+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5a31 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
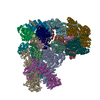
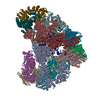
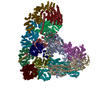
| Title | Structure of the human APC-Cdh1-Hsl1-UbcH10 complex. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  CELL CYCLE / CELL CYCLE /  UBIQUITINATION / UBIQUITINATION /  APC/C APC/C | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of mitotic spindle pole body separation / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / : / deactivation of mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of exit from mitosis / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of synapse maturation ...negative regulation of mitotic spindle pole body separation / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / : / deactivation of mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint / positive regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / positive regulation of exit from mitosis / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of synapse maturation / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins /  anaphase-promoting complex / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / regulation of exit from mitosis / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / anaphase-promoting complex / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / regulation of exit from mitosis / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / Phosphorylation of the APC/C /  anaphase-promoting complex binding / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / exit from mitosis / positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / anaphase-promoting complex binding / ubiquitin ligase activator activity / positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / exit from mitosis / positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity /  E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / cullin family protein binding / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of axon extension / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / cullin family protein binding / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of axon extension /  heterochromatin / heterochromatin /  ubiquitin ligase complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / nuclear periphery / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / ubiquitin ligase complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / nuclear periphery / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes /  cyclin binding / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / cyclin binding / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A /  brain development / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / brain development / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 /  mitotic spindle / spindle / mitotic spindle / spindle /  kinetochore / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / protein polyubiquitination / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / Separation of Sister Chromatids / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / kinetochore / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / protein polyubiquitination / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / Separation of Sister Chromatids / positive regulation of protein catabolic process /  ubiquitin protein ligase activity / microtubule cytoskeleton / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / mitotic cell cycle / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / microtubule cytoskeleton / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / mitotic cell cycle /  nervous system development / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / nervous system development / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) /  protein phosphatase binding / protein phosphatase binding /  cell differentiation / molecular adaptor activity / protein ubiquitination / cell differentiation / molecular adaptor activity / protein ubiquitination /  cell cycle / cell cycle /  cell division / negative regulation of gene expression / cell division / negative regulation of gene expression /  centrosome / centrosome /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding /  nucleolus / zinc ion binding / nucleolus / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
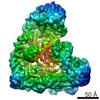
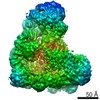
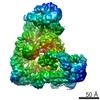
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chang, L. / Zhang, Z. / Yang, J. / Mclaughlin, S.H. / Barford, D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of protein ubiquitination. Authors: Leifu Chang / Ziguo Zhang / Jing Yang / Stephen H McLaughlin / David Barford /  Abstract: The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the ...The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is a multimeric RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Its regulation by coactivator subunits, phosphorylation, the mitotic checkpoint complex and interphase early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) ensures the correct order and timing of distinct cell-cycle transitions. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine atomic structures of APC/C-coactivator complexes with either Emi1 or a UbcH10-ubiquitin conjugate. These structures define the architecture of all APC/C subunits, the position of the catalytic module and explain how Emi1 mediates inhibition of the two E2s UbcH10 and Ube2S. Definition of Cdh1 interactions with the APC/C indicates how they are antagonized by Cdh1 phosphorylation. The structure of the APC/C with UbcH10-ubiquitin reveals insights into the initiating ubiquitination reaction. Our results provide a quantitative framework for the design of future experiments to investigate APC/C functions in vivo. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5a31.cif.gz 5a31.cif.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5a31.ent.gz pdb5a31.ent.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5a31.json.gz 5a31.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a3/5a31 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a3/5a31 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a3/5a31 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a3/5a31 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2925MC  2924C  2926C  4ui9C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
- Components
Components
-ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT ... , 14 types, 17 molecules ABDEFHGWIJKLMNOXY
| #1: Protein |  / APC1 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 1 / MITOTIC CHECKPOINT REGULATOR / TESTIS-SPECIFIC GENE 24 PROTEIN / APC1 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 1 / MITOTIC CHECKPOINT REGULATOR / TESTIS-SPECIFIC GENE 24 PROTEINMass: 159616.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4*PLUS TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4*PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein |  / APC11 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 11 / HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA-ASSOC IATED RING FINGER PROTEIN / APC11 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 11 / HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA-ASSOC IATED RING FINGER PROTEINMass: 9866.702 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| #4: Protein |  / APC15 / APC15Mass: 14302.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 | ||||||||||||||||||
| #5: Protein |  / APC16 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 16 / APC16 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 16Mass: 11677.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| #6: Protein |  / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 27 HOMOLOG / APC3 / CDC27 HOMOLOG / CDC27HS / H-NUC / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 27 HOMOLOG / APC3 / CDC27 HOMOLOG / CDC27HS / H-NUCMass: 92005.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260#7: Protein |  / ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 12 / APC12 / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 26 HOMOLOG / ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 12 / APC12 / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 26 HOMOLOGMass: 9793.999 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8#8: Protein | |  / APC4 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 4 / APC4 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 4Mass: 92205.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5#9: Protein | |  / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 16 HOMOLOG / APC6 / CDC16 HOMOLOG / CDC16HS / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 6 / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 16 HOMOLOG / APC6 / CDC16 HOMOLOG / CDC16HS / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 6Mass: 71631.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042#10: Protein | |  / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 16 HOMOLOG / APC6 / CDC16 HOMOLOG / CDC16HS / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 6 / CELL DIVISION CYCLE PROTEIN 16 HOMOLOG / APC6 / CDC16 HOMOLOG / CDC16HS / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 6Mass: 71806.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042#11: Protein | |  / APC10 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 10 / APC10 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 10Mass: 21282.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13#12: Protein | |  / APC13 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 13 / APC13 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 13Mass: 8528.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q2NKV2, UniProt: Q9BS18*PLUS TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q2NKV2, UniProt: Q9BS18*PLUS#13: Protein | |  / APC2 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 2 / APC2 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 2Mass: 79116.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6*PLUS TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6*PLUS#14: Protein | |  / APC5 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 5 / APC5 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 5Mass: 85087.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4#20: Protein |  / APC7 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 7 / THE ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX / APC7 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 7 / THE ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEXMass: 66832.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 |
-Protein , 2 types, 3 molecules CPQ
| #3: Protein |  Cell cycle / ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 8 / APC8 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 8 / THE ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX Cell cycle / ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX SUBUNIT 8 / APC8 / CYCLOSOME SUBUNIT 8 / THE ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEXMass: 68905.008 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2 TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2#15: Protein | |  / (E3-INDEPENDENT) E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / UBCH10 / ...(E3-INDEPENDENT) E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / UBCH10 / UBIQUITIN CARRIER PROTEIN C / UBIQUITIN-PROTEIN LIGASE C / UBIQUITIN CARRIER PROTEIN S / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME S / UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2-24 KDA / E2-EPF / UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2-EPF5 / UBIQUITIN-PROTEIN LIGASE S / (E3-INDEPENDENT) E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / UBCH10 / ...(E3-INDEPENDENT) E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME C / UBCH10 / UBIQUITIN CARRIER PROTEIN C / UBIQUITIN-PROTEIN LIGASE C / UBIQUITIN CARRIER PROTEIN S / E2 UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME S / UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2-24 KDA / E2-EPF / UBIQUITIN-CONJUGATING ENZYME E2-EPF5 / UBIQUITIN-PROTEIN LIGASE SMass: 17793.396 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: O00762*PLUS,  E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme,  E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
|---|
-THE ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX CHAIN ... , 4 types, 4 molecules RTUV
| #16: Protein | Mass: 42944.512 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P53197*PLUS TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P53197*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #17: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1876.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) |
| #18: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2060.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) |
| #19: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1421.707 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Production host:   TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) TRICHOPLUSIA NI (cabbage looper) |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 3 molecules 
| #21: Chemical |
|---|
-Details
| Sequence details | THE CHAINS A AND N CORRESPOND TO UNIPROT Q9H1A4 AND Q9UJX6 RESPECTIVELY. CHAIN Q RESIDUES 1-179 AND ...THE CHAINS A AND N CORRESPOND |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: HUMAN ANAPHASE-PROMOTING COMPLEX / Type: COMPLEX / Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 / Date: Jul 12, 2014 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 78000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 78000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 16 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Num. of particles: 19939 / Nominal pixel size: 1.36 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.36 Å / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 4.3 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj

















