+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6o6c | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
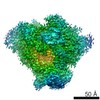
| Title | RNA polymerase II elongation complex arrested at a CPD lesion | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE/DNA/RNA /  RNA polymerase / CPD / elongation complex / streptavidin grids / RNA polymerase / CPD / elongation complex / streptavidin grids /  transcription / transferase-DNA-RNA complex transcription / transferase-DNA-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / : / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes ...RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / : / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / termination of RNA polymerase II transcription / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA-templated transcription / termination of RNA polymerase III transcription / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Dual incision in TC-NER /  RNA polymerase I activity / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / RNA polymerase I activity / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoter / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase III promoter / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I /  RNA polymerase II activity / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / RNA polymerase II activity / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair /  translesion synthesis / translesion synthesis /  RNA polymerase I complex / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA polymerase I complex / transcription by RNA polymerase I /  RNA polymerase III complex / transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase III complex / transcription by RNA polymerase III /  RNA polymerase II, core complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RNA polymerase II, core complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter /  ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cytoplasmic stress granule / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cytoplasmic stress granule /  peroxisome / peroxisome /  ribosome biogenesis / transcription by RNA polymerase II / ribosome biogenesis / transcription by RNA polymerase II /  nucleic acid binding / nucleic acid binding /  protein dimerization activity / protein dimerization activity /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  nucleolus / nucleolus /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  DNA binding / zinc ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lahiri, I. / Leshziner, A.E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2019Title: 3.1 Å structure of yeast RNA polymerase II elongation complex stalled at a cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer lesion solved using streptavidin affinity grids. Authors: Indrajit Lahiri / Jun Xu / Bong Gyoon Han / Juntaek Oh / Dong Wang / Frank DiMaio / Andres E Leschziner /  Abstract: Despite significant advances in all aspects of single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), specimen preparation still remains a challenge. During sample preparation, macromolecules interact ...Despite significant advances in all aspects of single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), specimen preparation still remains a challenge. During sample preparation, macromolecules interact with the air-water interface, which often leads to detrimental effects such as denaturation or adoption of preferred orientations, ultimately hindering structure determination. Randomly biotinylating the protein of interest (for example, at its primary amines) and then tethering it to a cryo-EM grid coated with two-dimensional crystals of streptavidin (acting as an affinity surface) can prevent the protein from interacting with the air-water interface. Recently, this approach was successfully used to solve a high-resolution structure of a test sample, a bacterial ribosome. However, whether this method can be used for samples where interaction with the air-water interface has been shown to be problematic remains to be determined. Here we report a 3.1 Å structure of an RNA polymerase II elongation complex stalled at a cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer lesion (Pol II EC(CPD)) solved using streptavidin grids. Our previous attempt to solve this structure using conventional sample preparation methods resulted in a poor quality cryo-EM map due to Pol II EC(CPD)'s adopting a strong preferred orientation. Imaging the same sample on streptavidin grids improved the angular distribution of its view, resulting in a high-resolution structure. This work shows that streptavidin affinity grids can be used to address known challenges posed by the interaction with the air-water interface. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6o6c.cif.gz 6o6c.cif.gz | 774.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6o6c.ent.gz pdb6o6c.ent.gz | 611.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6o6c.json.gz 6o6c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/6o6c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/6o6c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/6o6c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/6o6c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 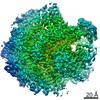 0633MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 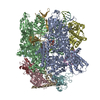
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules ABCGI
| #1: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B1 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase III largest subunit / RNA polymerase II ...RNA polymerase II subunit B1 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase III largest subunit / RNA polymerase II subunit B220 Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B1 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase III largest subunit / RNA polymerase II ...RNA polymerase II subunit B1 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase III largest subunit / RNA polymerase II subunit B220Mass: 191821.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P04050, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P04050,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit 2 / B150 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 140 kDa polypeptide Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit 2 / B150 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 140 kDa polypeptideMass: 138937.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P08518, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P08518,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #3: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B3 / B44.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 45 kDa polypeptide Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B3 / B44.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 45 kDa polypeptideMass: 35330.457 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P16370 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P16370 |
| #7: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / B12.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 14.2 kDa polypeptide / DNA- ...RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / B12.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 14.2 kDa polypeptide / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit 9 Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / B12.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 14.2 kDa polypeptide / DNA- ...RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / B12.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 14.2 kDa polypeptide / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit 9Mass: 14308.161 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P27999 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P27999 |
| #9: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B11 / B13.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 13.6 kDa polypeptide Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B11 / B13.6 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II 13.6 kDa polypeptideMass: 13633.493 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38902 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38902 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules DEFHJ
| #4: Protein |  RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC1 / ABC27 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 27 ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC1 / ABC27 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 27 kDa polypeptide RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC1 / ABC27 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 27 ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC1 / ABC27 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 27 kDa polypeptideMass: 25117.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20434 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20434 |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein |  RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC2 / ABC23 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 23 ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC2 / ABC23 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 23 kDa polypeptide RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC2 / ABC23 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 23 ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC2 / ABC23 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 23 kDa polypeptideMass: 17931.834 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20435 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20435 |
| #6: Protein |  RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC3 / ABC14.4 / ABC14.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC3 / ABC14.4 / ABC14.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 14.5 kDa polypeptide RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC3 / ABC14.4 / ABC14.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC3 / ABC14.4 / ABC14.5 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 14.5 kDa polypeptideMass: 16525.363 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20436 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P20436 |
| #8: Protein |  RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC5 / ABC10-beta / ABC8 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC5 / ABC10-beta / ABC8 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 8.3 kDa polypeptide RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC5 / ABC10-beta / ABC8 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I ...RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC5 / ABC10-beta / ABC8 / DNA-directed RNA polymerases I / and III 8.3 kDa polypeptideMass: 8290.732 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P22139 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P22139 |
| #10: Protein |  RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC4 / ABC10-alpha RNA polymerase / RNA polymerases I / II / and III subunit ABC4 / ABC10-alphaMass: 7729.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P40422 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P40422 |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules K
| #11: RNA chain | Mass: 2934.831 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules LM
| #12: DNA chain | Mass: 5046.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
|---|---|
| #13: DNA chain | Mass: 8376.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 9 molecules 


| #14: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #15: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RNA polymerase II elongation complex stalled at a CPD lesion Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#13 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: The grids had a monolayer of streptavidin crystals on them. Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293.15 K Details: The sample was manually wicked from the grid. 1.2 uL sample buffer was then applied to the streptavidin side. The grid was then blotted. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 6 sec. / Electron dose: 51.7 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 61654 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




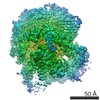
 PDBj
PDBj










































