+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7z37 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
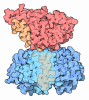
| Title | Structure of the RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 complex (RHC-II) | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSFERASE / RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 / TRANSFERASE / RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 /  complex / complex /  proto-oncogene / proto-oncogene /  serine/threonine kinase / serine/threonine kinase /  cancer / cancer /  chaperone chaperone | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / : / HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex / positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity /  death-inducing signaling complex assembly / positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / dynein axonemal particle / death-inducing signaling complex assembly / positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / dynein axonemal particle /  aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex ...regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / : / HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex / positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex ...regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / : / HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex / positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity /  death-inducing signaling complex assembly / positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / dynein axonemal particle / death-inducing signaling complex assembly / positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / dynein axonemal particle /  aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex / intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization / aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex / intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization /  histone methyltransferase binding / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / protein kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / Rap1 signalling / ATP-dependent protein binding / histone methyltransferase binding / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / protein kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / Rap1 signalling / ATP-dependent protein binding /  regulation of cell motility / protein folding chaperone complex / negative regulation of protein metabolic process / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / positive regulation of tau-protein kinase activity / post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression / regulation of cell motility / protein folding chaperone complex / negative regulation of protein metabolic process / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / positive regulation of tau-protein kinase activity / post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression /  telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / IFNG signaling activates MAPKs / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / IFNG signaling activates MAPKs / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib /  Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / TPR domain binding / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / TPR domain binding /  regulation of cell differentiation / face development / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of cell differentiation / face development / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity /  pseudopodium / dendritic growth cone / somatic stem cell population maintenance / neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway / thyroid gland development / regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / The NLRP3 inflammasome / regulation of protein ubiquitination / HSF1-dependent transactivation / telomere maintenance via telomerase / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / response to unfolded protein / pseudopodium / dendritic growth cone / somatic stem cell population maintenance / neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway / thyroid gland development / regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / The NLRP3 inflammasome / regulation of protein ubiquitination / HSF1-dependent transactivation / telomere maintenance via telomerase / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / response to unfolded protein /  MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity /  protein targeting / HSF1 activation / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / Attenuation phase / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / protein targeting / HSF1 activation / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / Attenuation phase / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle /  DNA polymerase binding / DNA polymerase binding /  Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / supramolecular fiber organization / Schwann cell development / axonal growth cone / type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / Signaling by ERBB2 / positive regulation of telomerase activity / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / supramolecular fiber organization / Schwann cell development / axonal growth cone / type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / Signaling by ERBB2 / positive regulation of telomerase activity /  heat shock protein binding / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / response to muscle stretch / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / heat shock protein binding / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / response to muscle stretch / activation of adenylate cyclase activity /  myelination / cellular response to interleukin-4 / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / ESR-mediated signaling / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / thymus development / placenta development / positive regulation of cell differentiation / myelination / cellular response to interleukin-4 / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / ESR-mediated signaling / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / thymus development / placenta development / positive regulation of cell differentiation /  peptide binding / ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone / Signaling by ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / peptide binding / ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone / Signaling by ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants /  Hsp90 protein binding / RAF activation / tau protein binding / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants Hsp90 protein binding / RAF activation / tau protein binding / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutantsSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.67 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.67 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mesa, P. / Garcia-Alonso, S. / Barbacid, M. / Montoya, G. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 4items Denmark, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 complex reveals the basis of RAF1 regulation. Authors: Sara García-Alonso / Pablo Mesa / Laura de la Puente Ovejero / Gonzalo Aizpurua / Carmen G Lechuga / Eduardo Zarzuela / Clara M Santiveri / Manuel Sanclemente / Javier Muñoz / Mónica ...Authors: Sara García-Alonso / Pablo Mesa / Laura de la Puente Ovejero / Gonzalo Aizpurua / Carmen G Lechuga / Eduardo Zarzuela / Clara M Santiveri / Manuel Sanclemente / Javier Muñoz / Mónica Musteanu / Ramón Campos-Olivas / Jorge Martínez-Torrecuadrada / Mariano Barbacid / Guillermo Montoya /   Abstract: RAF kinases are RAS-activated enzymes that initiate signaling through the MAPK cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Here, we describe the structure of the full- ...RAF kinases are RAS-activated enzymes that initiate signaling through the MAPK cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Here, we describe the structure of the full-length RAF1 protein in complex with HSP90 and CDC37 obtained by cryoelectron microscopy. The reconstruction reveals a RAF1 kinase with an unfolded N-lobe separated from its C-lobe. The hydrophobic core of the N-lobe is trapped in the HSP90 dimer, while CDC37 wraps around the chaperone and interacts with the N- and C-lobes of the kinase. The structure indicates how CDC37 can discriminate between the different members of the RAF family. Our structural analysis also reveals that the folded RAF1 assembles with 14-3-3 dimers, suggesting that after folding RAF1 follows a similar activation as B-RAF. Finally, disruption of the interaction between CDC37 and the DFG segment of RAF1 unveils potential vulnerabilities in attempting the pharmacological degradation of RAF1 for therapeutic purposes. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7z37.cif.gz 7z37.cif.gz | 393.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7z37.ent.gz pdb7z37.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7z37.json.gz 7z37.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z3/7z37 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z3/7z37 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z3/7z37 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z3/7z37 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14472MC 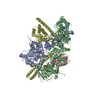 7z38C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Heat shock response / HSP 90 / Heat shock 84 kDa / HSP 84 / HSP84 Heat shock response / HSP 90 / Heat shock 84 kDa / HSP 84 / HSP84Mass: 84371.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: N-terminal HA-tag + HSP90-beta / Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AB1, HSP90B, HSPC2, HSPCB / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AB1, HSP90B, HSPC2, HSPCB / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P08238 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P08238#2: Protein | | Mass: 74409.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: RAF1 + linker Gly-Ser-Ala + C-terminal StrepTagII / Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAF1, RAF / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAF1, RAF / Plasmid: pcDNA3 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P04049,  non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase#3: Protein | | Mass: 46535.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: CDC37 + C-terminal Myc-DDK tag / Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC37, CDC37A / Plasmid: pCMV6 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC37, CDC37A / Plasmid: pCMV6 / Cell line (production host): Expi293F / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16543 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q16543#4: Chemical |  Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine triphosphateHas ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 complex, RHC-II / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.28913380 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293F cells Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293F cells | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: blot for 3 seconds before plunging |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 8138 Details: 8138 images (4430 non-tilted and 3708 30 degrees tilted) |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3760000 Details: 3760k in total: 1353k RAF1:HSP90:CDC37 complex, 1127k 14-3-3 dimer, RAF1:14-3-3 complex 1245k | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.67 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 46000 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 110.87 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj