+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dfp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
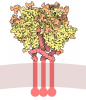
| Title | Ectodomain of full-length KIT(DupA502,Y503)-SCF dimers | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE /  receptor tyrosine kinase / receptor tyrosine kinase /  cell signaling / cell signaling /  cancer / cancer /  cryo-EM / KIT / stem cell factor / oncogenic mutant / cryo-EM / KIT / stem cell factor / oncogenic mutant /  extracellular domain / asymmetric interface / extracellular domain / asymmetric interface /  structural plasticity structural plasticity | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation / negative regulation of mast cell apoptotic process /  stem cell factor receptor binding / mast cell migration / positive regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / Dasatinib-resistant KIT mutants / Imatinib-resistant KIT mutants / KIT mutants bind TKIs / Masitinib-resistant KIT mutants ...positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation / negative regulation of mast cell apoptotic process / stem cell factor receptor binding / mast cell migration / positive regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / Dasatinib-resistant KIT mutants / Imatinib-resistant KIT mutants / KIT mutants bind TKIs / Masitinib-resistant KIT mutants ...positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation / negative regulation of mast cell apoptotic process /  stem cell factor receptor binding / mast cell migration / positive regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / Dasatinib-resistant KIT mutants / Imatinib-resistant KIT mutants / KIT mutants bind TKIs / Masitinib-resistant KIT mutants / Nilotinib-resistant KIT mutants / Regorafenib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by kinase domain mutants of KIT / Sunitinib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by juxtamembrane domain KIT mutants / Sorafenib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by extracellular domain mutants of KIT / stem cell factor receptor binding / mast cell migration / positive regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / Dasatinib-resistant KIT mutants / Imatinib-resistant KIT mutants / KIT mutants bind TKIs / Masitinib-resistant KIT mutants / Nilotinib-resistant KIT mutants / Regorafenib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by kinase domain mutants of KIT / Sunitinib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by juxtamembrane domain KIT mutants / Sorafenib-resistant KIT mutants / Signaling by extracellular domain mutants of KIT /  stem cell factor receptor activity / hematopoietic stem cell migration / melanocyte adhesion / positive regulation of pyloric antrum smooth muscle contraction / positive regulation of colon smooth muscle contraction / erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation / melanocyte migration / positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production / Kit signaling pathway / positive regulation of melanocyte differentiation / regulation of bile acid metabolic process / positive regulation of small intestine smooth muscle contraction / mast cell apoptotic process / mast cell differentiation / positive regulation of mast cell proliferation / mast cell chemotaxis / myeloid leukocyte differentiation / Fc receptor signaling pathway / glycosphingolipid metabolic process / mast cell proliferation / positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly / positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production / immature B cell differentiation / melanocyte differentiation / germ cell migration / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / digestive tract development / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / negative regulation of programmed cell death / stem cell factor receptor activity / hematopoietic stem cell migration / melanocyte adhesion / positive regulation of pyloric antrum smooth muscle contraction / positive regulation of colon smooth muscle contraction / erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation / melanocyte migration / positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production / Kit signaling pathway / positive regulation of melanocyte differentiation / regulation of bile acid metabolic process / positive regulation of small intestine smooth muscle contraction / mast cell apoptotic process / mast cell differentiation / positive regulation of mast cell proliferation / mast cell chemotaxis / myeloid leukocyte differentiation / Fc receptor signaling pathway / glycosphingolipid metabolic process / mast cell proliferation / positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly / positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production / immature B cell differentiation / melanocyte differentiation / germ cell migration / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / digestive tract development / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / negative regulation of programmed cell death /  neural crest cell migration / embryonic hemopoiesis / neural crest cell migration / embryonic hemopoiesis /  lamellipodium assembly / lamellipodium assembly /  pigmentation / positive regulation of leukocyte migration / tongue development / megakaryocyte development / Regulation of KIT signaling / mast cell degranulation / stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway / pigmentation / positive regulation of leukocyte migration / tongue development / megakaryocyte development / Regulation of KIT signaling / mast cell degranulation / stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway /  cytokine binding / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / spermatid development / cytokine binding / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / spermatid development /  growth factor binding / somatic stem cell population maintenance / growth factor binding / somatic stem cell population maintenance /  hemopoiesis / T cell differentiation / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of phospholipase C activity / response to cadmium ion / T cell proliferation / ovarian follicle development / positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / positive regulation of T cell proliferation / TFAP2 (AP-2) family regulates transcription of growth factors and their receptors / hemopoiesis / T cell differentiation / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of phospholipase C activity / response to cadmium ion / T cell proliferation / ovarian follicle development / positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / positive regulation of T cell proliferation / TFAP2 (AP-2) family regulates transcription of growth factors and their receptors /  transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity /  SH2 domain binding / cell chemotaxis / B cell differentiation / SH2 domain binding / cell chemotaxis / B cell differentiation /  erythrocyte differentiation / acrosomal vesicle / Signaling by phosphorylated juxtamembrane, extracellular and kinase domain KIT mutants / erythrocyte differentiation / acrosomal vesicle / Signaling by phosphorylated juxtamembrane, extracellular and kinase domain KIT mutants /  filopodium / epithelial cell proliferation / filopodium / epithelial cell proliferation /  cytokine activity / cytokine activity /  stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / stem cell differentiation / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT /  growth factor activity / growth factor activity /  visual learning / Signaling by SCF-KIT / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / response to organic cyclic compound / visual learning / Signaling by SCF-KIT / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / response to organic cyclic compound /  receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase /  fibrillar center / cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / male gonad development fibrillar center / cytokine-mediated signaling pathway / male gonad developmentSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.17 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.17 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bertoletti, N. / Krimmer, S.G. / Mi, W. / Schlessinger, J. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM analyses of KIT and oncogenic mutants reveal structural oncogenic plasticity and a target for therapeutic intervention. Authors: Stefan G Krimmer / Nicole Bertoletti / Yoshihisa Suzuki / Luka Katic / Jyotidarsini Mohanty / Sheng Shu / Sangwon Lee / Irit Lax / Wei Mi / Joseph Schlessinger /  Abstract: The receptor tyrosine kinase KIT and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) are required for the development of hematopoietic stem cells, germ cells, and other cells. A variety of human cancers, such as ...The receptor tyrosine kinase KIT and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) are required for the development of hematopoietic stem cells, germ cells, and other cells. A variety of human cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, and mast cell leukemia, are driven by somatic gain-of-function KIT mutations. Here, we report cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural analyses of full-length wild-type and two oncogenic KIT mutants, which show that the overall symmetric arrangement of the extracellular domain of ligand-occupied KIT dimers contains asymmetric D5 homotypic contacts juxtaposing the plasma membrane. Mutational analysis of KIT reveals in D5 region an "Achilles heel" for therapeutic intervention. A ligand-sensitized oncogenic KIT mutant exhibits a more comprehensive and stable D5 asymmetric conformation. A constitutively active ligand-independent oncogenic KIT mutant adopts a V-shaped conformation solely held by D5-mediated contacts. Binding of SCF to this mutant fully restores the conformation of wild-type KIT dimers, including the formation of salt bridges responsible for D4 homotypic contacts and other hallmarks of SCF-induced KIT dimerization. These experiments reveal an unexpected structural plasticity of oncogenic KIT mutants and a therapeutic target in D5. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dfp.cif.gz 8dfp.cif.gz | 411.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dfp.ent.gz pdb8dfp.ent.gz | 328.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dfp.json.gz 8dfp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/8dfp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/8dfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/8dfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/8dfp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27410MC  8dfmC  8dfqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 110891.258 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: K619A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KIT, SCFR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KIT, SCFR / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm)References: UniProt: P10721,  receptor protein-tyrosine kinase receptor protein-tyrosine kinase#2: Protein | Mass: 14742.981 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KITLG, MGF, SCF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KITLG, MGF, SCF / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain (production host): CodonPlus RIPL / References: UniProt: P21583 Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / Strain (production host): CodonPlus RIPL / References: UniProt: P21583#3: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose  / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 4Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #4: Sugar |  N-Acetylglucosamine N-AcetylglucosamineHas ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Full-length KIT(DupA502,Y503)-SCF dimers reconstituted in amphipol Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.25 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: membrane Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: membrane | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Plasmid Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / Plasmid : Bacmid : Bacmid | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 5.6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse. : YES / Details: This sample was monodisperse. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K / Details: Blotting time 3 sec, blotting force 0. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: SerialEM COMA-FREE ALIGNMENT |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 64000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 64000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 11.134 sec. / Electron dose: 64.52 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 8456 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3649954 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.17 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 865760 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 119.4 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 8DFM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj