[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6o22: Structure of Asf1-H3:H4-Rtt109-Vps75 histone chaperone-lysine ace... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6o22 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
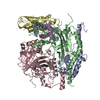
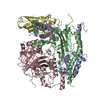
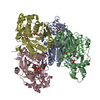
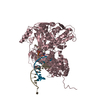
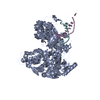
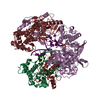
| Title | Structure of Asf1-H3:H4-Rtt109-Vps75 histone chaperone-lysine acetyltransferase complex with the histone substrate. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  CHAPERONE CHAPERONE | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information : / : /  : / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / : / : / histone H3K23 acetyltransferase activity / : / histone H3K56 acetyltransferase activity / : / H3 histone acetyltransferase complex ... : / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / : / : / histone H3K23 acetyltransferase activity / : / histone H3K56 acetyltransferase activity / : / H3 histone acetyltransferase complex ... : / : /  : / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / : / : / histone H3K23 acetyltransferase activity / : / histone H3K56 acetyltransferase activity / : / H3 histone acetyltransferase complex / DNA replication-dependent chromatin disassembly / : / histone H3K14 acetyltransferase activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / histone H3K9 acetyltransferase activity / maintenance of rDNA / acetyltransferase activator activity / peptidyl-lysine acetylation / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / histone H3 acetyltransferase activity / retrotransposon silencing / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / nucleosome disassembly / : / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / peptide-lysine-N-acetyltransferase activity / : / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / : / : / histone H3K23 acetyltransferase activity / : / histone H3K56 acetyltransferase activity / : / H3 histone acetyltransferase complex / DNA replication-dependent chromatin disassembly / : / histone H3K14 acetyltransferase activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / histone H3K9 acetyltransferase activity / maintenance of rDNA / acetyltransferase activator activity / peptidyl-lysine acetylation / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / histone H3 acetyltransferase activity / retrotransposon silencing / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / nucleosome disassembly / : / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / peptide-lysine-N-acetyltransferase activity /  protein acetylation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / protein acetylation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of DNA damage checkpoint /  regulation of DNA repair / regulation of DNA repair /  histone acetyltransferase / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / histone acetyltransferase / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  regulation of protein phosphorylation / regulation of protein phosphorylation /  nucleosome assembly / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome assembly / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / structural constituent of chromatin /  nucleosome / nucleosome /  protein transport / chromatin organization / protein transport / chromatin organization /  histone binding / histone binding /  regulation of gene expression / regulation of gene expression /  chromosome, telomeric region / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA damage response / chromosome, telomeric region / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA damage response /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) | ||||||
| Method |  SOLUTION NMR / SOLUTION NMR /  SOLUTION SCATTERING / SOLUTION SCATTERING /  simulated annealing simulated annealing | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Danilenko, N. / Carlomagno, T. / Kirkpatrick, J.P. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Histone chaperone exploits intrinsic disorder to switch acetylation specificity. Authors: Nataliya Danilenko / Lukas Lercher / John Kirkpatrick / Frank Gabel / Luca Codutti / Teresa Carlomagno /   Abstract: Histones, the principal protein components of chromatin, contain long disordered sequences, which are extensively post-translationally modified. Although histone chaperones are known to control both ...Histones, the principal protein components of chromatin, contain long disordered sequences, which are extensively post-translationally modified. Although histone chaperones are known to control both the activity and specificity of histone-modifying enzymes, the mechanisms promoting modification of highly disordered substrates, such as lysine-acetylation within the N-terminal tail of histone H3, are not understood. Here, to understand how histone chaperones Asf1 and Vps75 together promote H3 K9-acetylation, we establish the solution structural model of the acetyltransferase Rtt109 in complex with Asf1 and Vps75 and the histone dimer H3:H4. We show that Vps75 promotes K9-acetylation by engaging the H3 N-terminal tail in fuzzy electrostatic interactions with its disordered C-terminal domain, thereby confining the H3 tail to a wide central cavity faced by the Rtt109 active site. These fuzzy interactions between disordered domains achieve localization of lysine residues in the H3 tail to the catalytic site with minimal loss of entropy, and may represent a common mechanism of enzymatic reactions involving highly disordered substrates. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6o22.cif.gz 6o22.cif.gz | 411.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6o22.ent.gz pdb6o22.ent.gz | 329.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6o22.json.gz 6o22.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o2/6o22 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o2/6o22 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o2/6o22 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o2/6o22 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 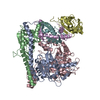
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Vacuole VacuoleMass: 30656.084 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: VPS75, YNL246W, N0890 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P53853 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P53853#2: Protein | | Mass: 50765.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RTT109, KIM2, REM50, YLL002W, L1377 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q07794, Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: Q07794,  histone acetyltransferase histone acetyltransferase#3: Protein | | Mass: 31585.139 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (yeast)Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: ASF1, CIA1, YJL115W, J0755 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P32447 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P32447#4: Protein | | Mass: 15421.101 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P84233#5: Protein | |  Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host: Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: P62799 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details |
|
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj



