+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8svf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
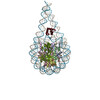
| Title | BAP1/ASXL1 bound to the H2AK119Ub Nucleosome | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | NUCLEAR PROTEIN/DNA/RNA / DNA complex protein /  hydrolase / hydrolase /  structural protein / NUCLEAR PROTEIN-DNA-RNA complex structural protein / NUCLEAR PROTEIN-DNA-RNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthrombocyte differentiation / nucleate erythrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / PR-DUB complex / leukocyte proliferation / platelet morphogenesis / histone H2A deubiquitinase activity / positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / macrophage homeostasis / lung saccule development ...thrombocyte differentiation / nucleate erythrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / PR-DUB complex / leukocyte proliferation / platelet morphogenesis / histone H2A deubiquitinase activity / positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / macrophage homeostasis / lung saccule development / podocyte development / neutrophil differentiation / regulation of kidney size / myeloid cell apoptotic process / hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis / monoubiquitinated protein deubiquitination / common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation / protein K48-linked deubiquitination / tissue homeostasis / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding / bone marrow development / positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation / protein deubiquitination / erythrocyte maturation / regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response /  hemopoiesis / homeostasis of number of cells / response to inorganic substance / heart morphogenesis / response to retinoic acid / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / hemopoiesis / homeostasis of number of cells / response to inorganic substance / heart morphogenesis / response to retinoic acid / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway /  Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of PTEN localization / Translesion synthesis by POLK /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / thymus development / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Josephin domain DUBs / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / thymus development / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / NOTCH3 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the NucleusSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Thomas, J.F. / Valencia-Sanchez, M.I. / Armache, K.-J. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of histone H2A lysine 119 deubiquitination by Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase BAP1/ASXL1. Authors: Jonathan F Thomas / Marco Igor Valencia-Sánchez / Simone Tamburri / Susan L Gloor / Samantha Rustichelli / Victoria Godínez-López / Pablo De Ioannes / Rachel Lee / Stephen Abini-Agbomson ...Authors: Jonathan F Thomas / Marco Igor Valencia-Sánchez / Simone Tamburri / Susan L Gloor / Samantha Rustichelli / Victoria Godínez-López / Pablo De Ioannes / Rachel Lee / Stephen Abini-Agbomson / Kristjan Gretarsson / Jonathan M Burg / Allison R Hickman / Lu Sun / Saarang Gopinath / Hailey F Taylor / Zu-Wen Sun / Ryan J Ezell / Anup Vaidya / Matthew J Meiners / Marcus A Cheek / William J Rice / Vladimir Svetlov / Evgeny Nudler / Chao Lu / Michael-Christopher Keogh / Diego Pasini / Karim-Jean Armache /   Abstract: Histone H2A lysine 119 (H2AK119Ub) is monoubiquitinated by Polycomb repressive complex 1 and deubiquitinated by Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase complex (PR-DUB). PR-DUB cleaves H2AK119Ub to ...Histone H2A lysine 119 (H2AK119Ub) is monoubiquitinated by Polycomb repressive complex 1 and deubiquitinated by Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase complex (PR-DUB). PR-DUB cleaves H2AK119Ub to restrict focal H2AK119Ub at Polycomb target sites and to protect active genes from aberrant silencing. The PR-DUB subunits (BAP1 and ASXL1) are among the most frequently mutated epigenetic factors in human cancers. How PR-DUB establishes specificity for H2AK119Ub over other nucleosomal ubiquitination sites and how disease-associated mutations of the enzyme affect activity are unclear. Here, we determine a cryo-EM structure of human BAP1 and the ASXL1 DEUBAD in complex with a H2AK119Ub nucleosome. Our structural, biochemical, and cellular data reveal the molecular interactions of BAP1 and ASXL1 with histones and DNA that are critical for restructuring the nucleosome and thus establishing specificity for H2AK119Ub. These results further provide a molecular explanation for how >50 mutations in BAP1 and ASXL1 found in cancer can dysregulate H2AK119Ub deubiquitination, providing insight into understanding cancer etiology. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8svf.cif.gz 8svf.cif.gz | 406.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8svf.ent.gz pdb8svf.ent.gz | 282.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8svf.json.gz 8svf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sv/8svf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sv/8svf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sv/8svf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sv/8svf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40789MC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 11 molecules AEBFCGDHKLM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15435.126 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: G103A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233#2: Protein |  Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799#3: Protein | Mass: 14093.436 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: G100R, K120C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P06897 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P06897#4: Protein | Mass: 13979.291 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S33T Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P02281#7: Protein | | Mass: 80472.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BAP1, KIAA0272, hucep-6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BAP1, KIAA0272, hucep-6 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q92560, Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q92560,  ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1 ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1#8: Protein | |  Polycomb-group proteins / Additional sex combs-like protein 1 Polycomb-group proteins / Additional sex combs-like protein 1Mass: 165635.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASXL1, KIAA0978 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASXL1, KIAA0978 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q8IXJ9 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q8IXJ9#9: Protein | |  Mass: 8576.831 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: G76C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBC / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0CG48 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P0CG48 |
|---|
-DNA/RNA hybrid , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA/RNA hybrid | Mass: 58568.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA/RNA hybrid | Mass: 102866.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: BAP1/ASXL1 bound to the H2AK119Ub Nucleosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil | ||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 900 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 900 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 57.12 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 39056 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj