+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7w1m | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
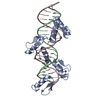
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human cohesin-CTCF-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA /  Cohesin / NIPBL / Cohesin / NIPBL /  CTCF / CTCF /  DNA / chromosome folding / topologically associating domain / chromatin loops / DNA loop extrusion / sister chromatid cohesion / DNA / chromosome folding / topologically associating domain / chromatin loops / DNA loop extrusion / sister chromatid cohesion /  complex / complex /  ATPase / ATPase /  HEAT repeat protein / HEAT repeat protein /  DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationeye morphogenesis / external genitalia morphogenesis / gallbladder development / SMC loading complex / Scc2-Scc4 cohesin loading complex / ear morphogenesis / mitotic cohesin loading / response to DNA damage checkpoint signaling /  regulation of hair cycle / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition ...eye morphogenesis / external genitalia morphogenesis / gallbladder development / SMC loading complex / Scc2-Scc4 cohesin loading complex / ear morphogenesis / mitotic cohesin loading / response to DNA damage checkpoint signaling / regulation of hair cycle / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition ...eye morphogenesis / external genitalia morphogenesis / gallbladder development / SMC loading complex / Scc2-Scc4 cohesin loading complex / ear morphogenesis / mitotic cohesin loading / response to DNA damage checkpoint signaling /  regulation of hair cycle / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / cohesin loader activity / chromatin insulator sequence binding / positive regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / meiotic cohesin complex / Cohesin Loading onto Chromatin / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / regulation of hair cycle / negative regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / cohesin loader activity / chromatin insulator sequence binding / positive regulation of sister chromatid cohesion / meiotic cohesin complex / Cohesin Loading onto Chromatin / maintenance of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion /  Establishment of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / forelimb morphogenesis / Establishment of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / forelimb morphogenesis /  integrator complex / embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis / establishment of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic cohesin complex / integrator complex / embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis / establishment of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic cohesin complex /  cohesin complex / negative regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of centromeric sister chromatid cohesion / uterus morphogenesis / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process / regulation of developmental growth / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / cohesin complex / negative regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of centromeric sister chromatid cohesion / uterus morphogenesis / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process / regulation of developmental growth / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis /  genomic imprinting / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / cellular response to X-ray / lateral element / positive regulation of neuron migration / genomic imprinting / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / cellular response to X-ray / lateral element / positive regulation of neuron migration /  mediator complex binding / mediator complex binding /  chromo shadow domain binding / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / chromatin looping / negative regulation of gene expression via chromosomal CpG island methylation / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / metanephros development / digestive tract development / positive regulation of ossification / reciprocal meiotic recombination / chromo shadow domain binding / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / chromatin looping / negative regulation of gene expression via chromosomal CpG island methylation / positive regulation of multicellular organism growth / metanephros development / digestive tract development / positive regulation of ossification / reciprocal meiotic recombination /  lncRNA binding / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / sister chromatid cohesion / face morphogenesis / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / lncRNA binding / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / sister chromatid cohesion / face morphogenesis / negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion /  microtubule motor activity / microtubule motor activity /  : / dynein complex binding / stem cell population maintenance / : / dynein complex binding / stem cell population maintenance /  beta-tubulin binding / fat cell differentiation / mitotic spindle pole / outflow tract morphogenesis / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / beta-tubulin binding / fat cell differentiation / mitotic spindle pole / outflow tract morphogenesis / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / somatic stem cell population maintenance /  regulation of DNA replication / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / regulation of DNA replication / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production /  regulation of embryonic development / regulation of embryonic development /  chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / chromosome, centromeric region / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production /  mitotic spindle assembly / developmental growth / localization / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / heart morphogenesis / condensed chromosome / protein localization to chromatin / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Meiotic synapsis / meiotic cell cycle / condensed nuclear chromosome / male germ cell nucleus / mitotic spindle assembly / developmental growth / localization / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / heart morphogenesis / condensed chromosome / protein localization to chromatin / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Meiotic synapsis / meiotic cell cycle / condensed nuclear chromosome / male germ cell nucleus /  chromosome segregation / promoter-specific chromatin binding / chromosome segregation / promoter-specific chromatin binding /  transcription coregulator binding / sensory perception of sound / transcription coregulator binding / sensory perception of sound /  brain development / response to radiation / brain development / response to radiation /  protein localization / protein localization /  kinetochore / kinetochore /  cognition / cognition /  nuclear matrix / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / nuclear matrix / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific /  spindle pole / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / spindle pole / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis /  histone deacetylase binding / Separation of Sister Chromatids / transcription corepressor activity / double-strand break repair / mitotic cell cycle / histone deacetylase binding / Separation of Sister Chromatids / transcription corepressor activity / double-strand break repair / mitotic cell cycle /  chromosome / midbody chromosome / midbodySimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 6.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 6.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shi, Z.B. / Bai, X.C. / Yu, H. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: CTCF and R-loops are boundaries of cohesin-mediated DNA looping. Authors: Hongshan Zhang / Zhubing Shi / Edward J Banigan / Yoori Kim / Hongtao Yu / Xiao-Chen Bai / Ilya J Finkelstein /   Abstract: Cohesin and CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) are key regulatory proteins of three-dimensional (3D) genome organization. Cohesin extrudes DNA loops that are anchored by CTCF in a polar orientation. Here, ...Cohesin and CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) are key regulatory proteins of three-dimensional (3D) genome organization. Cohesin extrudes DNA loops that are anchored by CTCF in a polar orientation. Here, we present direct evidence that CTCF binding polarity controls cohesin-mediated DNA looping. Using single-molecule imaging, we demonstrate that a critical N-terminal motif of CTCF blocks cohesin translocation and DNA looping. The cryo-EM structure of the cohesin-CTCF complex reveals that this CTCF motif ahead of zinc fingers can only reach its binding site on the STAG1 cohesin subunit when the N terminus of CTCF faces cohesin. Remarkably, a C-terminally oriented CTCF accelerates DNA compaction by cohesin. DNA-bound Cas9 and Cas12a ribonucleoproteins are also polar cohesin barriers, indicating that stalling may be intrinsic to cohesin itself. Finally, we show that RNA-DNA hybrids (R-loops) block cohesin-mediated DNA compaction in vitro and are enriched with cohesin subunits in vivo, likely forming TAD boundaries. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7w1m.cif.gz 7w1m.cif.gz | 837.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7w1m.ent.gz pdb7w1m.ent.gz | 631.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7w1m.json.gz 7w1m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w1/7w1m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w1/7w1m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w1/7w1m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w1/7w1m | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  32252MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 143485.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SMC1A, DXS423E, KIAA0178, SB1.8, SMC1, SMC1L1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SMC1A, DXS423E, KIAA0178, SB1.8, SMC1, SMC1L1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14683 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14683 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 141771.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SMC3, BAM, BMH, CSPG6, SMC3L1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SMC3, BAM, BMH, CSPG6, SMC3L1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UQE7 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UQE7 |
-Protein , 4 types, 4 molecules CDEH
| #3: Protein | Mass: 71556.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: R172A, D279A, R450A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD21, HR21, KIAA0078, NXP1, SCC1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD21, HR21, KIAA0078, NXP1, SCC1 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O60216 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O60216 |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein |  / SCC3 homolog 1 / Stromal antigen 1 / SCC3 homolog 1 / Stromal antigen 1Mass: 144616.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: STAG1, SA1, SCC3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: STAG1, SA1, SCC3 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8WVM7 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8WVM7 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 167830.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NIPBL, IDN3, SCC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NIPBL, IDN3, SCC2 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q6KC79 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q6KC79 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 82928.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CTCF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CTCF / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P49711 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P49711 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules FG
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 36202.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 36605.387 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 15 molecules 




| #9: Chemical |  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate#10: Chemical | #11: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2185704 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 42704 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 236.05 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj