+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7nmn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
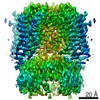
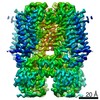
| Title | Rabbit HCN4 stabilised in amphipol A8-35 | ||||||
 Components Components | Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 4,Rabbit HCN4 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  cryo-EM / cryo-EM /  ion channels ion channels | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintracellularly cAMP-activated cation channel activity /  sodium channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex / sodium channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex /  voltage-gated potassium channel activity / voltage-gated potassium channel activity /  cAMP binding / cellular response to cAMP / potassium ion transmembrane transport / cAMP binding / cellular response to cAMP / potassium ion transmembrane transport /  regulation of heart rate / regulation of heart rate /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chaves-Sanjuan, A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Gating movements and ion permeation in HCN4 pacemaker channels. Authors: Andrea Saponaro / Daniel Bauer / M Hunter Giese / Paolo Swuec / Alessandro Porro / Federica Gasparri / Atiyeh Sadat Sharifzadeh / Antonio Chaves-Sanjuan / Laura Alberio / Giacomo Parisi / ...Authors: Andrea Saponaro / Daniel Bauer / M Hunter Giese / Paolo Swuec / Alessandro Porro / Federica Gasparri / Atiyeh Sadat Sharifzadeh / Antonio Chaves-Sanjuan / Laura Alberio / Giacomo Parisi / Gabriele Cerutti / Oliver B Clarke / Kay Hamacher / Henry M Colecraft / Filippo Mancia / Wayne A Hendrickson / Steven A Siegelbaum / Dario DiFrancesco / Martino Bolognesi / Gerhard Thiel / Bina Santoro / Anna Moroni /     Abstract: The HCN1-4 channel family is responsible for the hyperpolarization-activated cation current I/I that controls automaticity in cardiac and neuronal pacemaker cells. We present cryoelectron microscopy ...The HCN1-4 channel family is responsible for the hyperpolarization-activated cation current I/I that controls automaticity in cardiac and neuronal pacemaker cells. We present cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of HCN4 in the presence or absence of bound cAMP, displaying the pore domain in closed and open conformations. Analysis of cAMP-bound and -unbound structures sheds light on how ligand-induced transitions in the channel cytosolic portion mediate the effect of cAMP on channel gating and highlights the regulatory role of a Mg coordination site formed between the C-linker and the S4-S5 linker. Comparison of open/closed pore states shows that the cytosolic gate opens through concerted movements of the S5 and S6 transmembrane helices. Furthermore, in combination with molecular dynamics analyses, the open pore structures provide insights into the mechanisms of K/Na permeation. Our results contribute mechanistic understanding on HCN channel gating, cyclic nucleotide-dependent modulation, and ion permeation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7nmn.cif.gz 7nmn.cif.gz | 366.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7nmn.ent.gz pdb7nmn.ent.gz | 289.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7nmn.json.gz 7nmn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/7nmn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/7nmn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/7nmn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/nm/7nmn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 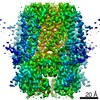 12466MC  7np3C  7np4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
NCS oper:
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98208.383 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Gene: HCN4, HAC4 / Production host: Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Gene: HCN4, HAC4 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9TV66 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9TV66 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rabbit HCN4 cAMP-unbound stabilised in amphipol A8-35 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK-293 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK-293 |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 62 sec. / Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1571 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 100130 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C4 (4 fold cyclic : C4 (4 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 11406 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 57.9 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj


