[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4av2: Single particle electron microscopy of PilQ dodecameric complexes... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4av2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
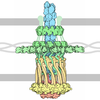
| Title | Single particle electron microscopy of PilQ dodecameric complexes from Neisseria meningitidis. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  PROTEIN TRANSPORT / PROTEIN TRANSPORT /  OUTER MEMBRANE PROTEIN / PILUS BIOGENESIS OUTER MEMBRANE PROTEIN / PILUS BIOGENESIS | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationestablishment of competence for transformation /  protein secretion / cell outer membrane protein secretion / cell outer membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) | ||||||
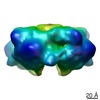
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 26 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 26 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Berry, J.L. / Phelan, M.M. / Collins, R.F. / Adomavicius, T. / Tonjum, T. / Frye, S.A. / Bird, L. / Owens, R. / Ford, R.C. / Lian, L.Y. / Derrick, J.P. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2012 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2012Title: Structure and assembly of a trans-periplasmic channel for type IV pili in Neisseria meningitidis. Authors: Jamie-Lee Berry / Marie M Phelan / Richard F Collins / Tomas Adomavicius / Tone Tønjum / Stefan A Frye / Louise Bird / Ray Owens / Robert C Ford / Lu-Yun Lian / Jeremy P Derrick /  Abstract: Type IV pili are polymeric fibers which protrude from the cell surface and play a critical role in adhesion and invasion by pathogenic bacteria. The secretion of pili across the periplasm and outer ...Type IV pili are polymeric fibers which protrude from the cell surface and play a critical role in adhesion and invasion by pathogenic bacteria. The secretion of pili across the periplasm and outer membrane is mediated by a specialized secretin protein, PilQ, but the way in which this large channel is formed is unknown. Using NMR, we derived the structures of the periplasmic domains from N. meningitidis PilQ: the N-terminus is shown to consist of two β-domains, which are unique to the type IV pilus-dependent secretins. The structure of the second β-domain revealed an eight-stranded β-sandwich structure which is a novel variant of the HSP20-like fold. The central part of PilQ consists of two α/β fold domains: the structure of the first of these is similar to domains from other secretins, but with an additional α-helix which links it to the second α/β domain. We also determined the structure of the entire PilQ dodecamer by cryoelectron microscopy: it forms a cage-like structure, enclosing a cavity which is approximately 55 Å in internal diameter at its largest extent. Specific regions were identified in the density map which corresponded to the individual PilQ domains: this allowed us to dock them into the cryoelectron microscopy density map, and hence reconstruct the entire PilQ assembly which spans the periplasm. We also show that the C-terminal domain from the lipoprotein PilP, which is essential for pilus assembly, binds specifically to the first α/β domain in PilQ and use NMR chemical shift mapping to generate a model for the PilP:PilQ complex. We conclude that passage of the pilus fiber requires disassembly of both the membrane-spanning and the β-domain regions in PilQ, and that PilP plays an important role in stabilising the PilQ assembly during secretion, through its anchorage in the inner membrane. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4av2.cif.gz 4av2.cif.gz | 804.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4av2.ent.gz pdb4av2.ent.gz | 631.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4av2.json.gz 4av2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/4av2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/4av2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/4av2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/av/4av2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2105MC  4aqzC  4ar0C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 80129.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q70M91 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q70M91#2: Protein | Mass: 20087.498 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q7DD77 NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS MC58 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q7DD77 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: OUTER MEMBRANE PROTEIN PILQ FROM NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS Type: COMPLEX / Details: PILQ ISOLATED IN DETERGENT |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 10 MM TRIS-HCL, PH 7.5, 150 MM NACL, 5 MM EDTA, AND 0.1% (W/V) ZWITTERGENT 3-10 pH: 7.5 Details: 10 MM TRIS-HCL, PH 7.5, 150 MM NACL, 5 MM EDTA, AND 0.1% (W/V) ZWITTERGENT 3-10 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: VITRIFICATION 1 -- CRYOGEN- ETHANE, HUMIDITY- 90, TEMPERATURE- 100K, INSTRUMENT- FEI VITROBOT MARK III, METHOD- BOTH SIDES OF THE GRID WERE BRIEFLY BLOTTED DRY WITH WHATMAN NO. 1 FILTER ...Details: VITRIFICATION 1 -- CRYOGEN- ETHANE, HUMIDITY- 90, TEMPERATURE- 100K, INSTRUMENT- FEI VITROBOT MARK III, METHOD- BOTH SIDES OF THE GRID WERE BRIEFLY BLOTTED DRY WITH WHATMAN NO. 1 FILTER PAPER IN A HUMIDITY-CONTROLLED CHAMBER USING A VITROBOT (FEI) DEVICE (90PERCENT RELATIVE HUMIDITY), AND THE GRID WAS THEN PLUNGED INTO LIQUID ETHANE MAINTAINED AT LESS THAN 100K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 / Date: Nov 27, 2007 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 33000 X / Calibrated magnification: 33112 X / Nominal defocus max: 5100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 33000 X / Calibrated magnification: 33112 X / Nominal defocus max: 5100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs : 2 mm : 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 97 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 55 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: EMAN / Category: 3D reconstruction | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Details: CTFFIT EACH MICROGRAPH | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C12 (12 fold cyclic : C12 (12 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Method: EMAN / Resolution: 26 Å / Num. of particles: 25303 / Nominal pixel size: 4.53 Å / Actual pixel size: 4.53 Å / Magnification calibration: 33113 Details: SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-2105. (DEPOSITION ID: 10821). Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL / Details: METHOD--LOCAL CORRELATION | ||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 26 Å | ||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 26 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj