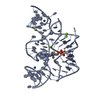
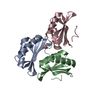
Entry Database : PDB / ID : 7csqTitle Solution structure of the complex between p75NTR-DD and TRADD-DD Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16 Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein Keywords / / / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / Authors Lin, Z. / Zhang, N. Funding support Organization Grant number Country National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
Journal : J.Biol.Chem. / Year : 2021Title : Structural basis of NF-kappa B signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor interaction with adaptor protein TRADD through their respective death domains.Authors : Zhang, N. / Kisiswa, L. / Ramanujan, A. / Li, Z. / Sim, E.W. / Tian, X. / Yuan, W. / Ibanez, C.F. / Lin, Z. History Deposition Aug 16, 2020 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Aug 25, 2021 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Mar 16, 2022 Group / Category / citation_authorItem _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev ... _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.journal_id_ASTM / _citation.journal_id_CSD / _citation.journal_id_ISSN / _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI / _citation.pdbx_database_id_PubMed / _citation.title / _citation.year Revision 1.2 May 15, 2024 Group / Database references / Category / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / Item
Show all Show less
 Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords APOPTOSIS / p75 NTR /
APOPTOSIS / p75 NTR /  death domain /
death domain /  TRADD
TRADD Function and homology information
Function and homology information death receptor activity / positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth /
death receptor activity / positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth /  tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily complex /
tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily complex /  death domain binding / negative regulation of hair follicle development / negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway ...NFG and proNGF binds to p75NTR / detection of temperature stimulus / dorsal aorta development / Ceramide signalling /
death domain binding / negative regulation of hair follicle development / negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway ...NFG and proNGF binds to p75NTR / detection of temperature stimulus / dorsal aorta development / Ceramide signalling /  death receptor activity / positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth /
death receptor activity / positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth /  tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily complex /
tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily complex /  death domain binding / negative regulation of hair follicle development / negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / Defective RIPK1-mediated regulated necrosis /
death domain binding / negative regulation of hair follicle development / negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / Defective RIPK1-mediated regulated necrosis /  neurotrophin binding / positive regulation of hair follicle development / Regulation by c-FLIP / CASP8 activity is inhibited / Dimerization of procaspase-8 / TNF signaling / Caspase activation via Death Receptors in the presence of ligand / nerve development / Axonal growth inhibition (RHOA activation) / Axonal growth stimulation /
neurotrophin binding / positive regulation of hair follicle development / Regulation by c-FLIP / CASP8 activity is inhibited / Dimerization of procaspase-8 / TNF signaling / Caspase activation via Death Receptors in the presence of ligand / nerve development / Axonal growth inhibition (RHOA activation) / Axonal growth stimulation /  nerve growth factor binding / NADE modulates death signalling / Regulated proteolysis of p75NTR /
nerve growth factor binding / NADE modulates death signalling / Regulated proteolysis of p75NTR /  death-inducing signaling complex /
death-inducing signaling complex /  transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity /
transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity /  tumor necrosis factor receptor binding / TNFR1-induced proapoptotic signaling / RIPK1-mediated regulated necrosis / hair follicle morphogenesis / NRAGE signals death through JNK / intracellular glucose homeostasis / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / Rho protein signal transduction / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway /
tumor necrosis factor receptor binding / TNFR1-induced proapoptotic signaling / RIPK1-mediated regulated necrosis / hair follicle morphogenesis / NRAGE signals death through JNK / intracellular glucose homeostasis / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / Rho protein signal transduction / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway /  coreceptor activity / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / negative regulation of cell migration / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway /
coreceptor activity / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / negative regulation of cell migration / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway /  central nervous system development / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling /
central nervous system development / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / Regulation of TNFR1 signaling /  axon guidance /
axon guidance /  intracellular protein transport / circadian regulation of gene expression /
intracellular protein transport / circadian regulation of gene expression /  neuromuscular junction / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane /
neuromuscular junction / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane /  small GTPase binding /
small GTPase binding /  kinase binding / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / cellular response to amyloid-beta / activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / cell-cell junction / presynapse /
kinase binding / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / cellular response to amyloid-beta / activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / cell-cell junction / presynapse /  glucose homeostasis /
glucose homeostasis /  signaling receptor activity / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity /
signaling receptor activity / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity /  amyloid-beta binding /
amyloid-beta binding /  growth cone / fibroblast proliferation /
growth cone / fibroblast proliferation /  perikaryon / neuron apoptotic process / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction /
perikaryon / neuron apoptotic process / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction /  dendritic spine /
dendritic spine /  postsynaptic density / molecular adaptor activity /
postsynaptic density / molecular adaptor activity /  cytoskeleton /
cytoskeleton /  receptor complex /
receptor complex /  calmodulin binding /
calmodulin binding /  endosome / positive regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of apoptotic process / apoptotic process /
endosome / positive regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of apoptotic process / apoptotic process /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / protein-containing complex binding /
ubiquitin protein ligase binding / protein-containing complex binding /  cell surface /
cell surface /  signal transduction / extracellular region /
signal transduction / extracellular region /  nucleoplasm /
nucleoplasm /  membrane / identical protein binding /
membrane / identical protein binding /  nucleus /
nucleus /  plasma membrane /
plasma membrane /  cytosol /
cytosol /  cytoplasm
cytoplasm
 Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) SOLUTION NMR / torsion angle dynamics
SOLUTION NMR / torsion angle dynamics  Authors
Authors China, 1items
China, 1items  Citation
Citation Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2021
Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 2021 Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 7csq.cif.gz
7csq.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb7csq.ent.gz
pdb7csq.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 7csq.json.gz
7csq.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cs/7csq
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cs/7csq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cs/7csq
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cs/7csq Links
Links Assembly
Assembly
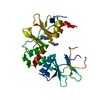
 Components
Components
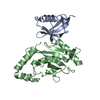
 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NGFR, TNFRSF16 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NGFR, TNFRSF16 / Production host: 
 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P08138
Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P08138
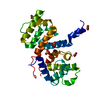
 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRADD / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRADD / Production host: 
 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q15628
Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q15628 SOLUTION NMR
SOLUTION NMR Sample preparation
Sample preparation : AVANCE / Field strength: 800 MHz
: AVANCE / Field strength: 800 MHz Processing
Processing Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj










