[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8u7i: Structure of the phage immune evasion protein Gad1 bound to the G... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8u7i | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the phage immune evasion protein Gad1 bound to the Gabija GajAB complex | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRAL PROTEIN / viral immune evasion / VIRAL PROTEIN / viral immune evasion /  phage / phage /  bacteria / anti-phage defense complex / DNA nuclease / bacteria / anti-phage defense complex / DNA nuclease /  DNA helicase DNA helicase | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information DNA helicase activity / defense response to virus / DNA helicase activity / defense response to virus /  endonuclease activity / endonuclease activity /  Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds /  hydrolase activity / hydrolase activity /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Bacillus phage phi3T (virus) Bacillus phage phi3T (virus) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.57 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.57 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Antine, S.P. / Johnson, A.G. / Mooney, S.E. / Mayer, M.L. / Kranzsuch, P.J. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis of Gabija anti-phage defence and viral immune evasion. Authors: Sadie P Antine / Alex G Johnson / Sarah E Mooney / Azita Leavitt / Megan L Mayer / Erez Yirmiya / Gil Amitai / Rotem Sorek / Philip J Kranzusch /   Abstract: Bacteria encode hundreds of diverse defence systems that protect them from viral infection and inhibit phage propagation. Gabija is one of the most prevalent anti-phage defence systems, occurring in ...Bacteria encode hundreds of diverse defence systems that protect them from viral infection and inhibit phage propagation. Gabija is one of the most prevalent anti-phage defence systems, occurring in more than 15% of all sequenced bacterial and archaeal genomes, but the molecular basis of how Gabija defends cells from viral infection remains poorly understood. Here we use X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to define how Gabija proteins assemble into a supramolecular complex of around 500 kDa that degrades phage DNA. Gabija protein A (GajA) is a DNA endonuclease that tetramerizes to form the core of the anti-phage defence complex. Two sets of Gabija protein B (GajB) dimers dock at opposite sides of the complex and create a 4:4 GajA-GajB assembly (hereafter, GajAB) that is essential for phage resistance in vivo. We show that a phage-encoded protein, Gabija anti-defence 1 (Gad1), directly binds to the Gabija GajAB complex and inactivates defence. A cryo-EM structure of the virally inhibited state shows that Gad1 forms an octameric web that encases the GajAB complex and inhibits DNA recognition and cleavage. Our results reveal the structural basis of assembly of the Gabija anti-phage defence complex and define a unique mechanism of viral immune evasion. #1:  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Phages overcome bacterial immunity via diverse anti-defense proteins Authors: Yirmiya, E. / Leavitt, A. / Lu, A. / Avraham, C. / Osterman, I. / Garb, J. / Antine, S.P. / Mooney, S.E. / Hobbs, S.J. / Kranzusch, P.J. / Amitai, G. / Sorek, R. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8u7i.cif.gz 8u7i.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8u7i.ent.gz pdb8u7i.ent.gz | 785.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8u7i.json.gz 8u7i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u7/8u7i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u7/8u7i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u7/8u7i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u7/8u7i | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 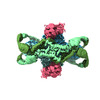 41983MC  8sm3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 78045.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)    Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: J8H9C1 Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: J8H9C1#2: Protein | Mass: 57139.992 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)    Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: J8HQ06 Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: J8HQ06#3: Protein | Mass: 34919.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Bacillus phage phi3T (virus) / Gene: phi3T_128 / Production host: Bacillus phage phi3T (virus) / Gene: phi3T_128 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1P8CWZ3 Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A1P8CWZ3 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 3D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM HEPES-KOH pH 7.5, 20 mM KCl, and 1 mM TCEP-KOH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 41.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.57 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 351193 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 170.99 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj

