+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7r1c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Bacillus megaterium gas vesicles | ||||||
 Components Components | Gas vesicle structural protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  gas vesicle / gas vesicle /  buoyancy / helical / microbial motility buoyancy / helical / microbial motility | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationgas vesicle shell / vesicle membrane /  vacuole / structural molecule activity vacuole / structural molecule activitySimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria) Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Huber, S.T. / Evers, W. / Jakobi, A.J. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM structure of gas vesicles for buoyancy-controlled motility. Authors: Stefan T Huber / Dion Terwiel / Wiel H Evers / David Maresca / Arjen J Jakobi /  Abstract: Gas vesicles are gas-filled nanocompartments that allow a diverse group of bacteria and archaea to control their buoyancy. The molecular basis of their properties and assembly remains unclear. Here, ...Gas vesicles are gas-filled nanocompartments that allow a diverse group of bacteria and archaea to control their buoyancy. The molecular basis of their properties and assembly remains unclear. Here, we report the 3.2 Å cryo-EM structure of the gas vesicle shell made from the structural protein GvpA that self-assembles into hollow helical cylinders closed off by cone-shaped tips. Two helical half shells connect through a characteristic arrangement of GvpA monomers, suggesting a mechanism of gas vesicle biogenesis. The fold of GvpA features a corrugated wall structure typical for force-bearing thin-walled cylinders. Small pores enable gas molecules to diffuse across the shell, while the exceptionally hydrophobic interior surface effectively repels water. Comparative structural analysis confirms the evolutionary conservation of gas vesicle assemblies and demonstrates molecular features of shell reinforcement by GvpC. Our findings will further research into gas vesicle biology and facilitate molecular engineering of gas vesicles for ultrasound imaging. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2022 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structure of gas vesicles for buoyancy-controlled motility Authors: Huber, S.T. / Terwiel, D. / Evers, W.H. / Maresca, D. / Jakobi, A.J. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7r1c.cif.gz 7r1c.cif.gz | 43.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7r1c.ent.gz pdb7r1c.ent.gz | 40.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7r1c.json.gz 7r1c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r1/7r1c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r1/7r1c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r1/7r1c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/r1/7r1c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14238MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 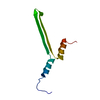
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 5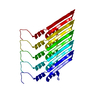
|
| 2 | x 100
|
| 3 | x 930
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 9626.850 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria) Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 14581 / DSM 32 / JCM 2506 / NBRC 15308 / NCIMB 9376 / NCTC 10342 / NRRL B-14308 / VKM B-512 Gene: gvpA, BG04_216, G3M54_29730 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21-DE3-pLysS / References: UniProt: A0A0B6AAV2 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21-DE3-pLysS / References: UniProt: A0A0B6AAV2 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Helical assembly of GvpB monomers forming the gas vesicle wall Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 9.99 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria) Priestia megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: BL21-DE3-pLysS Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: BL21-DE3-pLysS | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.45 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: Concentration measured by OD(500)=3.12 against a sonicated blank. | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K / Details: Blot times between 5 and 11 seconds. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 64000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 250 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 64000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 250 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.4 sec. / Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4351 Details: One shot per hole 1.37 A/pix 60 fractions over 30 e-/A2 |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -3.874 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 0.525 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 36295 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1460 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION Details: Final reconstruction in cryoSPARC 3.3 using local refinement in a small section of the cylinder Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj