+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2917 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
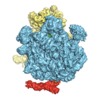
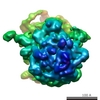
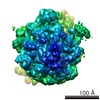
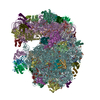
| Title | EM structure of ribosome-SRP-FtsY complex in "closed" state | |||||||||
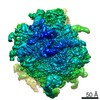
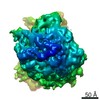
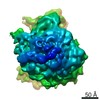
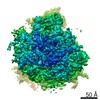
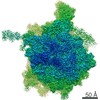
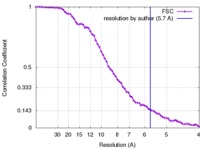
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of ribosome-SRP-FtsY complex in the "closed" state. The map has been b-factor sharpened. The authors report resolution of 5.7 angstrom according to FSC=0.143, which was obtained from RELION post-process (for b-factor sharpening). Since the RELION post-process does not generate new half maps, the maps uploaded for FSC validation were the half maps before b-factor sharpening. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  protein targeting / protein targeting /  signal recognition particle / signal recognition particle /  signal sequence / signal sequence /  ribosome ribosome | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information signal recognition particle / signal recognition particle /  signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation /  stringent response / stringent response /  transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity ... transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity ... signal recognition particle / signal recognition particle /  signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein targeting to membrane / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation /  stringent response / stringent response /  transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / translational termination / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / translational initiation / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / translational termination / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / translational initiation / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation /  ribosome assembly / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / response to reactive oxygen species / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / ribosome assembly / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / response to reactive oxygen species / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome /  : / cytosolic ribosome assembly / : / cytosolic ribosome assembly /  regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / mRNA 5'-UTR binding /  ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding /  ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / large ribosomal subunit /  5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / 5S rRNA binding / cytoplasmic translation / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit /  transferase activity / negative regulation of translation / transferase activity / negative regulation of translation /  tRNA binding / tRNA binding /  rRNA binding / rRNA binding /  ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / structural constituent of ribosome /  translation / translation /  ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  GTPase activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / GTP binding / GTPase activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / GTP binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  RNA binding / zinc ion binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | von Loeffelholz O / Jiang Q / Ariosa A / Karuppasamy M / Huard K / Berger I / Shan S / Schaffitzel C | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015Title: Ribosome-SRP-FtsY cotranslational targeting complex in the closed state. Authors: Ottilie von Loeffelholz / Qiyang Jiang / Aileen Ariosa / Manikandan Karuppasamy / Karine Huard / Imre Berger / Shu-ou Shan / Christiane Schaffitzel /    Abstract: The signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent pathway is essential for correct targeting of proteins to the membrane and subsequent insertion in the membrane or secretion. In Escherichia coli, the ...The signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent pathway is essential for correct targeting of proteins to the membrane and subsequent insertion in the membrane or secretion. In Escherichia coli, the SRP and its receptor FtsY bind to ribosome-nascent chain complexes with signal sequences and undergo a series of distinct conformational changes, which ensures accurate timing and fidelity of protein targeting. Initial recruitment of the SRP receptor FtsY to the SRP-RNC complex results in GTP-independent binding of the SRP-FtsY GTPases at the SRP RNA tetraloop. In the presence of GTP, a closed state is adopted by the SRP-FtsY complex. The cryo-EM structure of the closed state reveals an ordered SRP RNA and SRP M domain with a signal sequence-bound. Van der Waals interactions between the finger loop and ribosomal protein L24 lead to a constricted signal sequence-binding pocket possibly preventing premature release of the signal sequence. Conserved M-domain residues contact ribosomal RNA helices 24 and 59. The SRP-FtsY GTPases are detached from the RNA tetraloop and flexible, thus liberating the ribosomal exit site for binding of the translocation machinery. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2917.map.gz emd_2917.map.gz | 20.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2917-v30.xml emd-2917-v30.xml emd-2917.xml emd-2917.xml | 12.1 KB 12.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_2917_fsc.xml emd_2917_fsc.xml | 7.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_2917.png emd_2917.png | 257.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2917 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2917 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2917 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2917 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5akaMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2917.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 21.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2917.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 21.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of ribosome-SRP-FtsY complex in the "closed" state. The map has been b-factor sharpened. The authors report resolution of 5.7 angstrom according to FSC=0.143, which was obtained from RELION post-process (for b-factor sharpening). Since the RELION post-process does not generate new half maps, the maps uploaded for FSC validation were the half maps before b-factor sharpening. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : E. coli SRP-FtsY binds to E. coli ribosome with Lep50 nascent chain
| Entire | Name: E. coli SRP-FtsY binds to E. coli ribosome with Lep50 nascent chain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: E. coli SRP-FtsY binds to E. coli ribosome with Lep50 nascent chain
| Supramolecule | Name: E. coli SRP-FtsY binds to E. coli ribosome with Lep50 nascent chain type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.7 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: E. coli 70S ribosome displaying Lep50 nascent chain
| Supramolecule | Name: E. coli 70S ribosome displaying Lep50 nascent chain / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: RNC Details: Ribosome-nascent chain complexes (RNCs) were prepared by in vitro transcription and translation from pUC19StrepLep50 and purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation and affinity chromatography. Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Signal recongnition particle and SRP receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Signal recongnition particle and SRP receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: scSRP219 Details: This is a single-chain construct comprising E.coli FtsY219 (truncated version lacking the N-terminal A-domain and the first helix of the N-domain) fused via a 31-amino acid glycine-serine- ...Details: This is a single-chain construct comprising E.coli FtsY219 (truncated version lacking the N-terminal A-domain and the first helix of the N-domain) fused via a 31-amino acid glycine-serine-rich linker to full-length Ffh. Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 150 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21 (bacteria) / Recombinant plasmid: pET24 and pUC19 Escherichia coli BL21 (bacteria) / Recombinant plasmid: pET24 and pUC19 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 50mM Hepes-KOH, 100mM KOAc, 8mM Mg(OAc)2, 500ug/ml chloramphenicol |
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh quantifoil grid type R1.2/1.3 coated with a thin continuous carbon layer, glow-discharged for 30 s |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 77 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Method: Blot for 2 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 77769 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Date | Jan 24, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 2840 / Average electron dose: 24 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID:  2aw4 |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Coot |
| Details | The structures were fitted by initial rigid body fitting in Chimera, followed by local refinement in Coot. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-5aka: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Coot, HHpred, CNS |
| Details | The structures were fitted by initial rigid body fitting in Chimera, followed by local refinement in Coot. The finger loop region was modelled in HHpred. The whole structure was finally energy minimization in CNS Version 1.0. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-5aka: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller