+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1kju | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
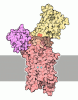
| Title | Ca2+-ATPase in the E2 State | ||||||
 Components Components | Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 1a | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE /  ION PUMP / ION PUMP /  CALCIUM / CALCIUM /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  P-TYPE ATPASE / P-TYPE ATPASE /  ACTIVE TRANSPORT / E2 / ACTIVE TRANSPORT / E2 /  CRYO-EM CRYO-EM | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction / positive regulation of calcium ion import into sarcoplasmic reticulum / H zone / positive regulation of fast-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / calcium ion import into sarcoplasmic reticulum / regulation of striated muscle contraction / negative regulation of striated muscle contraction / positive regulation of ATPase-coupled calcium transmembrane transporter activity / P-type Ca2+ transporter / P-type calcium transporter activity ...positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction / positive regulation of calcium ion import into sarcoplasmic reticulum / H zone / positive regulation of fast-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / calcium ion import into sarcoplasmic reticulum / regulation of striated muscle contraction / negative regulation of striated muscle contraction / positive regulation of ATPase-coupled calcium transmembrane transporter activity / P-type Ca2+ transporter / P-type calcium transporter activity / I band /  endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane /  sarcoplasmic reticulum / calcium ion transport / sarcoplasmic reticulum / calcium ion transport /  calcium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / calcium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu, C. / Rice, W.J. / He, W. / Stokes, D.L. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2002 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2002Title: A structural model for the catalytic cycle of Ca(2+)-ATPase. Authors: Chen Xu / William J Rice / Wanzhong He / David L Stokes /  Abstract: Ca(2+)-ATPase is responsible for active transport of calcium ions across the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. This coupling involves an ordered sequence of reversible reactions occurring alternately ...Ca(2+)-ATPase is responsible for active transport of calcium ions across the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. This coupling involves an ordered sequence of reversible reactions occurring alternately at the ATP site within the cytoplasmic domains, or at the calcium transport sites within the transmembrane domain. These two sites are separated by a large distance and conformational changes have long been postulated to play an important role in their coordination. To characterize the nature of these conformational changes, we have built atomic models for two reaction intermediates and postulated the mechanisms governing the large structural changes. One model is based on fitting the X-ray crystallographic structure of Ca(2+)-ATPase in the E1 state to a new 6 A structure by cryoelectron microscopy in the E2 state. This fit indicates that calcium binding induces enormous movements of all three cytoplasmic domains as well as significant changes in several transmembrane helices. We found that fluorescein isothiocyanate displaced a decavanadate molecule normally located at the intersection of the three cytoplasmic domains, but did not affect their juxtaposition; this result indicates that our model likely reflects a native E2 conformation and not an artifact of decavanadate binding. To explain the dramatic structural effect of calcium binding, we propose that M4 and M5 transmembrane helices are responsive to calcium binding and directly induce rotation of the phosphorylation domain. Furthermore, we hypothesize that both the nucleotide-binding and beta-sheet domains are highly mobile and driven by Brownian motion to elicit phosphoenzyme formation and calcium transport, respectively. If so, the reaction cycle of Ca(2+)-ATPase would have elements of a Brownian ratchet, where the chemical reactions of ATP hydrolysis are used to direct the random thermal oscillations of an innately flexible molecule. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2000 Journal: Nature / Year: 2000Title: Crystal Structure of the Calcium Pump of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum at 2.6 A Resolution Authors: Toyoshima, C. / Nakasako, M. / Nomura, H. / Ogawa, H. #2:  Journal: Nature / Year: 1998 Journal: Nature / Year: 1998Title: Structure of the Calcium Pump from Sarcoplasmic Reticulum at 8-A Resolution Authors: Zhang, P. / Toyoshima, C. / Yonekura, K. / Green, N.M. / Stokes, D.L. #3:  Journal: Ultramicroscopy / Year: 1997 Journal: Ultramicroscopy / Year: 1997Title: Distortion Correction of Tubular Crystals: Improvements in the Acetylcholine Receptor Structure Authors: Beroukhim, R. / Unwin, N. #4:  Journal: Biophys.J. / Year: 2000 Journal: Biophys.J. / Year: 2000Title: Modeling a Dehalogenase Fold into the 8-A Density Map for Ca(2+)-ATPase Defines a New Domain Structure Authors: Stokes, D.L. / Green, N.M. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 999 | SEQUENCE THE SEQUENCE IN THIS ENTRY IS AN ISOFORM OF THE SEQUENCE IN SWISSPROT ENTRY P04191. THE C- ...SEQUENCE THE SEQUENCE IN THIS ENTRY IS AN ISOFORM OF THE SEQUENCE IN SWISSPROT ENTRY P04191. THE C-TERMINAL REGION OF P04191 CONSISTS OF RESIDUES 994-1001, DPEDERRK. IN THIS ENTRY, THE C-TERMINAL RESIDUE IS 994, G. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1kju.cif.gz 1kju.cif.gz | 200.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1kju.ent.gz pdb1kju.ent.gz | 159.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1kju.json.gz 1kju.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kj/1kju https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kj/1kju ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kj/1kju ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kj/1kju | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 109602.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P04191, EC: 3.6.3.8 Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / References: UniProt: P04191, EC: 3.6.3.8 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ca2+-ATPase tubular crystals / Type: COMPLEX Details: Crystals formed in presence of decavanadate and thapsigargin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20 mM imidazole pH 7.4, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM decavanadate, 0.01 mM thapsigargin pH: 7.4 Details: 20 mM imidazole pH 7.4, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM decavanadate, 0.01 mM thapsigargin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Details: Samples at approximately 1 mg/ml were diluted 1/20 immediately prior to application to glow-discharged fenestrated carbon grids. All freezing was done in cold room. After blotting, samples ...Details: Samples at approximately 1 mg/ml were diluted 1/20 immediately prior to application to glow-discharged fenestrated carbon grids. All freezing was done in cold room. After blotting, samples were plunged into liquid ethane for freezing and stored in liquid nitrogen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Crystal grow | *PLUS Temperature: 4 ℃ / Method: microdialysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI/PHILIPS CM200FEG / Date: Jan 1, 2000 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 51300 X / Nominal defocus max: 1400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 50000 X / Calibrated magnification: 51300 X / Nominal defocus max: 1400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 100 K / Tilt angle max: 0 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 10 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 58 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: CTF correction of each particle with 4.6% amplitude contrast | ||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: helical reconstruction / Resolution: 6 Å / Num. of particles: 95 / Actual pixel size: 2.53 Å Magnification calibration: light harvesting complex crystals Details: Combination of Fourier and real space averaging. Helical Reconstruction: A total of 95 repeats from 58 individual tubes were used for the reconstruction. These tubes fell into 5 helical ...Details: Combination of Fourier and real space averaging. Helical Reconstruction: A total of 95 repeats from 58 individual tubes were used for the reconstruction. These tubes fell into 5 helical symmetries, defined by the Bessel order (n) of the principal layer lines (1,0) and (0,1). These 5 symmetries were (-23,6), (-22,6), (-21,6), (-20,6) and (-19,6). For the reference symmetry (-22,6), the unit cell parameters were: a= 56.9A, b=117.1A, gamma=64.2 deg. Data within each helical symmetry were averaged in Fourier space and distortion-correction techniques were applied (Beroukhim and Unwin, 1997). For each repeat, unit cell parameters were calculated, and repeats differing by more than 1.5% of the average value were discarded. The CTF was used to correct phases and weight amplitudes prior to averaging within each helical symmetry. Finally, maps were calculated from each of the averaged datasets. Each of the 2 molecules composing the unit cell were masked and aligned with the corresponding molecule from the reference map (-22,6). The maps were averaged in real-space then back-transformed into Fourier space. Two-fold symmetry was constrained before calculating the final map. Effective resolution of the reconstruction: The resolution of the final reconstruction was determined to be 6 A by two methods. First, the dataset was split into two equal parts and two independant reconstructions were made. After masking and aligning molecules from these maps, Fourier shell correlation coefficients and associated phase residuals were calculated. Secondly, since the crystals had p2 symmetry, two-fold phase residuals of layer lined datasets were used to monitor resolution. Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL Details: DETAILS--The atomic coordinates of Ca-ATPase (1EUL) were divided into 4 domains by breaking the peptide at 3 hinge points. Each domain was separately fit into the electron density map by ...Details: DETAILS--The atomic coordinates of Ca-ATPase (1EUL) were divided into 4 domains by breaking the peptide at 3 hinge points. Each domain was separately fit into the electron density map by manual docking using the program O. Besides matching overall shape, the major criteria involved matching a-helices into strong columns of density in the map. Whereas cytoplasmic domains were treated as rigid bodies, elements of the transmembrane domain were bent or displaced to match strong densities in the cryo-em map. Finally, the loops composing the 3 hinges were rebuilt to reconnect the domains and X-PLOR was used to perform local energy minimization. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1EUL 1eul Accession code: 1EUL / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 6 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name:  X-PLOR / Classification: refinement X-PLOR / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj