[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
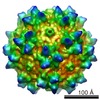
Yorodumi- EMDB-8100: Structure of the R432A variant of Adeno-associated virus type 2 VLP -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8100 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
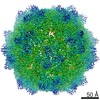
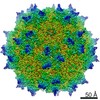
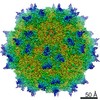
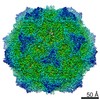
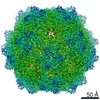
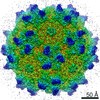
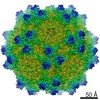
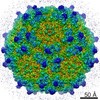
| Title | Structure of the R432A variant of Adeno-associated virus type 2 VLP | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | None | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Adeno-associated virus / R432A / Adeno-associated virus / R432A /  gene therapy / gene therapy /  icosahedral / icosahedral /  dependoparvovirus / dependoparvovirus /  VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpermeabilization of host organelle membrane involved in viral entry into host cell / symbiont entry into host cell via permeabilization of inner membrane / host cell nucleolus / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / structural molecule activity / virion attachment to host cell Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Adeno-associated virus - 2 Adeno-associated virus - 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Drouin LM / Lins B | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2016 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2016Title: Cryo-electron Microscopy Reconstruction and Stability Studies of the Wild Type and the R432A Variant of Adeno-associated Virus Type 2 Reveal that Capsid Structural Stability Is a Major Factor in Genome Packaging. Authors: Lauren M Drouin / Bridget Lins / Maria Janssen / Antonette Bennett / Paul Chipman / Robert McKenna / Weijun Chen / Nicholas Muzyczka / Giovanni Cardone / Timothy S Baker / Mavis Agbandje-McKenna /  Abstract: The adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are promising therapeutic gene delivery vectors and better understanding of their capsid assembly and genome packaging mechanism is needed for improved vector ...The adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are promising therapeutic gene delivery vectors and better understanding of their capsid assembly and genome packaging mechanism is needed for improved vector production. Empty AAV capsids assemble in the nucleus prior to genome packaging by virally encoded Rep proteins. To elucidate the capsid determinants of this process, structural differences between wild-type (wt) AAV2 and a packaging deficient variant, AAV2-R432A, were examined using cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction both at an ∼5.0-Å resolution (medium) and also at 3.8- and 3.7-Å resolutions (high), respectively. The high resolution structures showed that removal of the arginine side chain in AAV2-R432A eliminated hydrogen bonding interactions, resulting in altered intramolecular and intermolecular interactions propagated from under the 3-fold axis toward the 5-fold channel. Consistent with these observations, differential scanning calorimetry showed an ∼10°C decrease in thermal stability for AAV2-R432A compared to wt-AAV2. In addition, the medium resolution structures revealed differences in the juxtaposition of the less ordered, N-terminal region of their capsid proteins, VP1/2/3. A structural rearrangement in AAV2-R432A repositioned the βA strand region under the icosahedral 2-fold axis rather than antiparallel to the βB strand, eliminating many intramolecular interactions. Thus, a single amino acid substitution can significantly alter the AAV capsid integrity to the extent of reducing its stability and possibly rendering it unable to tolerate the stress of genome packaging. Furthermore, the data show that the 2-, 3-, and 5-fold regions of the capsid contributed to producing the packaging defect and highlight a tight connection between the entire capsid in maintaining packaging efficiency. IMPORTANCE: The mechanism of AAV genome packaging is still poorly understood, particularly with respect to the capsid determinants of the required capsid-Rep interaction. Understanding this mechanism ...IMPORTANCE: The mechanism of AAV genome packaging is still poorly understood, particularly with respect to the capsid determinants of the required capsid-Rep interaction. Understanding this mechanism may aid in the improvement of AAV packaging efficiency, which is currently ∼1:10 (10%) genome packaged to empty capsid in vector preparations. This report identifies regions of the AAV capsid that play roles in genome packaging and that may be important for Rep recognition. It also demonstrates the need to maintain capsid stability for the success of this process. This information is important for efforts to improve AAV genome packaging and will also inform the engineering of AAV capsid variants for improved tropism, specific tissue targeting, and host antibody escape by defining amino acids that cannot be altered without detriment to infectious vector production. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8100.map.gz emd_8100.map.gz | 28.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8100-v30.xml emd-8100-v30.xml emd-8100.xml emd-8100.xml | 14.5 KB 14.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8100.png emd_8100.png | 292 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8100.cif.gz emd-8100.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8100 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8100 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8100 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8100 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5ipkMC  8099C  5ipiC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8100.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 135.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8100.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 135.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Adeno-associated virus - 2
| Entire | Name:   Adeno-associated virus - 2 Adeno-associated virus - 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Adeno-associated virus - 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Adeno-associated virus - 2 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 10804 / Sci species name: Adeno-associated virus - 2 / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein VP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein VP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Adeno-associated virus - 2 Adeno-associated virus - 2 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 81.945234 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus unidentified baculovirus |
| Sequence | String: MAADGYLPDW LEDTLSEGIR QWWKLKPGPP PPKPAERHKD DSRGLVLPGY KYLGPFNGLD KGEPVNEADA AALEHDKAYD RQLDSGDNP YLKYNHADAE FQERLKEDTS FGGNLGRAVF QAKKRVLEPL GLVEEPVKTA PGKKRPVEHS PVEPDSSSGT G KAGQQPAR ...String: MAADGYLPDW LEDTLSEGIR QWWKLKPGPP PPKPAERHKD DSRGLVLPGY KYLGPFNGLD KGEPVNEADA AALEHDKAYD RQLDSGDNP YLKYNHADAE FQERLKEDTS FGGNLGRAVF QAKKRVLEPL GLVEEPVKTA PGKKRPVEHS PVEPDSSSGT G KAGQQPAR KRLNFGQTGD ADSVPDPQPL GQPPAAPSGL GTNTMATGSG APMADNNEGA DGVGNSSGNW HCDSTWMGDR VI TTSTRTW ALPTYNNHLY KQISSQSGAS NDNHYFGYST PWGYFDFNRF HCHFSPRDWQ RLINNNWGFR PKRLNFKLFN IQV KEVTQN DGTTTIANNL TSTVQVFTDS EYQLPYVLGS AHQGCLPPFP ADVFMVPQYG YLTLNNGSQA VGRSSFYCLE YFPS QMLRT GNNFTFSYTF EDVPFHSSYA HSQSLDALMN PLIDQYLYYL SRTNTPSGTT TQSRLQFSQA GASDIRDQSR NWLPG PCYR QQRVSKTSAD NNNSEYSWTG ATKYHLNGRD SLVNPGPAMA SHKDDEEKFF PQSGVLIFGK QGSEKTNVDI EKVMIT DEE EIRTTNPVAT EQYGSVSTNL QRGNRQAATA DVNTQGVLPG MVWQDRDVYL QGPIWAKIPH TDGHFHPSPL MGGFGLK HP PPQILIKNTP VPANPSTTFS AAKFASFITQ YSTGQVSVEI EWELQKENSK RWNPEIQYTS NYNKSVNVDF TVDTNGVY S EPRPIGTRYL TRNL UniProtKB:  Capsid protein VP1 Capsid protein VP1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: Grid was blotted for 5 seconds before plunge freezing.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 56924 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.26 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.26 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Temperature | Min: 90.0 K / Max: 97.0 K |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 49 / Average exposure time: 0.8 sec. / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Particle selection | Number selected: 19457 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Auto3DEM (ver. v4.05) / Number images used: 19457 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller