+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8adl | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  GTPase activating protein / GTPase activating protein /  coatomer / coatomer /  TOR signaling TOR signaling | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationurea transport / GATOR1 complex / negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / GATOR2 complex / pseudohyphal growth / proline transport / Seh1-associated complex / positive regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / COPII-coated vesicle budding ...urea transport / GATOR1 complex / negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / GATOR2 complex / pseudohyphal growth / proline transport / Seh1-associated complex / positive regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / COPII-coated vesicle budding / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / nuclear pore localization / regulation of TORC1 signaling / nuclear pore outer ring /  regulation of autophagosome assembly / COPII vesicle coat / TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / fungal-type vacuole / negative regulation of TOR signaling / structural constituent of nuclear pore / fungal-type vacuole membrane / nucleocytoplasmic transport / vacuolar membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of TOR signaling / mRNA transport / signaling adaptor activity / positive regulation of autophagy / regulation of autophagosome assembly / COPII vesicle coat / TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / fungal-type vacuole / negative regulation of TOR signaling / structural constituent of nuclear pore / fungal-type vacuole membrane / nucleocytoplasmic transport / vacuolar membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of TOR signaling / mRNA transport / signaling adaptor activity / positive regulation of autophagy /  nuclear pore / nuclear pore /  : / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / cellular response to amino acid starvation / : / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / cellular response to amino acid starvation /  GTPase activator activity / meiotic cell cycle / cell periphery / positive regulation of GTPase activity / protein import into nucleus / GTPase activator activity / meiotic cell cycle / cell periphery / positive regulation of GTPase activity / protein import into nucleus /  protein transport / protein transport /  nuclear envelope / nuclear envelope /  nuclear membrane / intracellular signal transduction / response to xenobiotic stimulus / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / structural molecule activity / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / nuclear membrane / intracellular signal transduction / response to xenobiotic stimulus / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / structural molecule activity / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription /  endoplasmic reticulum / endoplasmic reticulum /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tafur, L. / Loewith, R. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex. Authors: Lucas Tafur / Kerstin Hinterndorfer / Caroline Gabus / Chiara Lamanna / Ariane Bergmann / Yashar Sadian / Farzad Hamdi / Fotis L Kyrilis / Panagiotis L Kastritis / Robbie Loewith /   Abstract: The SEA complex (SEAC) is a growth regulator that acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) towards Gtr1, a Rag GTPase that relays nutrient status to the Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (TORC1) in ...The SEA complex (SEAC) is a growth regulator that acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) towards Gtr1, a Rag GTPase that relays nutrient status to the Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (TORC1) in yeast. Functionally, the SEAC has been divided into two subcomplexes: SEACIT, which has GAP activity and inhibits TORC1, and SEACAT, which regulates SEACIT. This system is conserved in mammals: the GATOR complex, consisting of GATOR1 (SEACIT) and GATOR2 (SEACAT), transmits amino acid and glucose signals to mTORC1. Despite its importance, the structure of SEAC/GATOR, and thus molecular understanding of its function, is lacking. Here, we solve the cryo-EM structure of the native eight-subunit SEAC. The SEAC has a modular structure in which a COPII-like cage corresponding to SEACAT binds two flexible wings, which correspond to SEACIT. The wings are tethered to the core via Sea3, which forms part of both modules. The GAP mechanism of GATOR1 is conserved in SEACIT, and GAP activity is unaffected by SEACAT in vitro. In vivo, the wings are essential for recruitment of the SEAC to the vacuole, primarily via the EGO complex. Our results indicate that rather than being a direct inhibitor of SEACIT, SEACAT acts as a scaffold for the binding of TORC1 regulators. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8adl.cif.gz 8adl.cif.gz | 2.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8adl.ent.gz pdb8adl.ent.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8adl.json.gz 8adl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8adl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8adl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8adl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ad/8adl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15364MC 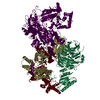 8ae6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 18 molecules CQEDFMLNGBOJHPAIWX
| #1: Protein | Mass: 131104.062 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q03897 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q03897#2: Protein | Mass: 39170.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53011 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53011#3: Protein | Mass: 117775.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38164 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38164#4: Protein |  Protein targeting Protein targetingMass: 33082.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q04491 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q04491#5: Protein | Mass: 149533.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q08281 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q08281#7: Protein | Mass: 182203.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P47170 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P47170 |
|---|
-Nitrogen permease regulator ... , 2 types, 4 molecules UVST
| #6: Protein | Mass: 130141.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38742 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38742#8: Protein | Mass: 69937.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P39923 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P39923 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 28 molecules 
| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Seh1-associated complex (SEAC) / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 2.09 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : TFS Selectris X / Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV : TFS Selectris X / Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C2 (2 fold cyclic : C2 (2 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.95 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 208379 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL Details: AlphaFold predictions were used as starting models for Sea1, Sea2, Sea3, Sea4, Npr2 and Npr3. Rigid body fit was performed in Chimera, and manual building in Coot. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj




