+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7u97 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
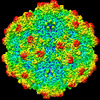
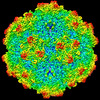
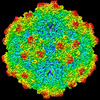
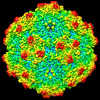
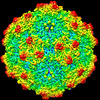
| Title | SAAV pH 4.0 capsid structure | ||||||
 Components Components | Capsid protein Capsid Capsid | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE / VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE /  Capsid / AAV / Capsid / AAV /  gene therapy / gene therapy /  receptor / endosomal trafficking / receptor / endosomal trafficking /  antigenicity antigenicity | ||||||
| Function / homology | Phospholipase A2-like domain / Phospholipase A2-like domain / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP1/VP2 / Parvovirus coat protein VP2 / Capsid/spike protein, ssDNA virus / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / structural molecule activity /  Capsid protein Capsid protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Snake adeno-associated virus Snake adeno-associated virus | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.66 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.66 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Mietzsch, M. / McKenna, R. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2022 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2022Title: Characterization of the Serpentine Adeno-Associated Virus (SAAV) Capsid Structure: Receptor Interactions and Antigenicity. Authors: Mario Mietzsch / Joshua A Hull / Victoria E Makal / Alberto Jimenez Ybargollin / Jennifer C Yu / Kedrick McKissock / Antonette Bennett / Judit Penzes / Bridget Lins-Austin / Qian Yu / Paul ...Authors: Mario Mietzsch / Joshua A Hull / Victoria E Makal / Alberto Jimenez Ybargollin / Jennifer C Yu / Kedrick McKissock / Antonette Bennett / Judit Penzes / Bridget Lins-Austin / Qian Yu / Paul Chipman / Nilakshee Bhattacharya / Duncan Sousa / David Strugatsky / Peter Tijssen / Robert McKenna / Mavis Agbandje-McKenna /   Abstract: Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are being developed as clinical gene therapy vectors. One issue undermining their broad use in the clinical setting is the high prevalence of circulating antibodies in ...Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are being developed as clinical gene therapy vectors. One issue undermining their broad use in the clinical setting is the high prevalence of circulating antibodies in the general population capable of neutralizing AAV vectors. Hence, there is a need for AAV vectors that can evade the preexisting immune response. One possible source of human naive vectors are AAVs that do not disseminate in the primate population, and one such example is serpentine AAV (SAAV). This study characterizes the structural and biophysical properties of the SAAV capsid and its receptor interactions and antigenicity. Single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and thermal stability studies were conducted to characterize the SAAV capsid structure at pH 7.4, 6.0, 5.5, and 4.0, conditions experienced during cellular trafficking. Cell binding assays using Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines identified terminal sialic acid as the primary attachment receptor for SAAV similar to AAV1, 4, 5, and 6. The binding site of sialic acid to the SAAV capsid was mapped near the 2-fold axis toward the 2/5-fold wall, in a different location than AAV1, 4, 5, and 6. Towards determining the SAAV capsid antigenicity native immunodot blots showed that SAAV evades AAV serotype-specific mouse monoclonal antibodies. However, despite its reptilian origin, it was recognized by ~25% of 50 human sera tested, likely due to the presence of cross-reactive antibodies. These findings will inform future gene delivery applications using SAAV-based vectors and further aid the structural characterization and annotation of the repertoire of available AAV capsids. AAVs are widely studied therapeutic gene delivery vectors. However, preexisting antibodies and their detrimental effect on therapeutic efficacy are a primary challenge encountered during clinical trials. In order to circumvent preexisting neutralizing antibodies targeting mammalian AAV capsids, serpentine AAV (SAAV) was evaluated as a potential alternative to existing mammalian therapeutic vectors. The SAAV capsid was found to be thermostable at a wide range of environmental pH conditions, and its structure showed conservation of the core capsid topology but displays high structural variability on the surface. At the same time, it binds to a common receptor, sialic acid, that is also utilized by other AAVs already being utilized in gene therapy trials. Contrary to the initial hypothesis, SAAV capsids were recognized by one in four human sera tested, pointing to conserved amino acids around the 5-fold region as epitopes for cross-reacting antibodies. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7u97.cif.gz 7u97.cif.gz | 5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7u97.ent.gz pdb7u97.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7u97.json.gz 7u97.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u9/7u97 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u9/7u97 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u9/7u97 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u9/7u97 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 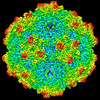 26393MC  7u94C  7u95C  7u96C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Capsid CapsidMass: 57217.203 Da / Num. of mol.: 60 / Fragment: UNP residues 206-726 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Snake adeno-associated virus / Gene: VP1 / Production host: Snake adeno-associated virus / Gene: VP1 / Production host:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q6V7U2 Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) / References: UniProt: Q6V7U2 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Snake adeno-associated virus / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Snake adeno-associated virus Snake adeno-associated virus |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Details of virus | Empty: YES / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: OTHER / Type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE |
| Buffer solution | pH: 4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.10-2155_2155: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: cisTEM / Category: 3D reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : I (icosahedral : I (icosahedral ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.66 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 149155 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj


