+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7lzi | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
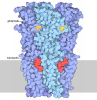
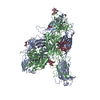
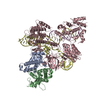
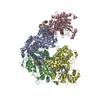
| Title | Structure of the glutamate receptor-like channel AtGLR3.4 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Glutamate receptor 3.4 | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSPORT PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN /  Arabidopsis thaliana / Arabidopsis thaliana /  Ion-Channel / glutamate receptor-like channel (GLR) Ion-Channel / glutamate receptor-like channel (GLR) | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to acetate /  chloroplast membrane / chloroplast membrane /  glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to cold / glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to cold /  plastid / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / plastid / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity /  chloroplast / calcium-mediated signaling / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / chloroplast / calcium-mediated signaling / cellular response to amino acid stimulus /  calcium channel activity ...cellular response to acetate / calcium channel activity ...cellular response to acetate /  chloroplast membrane / chloroplast membrane /  glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to cold / glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to cold /  plastid / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / plastid / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity /  chloroplast / calcium-mediated signaling / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / chloroplast / calcium-mediated signaling / cellular response to amino acid stimulus /  calcium channel activity / response to wounding / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / calcium ion transport / calcium channel activity / response to wounding / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / calcium ion transport /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.39 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.39 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gangwar, S.P. / Green, M.N. / Sobolevsky, A.I. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana glutamate receptor-like channel GLR3.4. Authors: Marriah N Green / Shanti Pal Gangwar / Erwan Michard / Alexander A Simon / Maria Teresa Portes / Juan Barbosa-Caro / Michael M Wudick / Michael A Lizzio / Oleg Klykov / Maria V Yelshanskaya ...Authors: Marriah N Green / Shanti Pal Gangwar / Erwan Michard / Alexander A Simon / Maria Teresa Portes / Juan Barbosa-Caro / Michael M Wudick / Michael A Lizzio / Oleg Klykov / Maria V Yelshanskaya / José A Feijó / Alexander I Sobolevsky /    Abstract: Glutamate receptor-like channels (GLRs) play vital roles in various physiological processes in plants, such as wound response, stomatal aperture control, seed germination, root development, innate ...Glutamate receptor-like channels (GLRs) play vital roles in various physiological processes in plants, such as wound response, stomatal aperture control, seed germination, root development, innate immune response, pollen tube growth, and morphogenesis. Despite the importance of GLRs, knowledge about their molecular organization is limited. Here we use X-ray crystallography and single-particle cryo-EM to solve structures of the Arabidopsis thaliana GLR3.4. Our structures reveal the tetrameric assembly of GLR3.4 subunits into a three-layer domain architecture, reminiscent of animal ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs). However, the non-swapped arrangement between layers of GLR3.4 domains, binding of glutathione through S-glutathionylation of cysteine C205 inside the amino-terminal domain clamshell, unique symmetry, inter-domain interfaces, and ligand specificity distinguish GLR3.4 from representatives of the iGluR family and suggest distinct features of the GLR gating mechanism. Our work elaborates on the principles of GLR architecture and symmetry and provides a molecular template for deciphering GLR-dependent signaling mechanisms in plants. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7lzi.cif.gz 7lzi.cif.gz | 299.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7lzi.ent.gz pdb7lzi.ent.gz | 230.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7lzi.json.gz 7lzi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lz/7lzi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lz/7lzi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lz/7lzi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/lz/7lzi | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23607MC  7lz0C  7lz1C  7lz2C  7lzhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
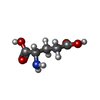
| #1: Protein | Mass: 107317.383 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) / Gene: GLR3.4, GLR4, GLUR3, At1g05200, YUP8H12.19 / Plasmid: BacMam / Cell line (production host): HEK293S-GnTi / Production host: Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) / Gene: GLR3.4, GLR4, GLUR3, At1g05200, YUP8H12.19 / Plasmid: BacMam / Cell line (production host): HEK293S-GnTi / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8GXJ4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8GXJ4#2: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose  / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mass: 424.401 Da / Num. of mol.: 4Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GLU /  Glutamic acid Glutamic acidHas ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GLR3.4 / Type: COMPLEX Details: Map displaying ligand binding and trans-membrane domain Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293S-GnTi / Plasmid Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293S-GnTi / Plasmid : BacMam : BacMam | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YESDetails: Protein extracted and reconstituted in a detergent micelle | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: 1mM L-Glutamate was added to the purified protein and incubated on ice for 30 min before specimen preparation. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.5 sec. / Electron dose: 58 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2161194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C2 (2 fold cyclic : C2 (2 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.39 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 174044 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj