.4 KB 12.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4343.png emd_4343.png | 143.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4343.cif.gz emd-4343.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4343 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4343 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4343 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4343 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6g2hMC  4342C  4344C  6g2dC  6g2iC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4343.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 202.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4343.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 202.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.058 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Multienzyme core
| Entire | Name: Multienzyme core |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Multienzyme core
| Supramolecule | Name: Multienzyme core / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 272.632844 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAHHHHHHHH HHGSTSGSGE QKLISEEDLG STSGSGDYKD DDDKLTSLYK KAGLENLYFQ GMDEPSPLAQ PLELNQHSRF IIGSVSEDN SEDEISNLVK LDLLEEKEGS LSPASVGSDT LSDLGISSLQ DGLALHIRSS MSGLHLVKQG RDRKKIDSQR D FTVASPAE ...String: MAHHHHHHHH HHGSTSGSGE QKLISEEDLG STSGSGDYKD DDDKLTSLYK KAGLENLYFQ GMDEPSPLAQ PLELNQHSRF IIGSVSEDN SEDEISNLVK LDLLEEKEGS LSPASVGSDT LSDLGISSLQ DGLALHIRSS MSGLHLVKQG RDRKKIDSQR D FTVASPAE FVTRFGGNKV IEKVLIANNG IAAVKCMRSI RRWSYEMFRN ERAIRFVVMV TPEDLKANAE YIKMADHYVP VP GGPNNNN YANVELILDI AKRIPVQAVW AGWGHASENP KLPELLLKNG IAFMGPPSQA MWALGDKIAS SIVAQTAGIP TLP WSGSGL RVDWQENDFS KRILNVPQEL YEKGYVKDVD DGLQAAEEVG YPVMIKASEG GGGKGIRKVN NADDFPNLFR QVQA EVPGS PIFVMRLAKQ SRHLEVQILA DQYGNAISLF GRDCSVQRRH QKIIEEAPAT IATPAVFEHM EQCAVKLAKM VGYVS AGTV EYLYSQDGSF YFLELNPRLQ VEHPCTEMVA DVNLPAAQLQ IAMGIPLYRI KDIRMMYGVS PWGDSPIDFE DSAHVP CPR GHVIAARITS ENPDEGFKPS SGTVQELNFR SNKNVWGYFS VAAAGGLHEF ADSQFGHCFS WGENREEAIS NMVVALK EL SIRGDFRTTV EYLIKLLETE SFQMNRIDTG WLDRLIAEKV QAERPDTMLG VVCGALHVAD VSLRNSVSNF LHSLERGQ V LPAHTLLNTV DVELIYEGVK YVLKVTRQSP NSYVVIMNGS CVEVDVHRLS DGGLLLSYDG SSYTTYMKEE VDRYRITIG NKTCVFEKEN DPSVMRSPSA GKLIQYIVED GGHVFAGQCY AEIEVMKMVM TLTAVESGCI HYVKRPGAAL DPGCVLAKMQ LDNPSKVQQ AELHTGSLPR IQSTALRGEK LHRVFHYVLD NLVNVMNGYC LPDPFFSSKV KDWVERLMKT LRDPSLPLLE L QDIMTSVS GRIPPNVEKS IKKEMAQYAS NITSVLCQFP SQQIANILDS HAATLNRKSE REVFFMNTQS IVQLVQRYRS GI RGHMKAV VMDLLRQYLR VETQFQNGHY DKCVFALREE NKSDMNTVLN YIFSHAQVTK KNLLVTMLID QLCGRDPTLT DEL LNILTE LTQLSKTTNA KVALRARQVL IASHLPSYEL RHNQVESIFL SAIDMYGHQF CIENLQKLIL SETSIFDVLP NFFY HSNQV VRMAALEVYV RRAYIAYELN SVQHRQLKDN TCVVEFQFML PTSHPNRGNI PTLNRMSFSS NLNHYGMTHV ASVSD VLLD NSFTPPCQRM GGMVSFRTFE DFVRIFDEVM GCFSDSPPQS PTFPEAGHTS LYDEDKVPRD EPIHILNVAI KTDCDI EDD RLAAMFREFT QQNKATLVDH GIRRLTFLVA QKDFRKQVNY EVDRRFHREF PKFFTFRARD KFEEDRIYRH LEPALAF QL ELNRMRNFDL TAIPCANHKM HLYLGAAKVE VGTEVTDYRF FVRAIIRHSD LVTKEASFEY LQNEGERLLL EAMDELEV A FNNTNVRTDC NHIFLNFVPT VIMDPSKIEE SVRSMVMRYG SRLWKLRVLQ AELKINIRLT PTGKAIPIRL FLTNESGYY LDISLYKEVT DSRTAQIMFQ AYGDKQGPLH GMLINTPYVT KDLLQSKRFQ AQSLGTTYIY DIPEMFRQSL IKLWESMSTQ AFLPSPPLP SDMLTYTELV LDDQGQLVHM NRLPGGNEIG MVAWKMTFKS PEYPEGRDII VIGNDITYRI GSFGPQEDLL F LRASELAR AEGIPRIYVS ANSGARIGLA EEIRHMFHVA WVDPEDPYKG YRYLYLTPQD YKRVSALNSV HCEHVEDEGE SR YKITDII GKEEGIGPEN LRGSGMIAGE SSLAYNEIIT ISLVTCRAIG IGAYLVRLGQ RTIQVENSHL ILTGAGALNK VLG REVYTS NNQLGGIQIM HNNGVTHCTV CDDFEGVFTV LHWLSYMPKS VHSSVPLLNS KDPIDRIIEF VPTKTPYDPR WMLA GRPHP TQKGQWLSGF FDYGSFSEIM QPWAQTVVVG RARLGGIPVG VVAVETRTVE LSIPADPANL DSEAKIIQQA GQVWF PDSA FKTYQAIKDF NREGLPLMVF ANWRGFSGGM KDMYDQVLKF GAYIVDGLRE CCQPVLVYIP PQAELRGGSW VVIDSS INP RHMEMYADRE SRGSVLEPEG TVEIKFRRKD LVKTMRRVDP VYIHLAERLG TPELSTAERK ELENKLKERE EFLIPIY HQ VAVQFADLHD TPGRMQEKGV ISDILDWKTS RTFFYWRLRR LLLEDLVKKK IHNANPELTD GQIQAMLRRW FVEVEGTV K AYVWDNNKDL AEWLEKQLTE EDGVHSVIEE NIKCISRDYV LKQIRSLVQA NPEVAMDSII HMTQHISPTQ RAEVIRILS TMDSPST UniProtKB: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 80.0 e/Å2 Details: Collected in movie-mode with total dose of 80 e-/A2 for a total of 80 frames. Frames 3-22 were used for final reconstruction. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER Details: Initial model was generated form 2D class averages using e2initialmodel.py in EMAN2 |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 2.01) / Number images used: 48483 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller