+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6461 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
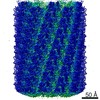
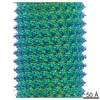
| Title | Electron cryo-microscopy of the IST1-CHMP1B ESCRT-III copolymer | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of IST1NTD-CHMP1B copolymer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  ESCRT-III / IST1 / ESCRT-III / IST1 /  CHMP1B / membrane tubulation / helical filament CHMP1B / membrane tubulation / helical filament | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationviral capsid secondary envelopment / MIT domain binding /  abscission / amphisome membrane / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport / abscission / amphisome membrane / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport /  ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule ...viral capsid secondary envelopment / MIT domain binding / ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule ...viral capsid secondary envelopment / MIT domain binding /  abscission / amphisome membrane / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport / abscission / amphisome membrane / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport /  ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / collateral sprouting / regulation of centrosome duplication / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / nuclear membrane reassembly / positive regulation of collateral sprouting / midbody abscission / multivesicular body sorting pathway / membrane coat / membrane fission / plasma membrane repair / late endosome to vacuole transport / multivesicular body membrane / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway / ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule / cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis / endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / collateral sprouting / regulation of centrosome duplication / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / nuclear membrane reassembly / positive regulation of collateral sprouting / midbody abscission / multivesicular body sorting pathway / membrane coat / membrane fission / plasma membrane repair / late endosome to vacuole transport / multivesicular body membrane / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway /  multivesicular body assembly / multivesicular body assembly /  regulation of mitotic spindle assembly / Flemming body / regulation of mitotic spindle assembly / Flemming body /  nucleus organization / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / viral budding via host ESCRT complex / autophagosome maturation / autophagosome membrane / positive regulation of proteolysis / viral release from host cell / nucleus organization / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / viral budding via host ESCRT complex / autophagosome maturation / autophagosome membrane / positive regulation of proteolysis / viral release from host cell /  endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment /  nuclear pore / nuclear pore /  multivesicular body / multivesicular body /  viral budding from plasma membrane / establishment of protein localization / viral budding from plasma membrane / establishment of protein localization /  protein localization / protein localization /  kinetochore / kinetochore /  autophagy / azurophil granule lumen / autophagy / azurophil granule lumen /  protein transport / protein transport /  nuclear envelope / midbody / endosome membrane / nuclear envelope / midbody / endosome membrane /  cadherin binding / cadherin binding /  cell division / lysosomal membrane / protein domain specific binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / cell division / lysosomal membrane / protein domain specific binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle /  centrosome / centrosome /  chromatin / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / chromatin / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region /  nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | McCullough J / Clippinger AK / Talledge N / Skowyra ML / Saunders MG / Naismith TV / Colf LA / Afonine P / Arthur C / Sundquist WI ...McCullough J / Clippinger AK / Talledge N / Skowyra ML / Saunders MG / Naismith TV / Colf LA / Afonine P / Arthur C / Sundquist WI / Hanson PI / Frost A | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2015 Journal: Science / Year: 2015Title: Structure and membrane remodeling activity of ESCRT-III helical polymers. Authors: John McCullough / Amy K Clippinger / Nathaniel Talledge / Michael L Skowyra / Marissa G Saunders / Teresa V Naismith / Leremy A Colf / Pavel Afonine / Christopher Arthur / Wesley I Sundquist ...Authors: John McCullough / Amy K Clippinger / Nathaniel Talledge / Michael L Skowyra / Marissa G Saunders / Teresa V Naismith / Leremy A Colf / Pavel Afonine / Christopher Arthur / Wesley I Sundquist / Phyllis I Hanson / Adam Frost /  Abstract: The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins mediate fundamental membrane remodeling events that require stabilizing negative membrane curvature. These include endosomal ...The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins mediate fundamental membrane remodeling events that require stabilizing negative membrane curvature. These include endosomal intralumenal vesicle formation, HIV budding, nuclear envelope closure, and cytokinetic abscission. ESCRT-III subunits perform key roles in these processes by changing conformation and polymerizing into membrane-remodeling filaments. Here, we report the 4 angstrom resolution cryogenic electron microscopy reconstruction of a one-start, double-stranded helical copolymer composed of two different human ESCRT-III subunits, charged multivesicular body protein 1B (CHMP1B) and increased sodium tolerance 1 (IST1). The inner strand comprises "open" CHMP1B subunits that interlock in an elaborate domain-swapped architecture and is encircled by an outer strand of "closed" IST1 subunits. Unlike other ESCRT-III proteins, CHMP1B and IST1 polymers form external coats on positively curved membranes in vitro and in vivo. Our analysis suggests how common ESCRT-III filament architectures could stabilize different degrees and directions of membrane curvature. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6461.map.gz emd_6461.map.gz | 121.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6461-v30.xml emd-6461-v30.xml emd-6461.xml emd-6461.xml | 18 KB 18 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6461.png emd_6461.png | 269.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6461 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6461 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6461 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6461 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 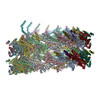 3jc1MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6461.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 126.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6461.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 126.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of IST1NTD-CHMP1B copolymer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ESCRT-III copolymer of IST1 and CHMP1B
| Entire | Name: ESCRT-III copolymer of IST1 and CHMP1B |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: ESCRT-III copolymer of IST1 and CHMP1B
| Supramolecule | Name: ESCRT-III copolymer of IST1 and CHMP1B / type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: 2-stranded helical filament composed of one strand of IST1 subunits and one strand of CHMP1B subunits Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: IST1
| Macromolecule | Name: IST1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Name.synonym: Increased Sodium Tolerance 1, hIST1, Putatuve MAPK-activating protein PM28 Details: IST1 N-terminal domain, residues 1-189 / Oligomeric state: Polymer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 22 KDa / Theoretical: 22 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant cell: BL21 (RIPL) / Recombinant plasmid: pGEX-2T-TEV Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant cell: BL21 (RIPL) / Recombinant plasmid: pGEX-2T-TEV |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: IST1 homolog |
-Macromolecule #2: Charged multivesicular body protein 1b
| Macromolecule | Name: Charged multivesicular body protein 1b / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Name.synonym: CHMP1B, Chromatin-modifying protein 1b (CHMP1.5), Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 46-2 (hVps46-2) Details: full-length CHMP1B / Oligomeric state: Polymer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 22 KDa / Theoretical: 22 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant cell: BL21 (RIPL) / Recombinant plasmid: pGEX-2T-TEV Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Recombinant cell: BL21 (RIPL) / Recombinant plasmid: pGEX-2T-TEV |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Charged multivesicular body protein 1b |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.7 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 25 mM Tris, 25 mM NaCl |
| Grid | Details: 3.5 uL of pelleted and resuspended liposome-nucleated IST1NTD-CHMP1B copolymers were applied to glow-discharged Quantifoil holey carbon grids (2 micron hole size, 2-4 micron spacing, 200 mesh). |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I Method: Blotted 7-9 seconds (-2 mm offset) and plunge-frozen |
- Electron microscopy #1
Electron microscopy #1
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Microscopy ID | 1 |
| Date | Jun 1, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: NIKON SUPER COOLSCAN 9000 / Number real images: 2493 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs ...Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs collected on a JEM3200FSC microscope with a DE-12 direct electron detector. |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #2
Electron microscopy #2
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Microscopy ID | 2 |
| Date | Jul 1, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON I (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Scanner: NIKON SUPER COOLSCAN 9000 / Number real images: 2493 / Average electron dose: 15 e/Å2 Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs ...Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs collected on a JEM3200FSC microscope with a DE-12 direct electron detector. |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Electron microscopy #3
Electron microscopy #3
| Microscope | JEOL 3200FSC |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 3.40 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 3.40 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: JEOL 3200FSC CRYOHOLDER |
| Microscopy ID | 3 |
| Date | Aug 1, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-12 (4k x 3k) / Digitization - Scanner: NIKON SUPER COOLSCAN 9000 / Number real images: 2493 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs ...Details: 118,467 particles were selected from 2454 micrographs collected on a Titan Krios microscope with a Falcon I direct electron detector; 12,142 particles were selected from 39 micrographs collected on a JEM3200FSC microscope with a DE-12 direct electron detector. |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Tilt angle max | 0 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle as implemented in RELION |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 2.96 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 21.060 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: CTFFIND3, EMAN2, IHRSR, SPIDER, RELION Details: 51 copies (3 complete turns) of the asymmetric RELION reconstruction were transformed according to the helical symmetry, resampled on the original grid, and summed together, with Iterative ...Details: 51 copies (3 complete turns) of the asymmetric RELION reconstruction were transformed according to the helical symmetry, resampled on the original grid, and summed together, with Iterative Helical Real Space Reconstruction (IHRSR) single-particle algorithm as implemented in SPIDER and high-resolution refinement in RELION. |
| Details | Particles were picked manually using the e2helixboxer.py function of EMAN2. Particles were aligned with IHRSR initially, followed by high resolution asymmetric refinement in RELION, followed by helical averaging in real space. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Coot, Chimera, NAMD MDFF, Rosetta |
| Details | 3FRR was docked manually into the segmented density using Chimera. Regions with poor fit to density were identified using the Rosetta loops-from-density algorithm and iteratively fitted using alternating cycles of Rosetta's rebuild and refine protocol and manual refinement in Coot. The full ring of IST1 structures was then refined using Rosetta's symmetry constraints. Finally, backbone hydrogen bonds in the helical regions were constrained and two cycles of loop rebuilding with constraints were performed. The IST1 model was then combined with the CHMP1B model to form a heterodimer and this structure was refined by iterating between manual rebuilding and refinement using MDFF |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Molprobity validation, cross-correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-3jc1: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller