[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
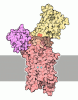
Yorodumi- PDB-7rd8: Structure of the S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7rd8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
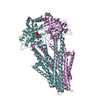
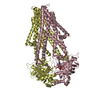
| Title | Structure of the S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state | ||||||
 Components Components | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSLOCASE / P4B ATPase lipid flippase TRANSLOCASE / P4B ATPase lipid flippase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / P-type phospholipid transporter / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum ...lysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / P-type phospholipid transporter / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / phospholipid translocation /  trans-Golgi network / trans-Golgi network /  endocytosis / late endosome / endocytosis / late endosome /  protein transport / endosome membrane / protein transport / endosome membrane /  endosome / endosome /  Golgi membrane / Golgi membrane /  Golgi apparatus / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / magnesium ion binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 5.64 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 5.64 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bai, L. / Jain, B.K. / You, Q. / Duan, H.D. / Graham, T.R. / Li, H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of the P4B ATPase lipid flippase activity. Authors: Lin Bai / Bhawik K Jain / Qinglong You / H Diessel Duan / Mehmet Takar / Todd R Graham / Huilin Li /   Abstract: P4 ATPases are lipid flippases that are phylogenetically grouped into P4A, P4B and P4C clades. The P4A ATPases are heterodimers composed of a catalytic α-subunit and accessory β-subunit, and the ...P4 ATPases are lipid flippases that are phylogenetically grouped into P4A, P4B and P4C clades. The P4A ATPases are heterodimers composed of a catalytic α-subunit and accessory β-subunit, and the structures of several heterodimeric flippases have been reported. The S. cerevisiae Neo1 and its orthologs represent the P4B ATPases, which function as monomeric flippases without a β-subunit. It has been unclear whether monomeric flippases retain the architecture and transport mechanism of the dimeric flippases. Here we report the structure of a P4B ATPase, Neo1, in its E1-ATP, E2P-transition, and E2P states. The structure reveals a conserved architecture as well as highly similar functional intermediate states relative to dimeric flippases. Consistently, structure-guided mutagenesis of residues in the proposed substrate translocation path disrupted Neo1's ability to establish membrane asymmetry. These observations indicate that evolutionarily distant P4 ATPases use a structurally conserved mechanism for substrate transport. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7rd8.cif.gz 7rd8.cif.gz | 181.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7rd8.ent.gz pdb7rd8.ent.gz | 138.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7rd8.json.gz 7rd8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rd/7rd8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rd/7rd8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rd/7rd8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rd/7rd8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24415MC  7rd6C  7rd7C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 130363.492 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)Gene: NEO1, YIL048W / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)References: UniProt: P40527, P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
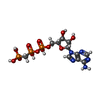
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ACP / |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.64 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 264891 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj