+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5jlf | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex (Reprocessed) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / CONTRACTILE FILAMENT / CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / CONTRACTILE FILAMENT /  MUSCLE / MUSCLE /  THIN FILAMENT / THIN FILAMENT /  CYTOSKELETON / CYTOSKELETON /  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  HYDROLASE COMPLEX / HYDROLASE COMPLEX /  F-actin / F-actin /  tropomyosin / tropomyosin /  filament / protein polymers / filament / protein polymers /  cryo EM cryo EM | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development /  stress fiber / stress fiber /  titin binding / actin filament polymerization / titin binding / actin filament polymerization /  filopodium / filopodium /  actin filament / actin filament /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding /  lamellipodium / lamellipodium /  cell body / cell body /  hydrolase activity / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / protein domain specific binding /  calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse)  Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | von der Ecken, J. / Raunser, S. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution. Abstract: The interaction of myosin with actin filaments is the central feature of muscle contraction and cargo movement along actin filaments of the cytoskeleton. The energy for these movements is generated ...The interaction of myosin with actin filaments is the central feature of muscle contraction and cargo movement along actin filaments of the cytoskeleton. The energy for these movements is generated during a complex mechanochemical reaction cycle. Crystal structures of myosin in different states have provided important structural insights into the myosin motor cycle when myosin is detached from F-actin. The difficulty of obtaining diffracting crystals, however, has prevented structure determination by crystallography of actomyosin complexes. Thus, although structural models exist of F-actin in complex with various myosins, a high-resolution structure of the F-actin–myosin complex is missing. Here, using electron cryomicroscopy, we present the structure of a human rigor actomyosin complex at an average resolution of 3.9 Å. The structure reveals details of the actomyosin interface, which is mainly stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. The negatively charged amino (N) terminus of actin interacts with a conserved basic motif in loop 2 of myosin, promoting cleft closure in myosin. Surprisingly, the overall structure of myosin is similar to rigor-like myosin structures in the absence of F-actin, indicating that F-actin binding induces only minimal conformational changes in myosin. A comparison with pre-powerstroke and intermediate (Pi-release) states of myosin allows us to discuss the general mechanism of myosin binding to F-actin. Our results serve as a strong foundation for the molecular understanding of cytoskeletal diseases, such as autosomal dominant hearing loss and diseases affecting skeletal and cardiac muscles, in particular nemaline myopathy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Structure of the F-actin-tropomyosin complex. Authors: Julian von der Ecken / Mirco Müller / William Lehman / Dietmar J Manstein / Pawel A Penczek / Stefan Raunser /   Abstract: Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead ...Filamentous actin (F-actin) is the major protein of muscle thin filaments, and actin microfilaments are the main component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Mutations in different actin isoforms lead to early-onset autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss, familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, and multiple variations of myopathies. In striated muscle fibres, the binding of myosin motors to actin filaments is mainly regulated by tropomyosin and troponin. Tropomyosin also binds to F-actin in smooth muscle and in non-muscle cells and stabilizes and regulates the filaments there in the absence of troponin. Although crystal structures for monomeric actin (G-actin) are available, a high-resolution structure of F-actin is still missing, hampering our understanding of how disease-causing mutations affect the function of thin muscle filaments and microfilaments. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of F-actin at a resolution of 3.7 Å in complex with tropomyosin at a resolution of 6.5 Å, determined by electron cryomicroscopy. The structure reveals that the D-loop is ordered and acts as a central region for hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions that stabilize the F-actin filament. We clearly identify map density corresponding to ADP and Mg(2+) and explain the possible effect of prominent disease-causing mutants. A comparison of F-actin with G-actin reveals the conformational changes during filament formation and identifies the D-loop as their key mediator. We also confirm that negatively charged tropomyosin interacts with a positively charged groove on F-actin. Comparison of the position of tropomyosin in F-actin-tropomyosin with its position in our previously determined F-actin-tropomyosin-myosin structure reveals a myosin-induced transition of tropomyosin. Our results allow us to understand the role of individual mutations in the genesis of actin- and tropomyosin-related diseases and will serve as a strong foundation for the targeted development of drugs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5jlf.cif.gz 5jlf.cif.gz | 390.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5jlf.ent.gz pdb5jlf.ent.gz | 323.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5jlf.json.gz 5jlf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jl/5jlf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jl/5jlf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jl/5jlf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jl/5jlf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8162MC  8163MC  8164C  8165C  5jlhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 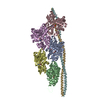
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
NCS oper:
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  / Alpha-actin-1 / Alpha-actin-1Mass: 41875.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P68135 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P68135#2: Protein | Mass: 11507.176 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: MOUSE TROPOMYSIN WAS USED (UNP P58771, RESIDUES 97-231). DUE TO THE LIMITED RESOLUTION OF THE CRYO-EM DENSITY IN THE REGION OF TROPOMYOSIN, TROPOMYOSIN HAS BEEN REPRESENTED AS POLY(UNK). Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)#3: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP /  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate#4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Sequence details | MOUSE TROPOMYSIN WAS USED (UNP P58771, TPM1_MOUSE, RESIDUES 97-231). DUE TO THE LIMITED RESOLUTION ...MOUSE TROPOMYSIN | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.2 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 5 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 100 mM KCl, and 2 mM MgCl2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % Details: Sample was applied to a glow-discharged holey carbon grid, incubated for 10 s and manually blotted for 3 s from the backside with filter paper. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: Cs corrected microscope |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2600 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2600 nm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 0.475 sec. / Electron dose: 16 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 8 / Used frames/image: 2-8 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0088 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 166.9 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.5 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 119000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 91000 Details: THE TROPOMYOSIN MAP FILTERED TO 6.5 ANGSTROM WAS MERGED WITH THE FINAL F-ACTIN MAP (3.6 ANGSTROM) TO OBTAIN A MAP OF THE ENTIRE F-ACTIN-TROPOMYOSIN COMPLEX. Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 3J8A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 3.6→193.6 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.857 / SU B: 33.198 / SU ML: 0.463 / ESU R: 1.724 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS MERGED WITH THE FINAL F-ACTIN MAP (3.6 ANGSTROM) TO OBTAIN A MAP OF THE ENTIRE F-ACTIN TROPOMYOSIN COMPLEX.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 97.923 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Total: 14450 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj






