+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5gar | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Thermus thermophilus V/A-ATPase, conformation 1 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  HYDROLASE / V/A-ATPase / HYDROLASE / V/A-ATPase /  V-ATPase / V-ATPase /  A-ATPase / A-ATPase /  Thermus thermophilus / rotary ATPase / Thermus thermophilus / rotary ATPase /  membrane protein membrane protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis /  H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 6.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 6.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Schep, D.G. / Zhao, J. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016Title: Models for the a subunits of the Thermus thermophilus V/A-ATPase and Saccharomyces cerevisiae V-ATPase enzymes by cryo-EM and evolutionary covariance. Authors: Daniel G Schep / Jianhua Zhao / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Rotary ATPases couple ATP synthesis or hydrolysis to proton translocation across a membrane. However, understanding proton translocation has been hampered by a lack of structural information for the ...Rotary ATPases couple ATP synthesis or hydrolysis to proton translocation across a membrane. However, understanding proton translocation has been hampered by a lack of structural information for the membrane-embedded a subunit. The V/A-ATPase from the eubacterium Thermus thermophilus is similar in structure to the eukaryotic V-ATPase but has a simpler subunit composition and functions in vivo to synthesize ATP rather than pump protons. We determined the T. thermophilus V/A-ATPase structure by cryo-EM at 6.4 Å resolution. Evolutionary covariance analysis allowed tracing of the a subunit sequence within the map, providing a complete model of the rotary ATPase. Comparing the membrane-embedded regions of the T. thermophilus V/A-ATPase and eukaryotic V-ATPase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae allowed identification of the α-helices that belong to the a subunit and revealed the existence of previously unknown subunits in the eukaryotic enzyme. Subsequent evolutionary covariance analysis enabled construction of a model of the a subunit in the S. cerevisae V-ATPase that explains numerous biochemical studies of that enzyme. Comparing the two a subunit structures determined here with a structure of the distantly related a subunit from the bovine F-type ATP synthase revealed a conserved pattern of residues, suggesting a common mechanism for proton transport in all rotary ATPases. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5gar.cif.gz 5gar.cif.gz | 696 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5gar.ent.gz pdb5gar.ent.gz | 427.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5gar.json.gz 5gar.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ga/5gar https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ga/5gar ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ga/5gar ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ga/5gar | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 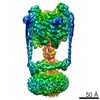 8016MC 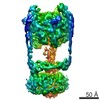 8017C  8070C  5gasC  5i1mC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type ATP synthase ... , 6 types, 11 molecules ABCDEFGHKLM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63628.902 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8References: UniProt: Q56403,  H+-transporting two-sector ATPase H+-transporting two-sector ATPase#2: Protein | Mass: 50850.738 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J73, UniProt: Q56404*PLUS Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J73, UniProt: Q56404*PLUS#3: Protein | Mass: 20481.418 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74901 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74901#5: Protein | | Mass: 23350.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J74, UniProt: O87880*PLUS Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J74, UniProt: O87880*PLUS#6: Protein | | Mass: 10824.321 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74903 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74903#7: Protein | | Mass: 35968.570 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74902 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74902 |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 15 molecules IJNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
| #4: Protein |  V-ATPase V-ATPaseMass: 11752.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J66, UniProt: Q5SIT5*PLUS Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: Q72J66, UniProt: Q5SIT5*PLUS#8: Protein | | Mass: 72272.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: H9ZQR4 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: H9ZQR4#9: Protein | Mass: 9841.714 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74900, UniProt: Q5SIT7*PLUS Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 / References: UniProt: P74900, UniProt: Q5SIT7*PLUS |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Intact Thermus thermophilus V/A-ATPase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) / Strain: AH8 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 7 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: Homemade nanofabricated 400 mesh copper/rhodium grid Grid material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Homemade nanofabricated |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: Plunged into liquid ethane/propane (FEI VITROBOT MARK III). |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 34483 X / Nominal defocus max: 6000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Calibrated magnification: 34483 X / Nominal defocus max: 6000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs : 2 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 30 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 30 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 15 sec. / Electron dose: 35.7 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 12 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 30 / Used frames/image: 1-30 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 197178 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj


