[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
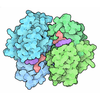
Yorodumi- PDB-6b79: Curved pair of sheets formed from SOD1 residues 28-38 with famili... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6b79 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Curved pair of sheets formed from SOD1 residues 28-38 with familial mutation G37R. | |||||||||
 Components Components | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL /  amyloid fibril amyloid fibril | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationaction potential initiation / neurofilament cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / protein phosphatase 2B binding / regulation of organ growth / relaxation of vascular associated smooth muscle / response to superoxide / anterograde axonal transport /  peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance / regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus ...action potential initiation / neurofilament cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / protein phosphatase 2B binding / regulation of organ growth / relaxation of vascular associated smooth muscle / response to superoxide / anterograde axonal transport / peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance / regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus ...action potential initiation / neurofilament cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / protein phosphatase 2B binding / regulation of organ growth / relaxation of vascular associated smooth muscle / response to superoxide / anterograde axonal transport /  peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance / regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / superoxide anion generation / retina homeostasis / negative regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process / auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization / retrograde axonal transport / peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance / regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / superoxide anion generation / retina homeostasis / negative regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process / auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization / retrograde axonal transport /  regulation of protein kinase activity / myeloid cell homeostasis / muscle cell cellular homeostasis / regulation of protein kinase activity / myeloid cell homeostasis / muscle cell cellular homeostasis /  regulation of GTPase activity / superoxide metabolic process / regulation of GTPase activity / superoxide metabolic process /  heart contraction / heart contraction /  superoxide dismutase / positive regulation of catalytic activity / Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species / transmission of nerve impulse / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / superoxide dismutase / positive regulation of catalytic activity / Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species / transmission of nerve impulse / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process /  superoxide dismutase activity / regulation of multicellular organism growth / response to axon injury / neuronal action potential / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / positive regulation of phagocytosis / ovarian follicle development / axon cytoplasm / glutathione metabolic process / reactive oxygen species metabolic process / superoxide dismutase activity / regulation of multicellular organism growth / response to axon injury / neuronal action potential / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / positive regulation of phagocytosis / ovarian follicle development / axon cytoplasm / glutathione metabolic process / reactive oxygen species metabolic process /  embryo implantation / Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after Interleukin-12 stimulation / dendrite cytoplasm / removal of superoxide radicals / : / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / thymus development / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / locomotory behavior / positive regulation of cytokine production / determination of adult lifespan / placenta development / sensory perception of sound / response to hydrogen peroxide / embryo implantation / Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after Interleukin-12 stimulation / dendrite cytoplasm / removal of superoxide radicals / : / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / thymus development / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / locomotory behavior / positive regulation of cytokine production / determination of adult lifespan / placenta development / sensory perception of sound / response to hydrogen peroxide /  mitochondrial intermembrane space / mitochondrial intermembrane space /  small GTPase binding / small GTPase binding /  regulation of blood pressure / negative regulation of inflammatory response / regulation of blood pressure / negative regulation of inflammatory response /  peroxisome / Platelet degranulation / peroxisome / Platelet degranulation /  gene expression / protein-folding chaperone binding / response to heat / cytoplasmic vesicle / gene expression / protein-folding chaperone binding / response to heat / cytoplasmic vesicle /  spermatogenesis / response to ethanol / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / spermatogenesis / response to ethanol / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process / positive regulation of MAPK cascade /  mitochondrial matrix / response to xenobiotic stimulus / positive regulation of apoptotic process / copper ion binding / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / protein-containing complex / mitochondrial matrix / response to xenobiotic stimulus / positive regulation of apoptotic process / copper ion binding / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / protein-containing complex /  mitochondrion / mitochondrion /  extracellular space / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / extracellular region / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / extracellular region /  nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.8 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.8 Å | |||||||||
| Model details | amyloid-related oligomer | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sangwan, S. / Sawaya, M.R. / Eisenberg, D.S. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Protein Sci. / Year: 2018 Journal: Protein Sci. / Year: 2018Title: Atomic structures of corkscrew-forming segments of SOD1 reveal varied oligomer conformations. Authors: Sangwan, S. / Sawaya, M.R. / Murray, K.A. / Hughes, M.P. / Eisenberg, D.S. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6b79.cif.gz 6b79.cif.gz | 18.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6b79.ent.gz pdb6b79.ent.gz | 9.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6b79.json.gz 6b79.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/6b79 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/6b79 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/6b79 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b7/6b79 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5wmjC  5worC  5dliS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
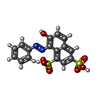
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1394.546 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P00441, Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P00441,  superoxide dismutase superoxide dismutase#2: Chemical | ChemComp-ORA / |  Orange G Orange G#3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water Water |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.12 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 42.06 % |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7.5 Details: HEPES pH 7.5, Sodium citrate, 2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 24-ID-E / Wavelength: 0.9792 Å / Beamline: 24-ID-E / Wavelength: 0.9792 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 315 / Detector: CCD / Date: Apr 3, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.9792 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.9792 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.8→35.73 Å / Num. obs: 2330 / % possible obs: 96.6 % / Observed criterion σ(I): -3 / Redundancy: 3.088 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 28.25 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.981 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.175 / Rrim(I) all: 0.211 / Χ2: 0.889 / Net I/σ(I): 4.06 / Num. measured all: 7194 / Scaling rejects: 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement |
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 5DLI Resolution: 1.8→35.73 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.9087 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.9164 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 0.168 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / SU R Blow DPI: 0.183 / SU Rfree Blow DPI: 0.158 / SU Rfree Cruickshank DPI: 0.151
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 88.55 Å2 / Biso mean: 30.08 Å2 / Biso min: 14.8 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze | Luzzati coordinate error obs: 0.298 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.8→35.73 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 1.8→2.01 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 5
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj