+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7nnp | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
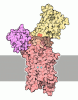
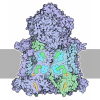
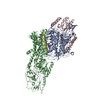
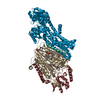
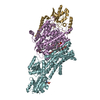
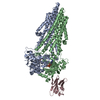
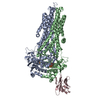
| Title | Rb-loaded cryo-EM structure of the E1-ATP KdpFABC complex. | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Potassium-transporting ATPase ...) x 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  P-type ATPase / superfamily of K+ transporters (SKT) / Rb substitution / intersubunit tunnel P-type ATPase / superfamily of K+ transporters (SKT) / Rb substitution / intersubunit tunnel | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationP-type K+ transporter / potassium:proton antiporter complex / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / P-type potassium transmembrane transporter activity / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / plasma membrane => GO:0005886 /  potassium ion binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport / potassium ion binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport /  hydrolase activity ...P-type K+ transporter / potassium:proton antiporter complex / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / P-type potassium transmembrane transporter activity / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / plasma membrane => GO:0005886 / hydrolase activity ...P-type K+ transporter / potassium:proton antiporter complex / potassium ion-transporting ATPase complex / P-type potassium transmembrane transporter activity / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / plasma membrane => GO:0005886 /  potassium ion binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport / potassium ion binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / potassium ion transport /  hydrolase activity / magnesium ion binding / hydrolase activity / magnesium ion binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Silberberg, J.M. / Corey, R.A. / Hielkema, L. / Stock, C. / Stansfeld, P.J. / Paulino, C. / Haenelt, I. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  Netherlands, Netherlands,  United Kingdom, 5items United Kingdom, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Deciphering ion transport and ATPase coupling in the intersubunit tunnel of KdpFABC. Authors: Jakob M Silberberg / Robin A Corey / Lisa Hielkema / Charlott Stock / Phillip J Stansfeld / Cristina Paulino / Inga Hänelt /     Abstract: KdpFABC, a high-affinity K pump, combines the ion channel KdpA and the P-type ATPase KdpB to secure survival at K limitation. Here, we apply a combination of cryo-EM, biochemical assays, and MD ...KdpFABC, a high-affinity K pump, combines the ion channel KdpA and the P-type ATPase KdpB to secure survival at K limitation. Here, we apply a combination of cryo-EM, biochemical assays, and MD simulations to illuminate the mechanisms underlying transport and the coupling to ATP hydrolysis. We show that ions are transported via an intersubunit tunnel through KdpA and KdpB. At the subunit interface, the tunnel is constricted by a phenylalanine, which, by polarized cation-π stacking, controls K entry into the canonical substrate binding site (CBS) of KdpB. Within the CBS, ATPase coupling is mediated by the charge distribution between an aspartate and a lysine. Interestingly, individual elements of the ion translocation mechanism of KdpFABC identified here are conserved among a wide variety of P-type ATPases from different families. This leads us to the hypothesis that KdpB might represent an early descendant of a common ancestor of cation pumps. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2021 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2021Title: Deciphering ion transport and ATPase coupling in the intersubunit tunnel of KdpFABC Authors: Silberberg, J.M. / Corey, R.A. / Hielkema, L. / Stock, C. / Stansfeld, P.J. / Paulino, C. / Hanelt, I. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7nnp.cif.gz 7nnp.cif.gz | 251.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7nnp.ent.gz pdb7nnp.ent.gz | 207.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7nnp.json.gz 7nnp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nn/7nnp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nn/7nnp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nn/7nnp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nn/7nnp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  12482MC  7nnlC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Potassium-transporting ATPase ... , 4 types, 4 molecules ACDB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 59276.652 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: G232D Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Gene: kdpA, D9J52_12825, SAMEA3752559_01047 / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Gene: kdpA, D9J52_12825, SAMEA3752559_01047 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A2S5ZPF1 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A2S5ZPF1 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 20281.035 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)Gene: kdpC, A9R57_11470, ACU57_12815, AM464_20755, AUQ13_21370, BANRA_01742, BANRA_03870, BHS87_03640, BJJ90_18865, BMA87_25495, BON98_02815, BUE81_20120, BvCms12BK_01599, BvCms2454_04067, ...Gene: kdpC, A9R57_11470, ACU57_12815, AM464_20755, AUQ13_21370, BANRA_01742, BANRA_03870, BHS87_03640, BJJ90_18865, BMA87_25495, BON98_02815, BUE81_20120, BvCms12BK_01599, BvCms2454_04067, BvCmsHHP001_00774, BvCmsHHP056_03395, BvCmsKSP026_01797, BW690_07920, C5F72_18220, C5F73_11285, C5N07_14650, C9E25_26865, CA593_25675, CG692_12945, CI694_20645, D0X26_17510, D2185_15885, D3821_21865, D3Y67_05220, D4718_15195, D9C99_19315, D9D20_12860, D9D44_15890, D9G69_25005, D9J52_12835, D9Z28_23025, DAH34_18920, DBQ99_18020, DJ503_06890, DL326_22940, DNC98_20170, DT034_24065, DTL43_19970, DXT73_03320, E2119_26465, E2134_18585, E2135_05100, E4K51_13735, E4K53_14000, E4K55_14005, E4K61_12665, E5P28_21685, EA213_10645, EAI52_22450, EC3234A_8c00230, ECTO6_03352, ED307_21640, EEP23_23705, EG808_19380, EI021_12890, EI028_12880, EI032_09320, EI041_12810, EIZ93_03125, EL75_3091, EL79_3184, EL80_5457, ERS085365_04786, ERS085416_02369, ERS139211_04506, ERS150873_01994, EYD11_15990, EYV18_15885, F1E19_24880, F9040_19740, FNW97_03505, FRV13_05295, FV293_12595, G5688_17415, GII66_07600, GKF39_08170, GKF74_06650, GKF86_08095, GKF89_05805, GP689_15935, GP954_16115, GP979_23630, GQE33_23970, GQE34_25250, GQE64_10530, GQM06_27255, GQM17_23755, GRW05_21650, GRW42_11025, GRW57_15570, GRW80_11135, GRW81_16520, HVY93_16490, HX136_18175, NCTC10963_03490, NCTC8500_03902, NCTC9045_04050, NCTC9058_03392, NCTC9062_04759, NCTC9073_02588, NCTC9706_00826, PGD_02635, RK56_025175, SAMEA3472044_02479, SAMEA3472047_02083, SAMEA3472080_00272, SAMEA3484427_03080, SAMEA3484429_03302, SAMEA3753097_03043, SAMEA3753300_04144, WP2S18E08_32510, WP7S17E04_30600 Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A037YI39 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A037YI39 |
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2853.463 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Gene: kdpF, b4513, JW0687 / Production host: Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Gene: kdpF, b4513, JW0687 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: P36937 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: P36937 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 72251.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: S162A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli)Gene: kdpB, ACU57_12810, AUQ13_21365, BANRA_01741, BANRA_03871, BJJ90_18860, BMA87_25490, BUE81_20115, BvCms12BK_01600, BvCms2454_04068, BvCmsHHP001_00773, BvCmsKSP026_01798, BW690_07915, C5F73_ ...Gene: kdpB, ACU57_12810, AUQ13_21365, BANRA_01741, BANRA_03871, BJJ90_18860, BMA87_25490, BUE81_20115, BvCms12BK_01600, BvCms2454_04068, BvCmsHHP001_00773, BvCmsKSP026_01798, BW690_07915, C5F73_11290, C5N07_14655, C9E25_26860, CA593_25670, CG692_12950, D0X26_17505, D2185_15880, D3821_21860, D3Y67_05225, D9C99_19310, D9D44_15885, D9G69_25000, D9J52_12830, D9Z28_23020, DBQ99_18015, DJ503_06885, DL326_22935, DNC98_20165, DT034_24060, DTL43_19975, DXT73_03325, E2119_26470, E2134_18590, E2135_05105, E4K51_13740, E4K53_14005, E4K55_14010, E4K61_12660, EA213_10640, EAI52_22455, EC3234A_8c00240, ECTO6_03351, ED307_21635, EEP23_23700, EG808_19375, EI021_12885, EI028_12885, EI041_12805, EPT01_08650, ERS085365_04785, ERS085416_02368, ERS139211_04507, ERS150873_01995, EXX71_13725, EYD11_15985, EYV18_15890, F1E19_24885, FNW97_03510, FV293_12590, FWK02_15235, GKF39_08175, GKF74_06655, GKF86_08100, GKF89_05800, GP689_15940, GQE33_23975, GQE34_25255, GQE64_10535, GQM17_23760, GRW05_21645, GRW42_11030, GRW80_11130, GRW81_16515, HVY93_16485, HX136_18170, NCTC8500_03901, NCTC9045_04049, NCTC9062_04760, PGD_02634, RK56_025170, SAMEA3472047_02084, SAMEA3484427_03079, SAMEA3484429_03303, SAMEA3753300_04145, WP2S18E08_32500, WP7S17E04_30590 Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A024L5I2, P-type K+ transporter Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): LB2003 / References: UniProt: A0A024L5I2, P-type K+ transporter |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 11 molecules 
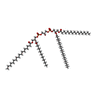
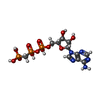


| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-RB /  Rubidium Rubidium#6: Chemical |  Cardiolipin Cardiolipin#7: Chemical | ChemComp-ACP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: KdpFABC / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.157 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: LB2003 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: LB2003 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM NaCl and 0.0125% DDM |
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: at 5 mA / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 49407 X / Calibrated magnification: 49407 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 49407 X / Calibrated magnification: 49407 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2000 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 105 K / Temperature (min): 90 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 9 sec. / Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 8 / Num. of real images: 22046 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 60 / Used frames/image: 1-60 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1_4122: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 756834 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 196682 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6HRA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj