[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
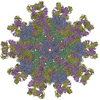
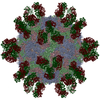
Yorodumi- EMDB-6964: Fit R10 Fab coordinates into the cryo-EM of EV71 in complex with A9 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6964 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Fit R10 Fab coordinates into the cryo-EM of EV71 in complex with A9 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MDA-5 activity /  picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane /  picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell /  viral capsid ...symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MDA-5 activity / viral capsid ...symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MDA-5 activity /  picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane /  picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell /  viral capsid / viral capsid /  : / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / protein complex oligomerization / monoatomic ion channel activity / host cell cytoplasm / : / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / protein complex oligomerization / monoatomic ion channel activity / host cell cytoplasm /  RNA helicase activity / induction by virus of host autophagy / symbiont entry into host cell / RNA helicase activity / induction by virus of host autophagy / symbiont entry into host cell /  RNA-directed RNA polymerase / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral RNA genome replication / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral RNA genome replication / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity /  RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / structural molecule activity / RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / structural molecule activity /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  proteolysis / proteolysis /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |    Enterovirus A71 / Enterovirus A71 /   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang X / Zhu L / Wang N | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2018 Journal: mBio / Year: 2018Title: Neutralization Mechanisms of Two Highly Potent Antibodies against Human Enterovirus 71. Authors: Ling Zhu / Kangwei Xu / Nan Wang / Lei Cao / Junlan Wu / Qiang Gao / Elizabeth E Fry / David I Stuart / Zihe Rao / Junzhi Wang / Xiangxi Wang /   Abstract: Despite significant advances in health care, outbreaks of infections by enteroviruses (EVs) continue to plague the Asia-Pacific region every year. Enterovirus 71 (EV71) causes hand-foot-and-mouth ...Despite significant advances in health care, outbreaks of infections by enteroviruses (EVs) continue to plague the Asia-Pacific region every year. Enterovirus 71 (EV71) causes hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD), for which there are currently no therapeutics. Here, we report two new antibodies, A9 and D6, that potently neutralize EV71. A9 exhibited a 50% neutralizing concentration (neut) value of 0.1 nM against EV71, which was 10-fold lower than that observed for D6. Investigation into the mechanisms of neutralization revealed that binding of A9 to EV71 blocks receptor binding but also destabilizes and damages the virus capsid structure. In contrast, D6 destabilizes the capsid only slightly but interferes more potently with the attachment of the virus to the host cells. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of A9 and D6 bound with EV71 shed light on the locations and nature of the epitopes recognized by the two antibodies. Although some regions of the epitopes recognized by the two antibodies overlap, there are differences that give rise to dissimilarities in potency as well as in the mechanisms of neutralization. Interestingly, the overlapping regions of the epitopes encompass the site that the virus uses to bind SCARB2, explaining the reason for the observed blocking of the virus-receptor interaction by the two antibodies. We also identified structural elements that might play roles in modulating the stability of the EV71 particles, including particle integrity. The molecular features of the A9 and D6 epitopes unveiled in this study open up new avenues for rationally designing antiviral drugs. During the course of viral infections, the human body produces neutralizing antibodies which play a defining role in clearing the virus. From this study, we report two new, highly potent neutralizing antibodies, A9 and D6, against enterovirus 71 (EV71), the causative agent of HFMD. Both antibodies prevent the virus from entering the host cell, a step that is important for establishing a successful infection. A9 destabilizes and damages the virus capsid that forms an outer protective covering around the genome of the virus, while also interfering with virus attachment to the host cells. In contrast, D6 only prevents binding of the virus to its receptor(s). The mechanism of neutralization of A9 is unique and has not been observed before for neutralizing antibodies targeting EVs. The two antibodies that we are reporting in this study have potential to be developed into much-needed therapeutic interventions for treatment of HFMD, outbreaks of which are reported every year in the Asia-Pacific region. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6964.map.gz emd_6964.map.gz | 395.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6964-v30.xml emd-6964-v30.xml emd-6964.xml emd-6964.xml | 15.1 KB 15.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6964.png emd_6964.png | 182.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6964 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6964 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6964 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6964 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5zufMC  6963C  5zudC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6964.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6964.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.35 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of EV71 and A9 neutralizing antibody Fab
| Entire | Name: Complex of EV71 and A9 neutralizing antibody Fab |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of EV71 and A9 neutralizing antibody Fab
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of EV71 and A9 neutralizing antibody Fab / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: EV71
| Supramolecule | Name: EV71 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Enterovirus A71 Enterovirus A71 |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) |
-Supramolecule #3: A9 neutralizing antibody Fab
| Supramolecule | Name: A9 neutralizing antibody Fab / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4-#5 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein VP1
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein VP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Enterovirus A71 Enterovirus A71 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.787902 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) |
| Sequence | String: GDRVADVIES SIEDSSSRAL THALPAPTGQ NTQVSSHRLD TGKVPALQAA EIGASSNASD ESMIETRCVL NSHSTAETTL DSFFSRAGL VGEIDLPLKG TTNPNGYANW DIDITGYAQM RRKVELFTYM RFDAEFTFVA CTPTGEVVPQ LLQYMFVPPG A PKPDSRES ...String: GDRVADVIES SIEDSSSRAL THALPAPTGQ NTQVSSHRLD TGKVPALQAA EIGASSNASD ESMIETRCVL NSHSTAETTL DSFFSRAGL VGEIDLPLKG TTNPNGYANW DIDITGYAQM RRKVELFTYM RFDAEFTFVA CTPTGEVVPQ LLQYMFVPPG A PKPDSRES LAWQTATNPS VFVKLSDPPA QVSVPFMSPA SAYQWFYDGY PTFGEHKQEK DLEYGAMPNN MMGTFSVRTV GT SKSKYPL VVRIYMRMKH VRAWIPRPMR NQNYLFKANP NYAGNSIKPT GASRTAITTL |
-Macromolecule #2: VP2
| Macromolecule | Name: VP2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Enterovirus A71 Enterovirus A71 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.874252 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) |
| Sequence | String: SDRVAQLTIG NSTITTQEAA NIIVGYGEWP SYCSDSDATA VDKPTRPDVS VNRFYTLDTK LWEKSSKGWY WKFPDVLTET GVFGQNAQF HYLYRSGFCI HVQCNASKFH QGALLVAVLP EYVIGTVAGG TGTEDTHPPY KQTQPGADGF ELQHPYVLDA G IPISQLTV ...String: SDRVAQLTIG NSTITTQEAA NIIVGYGEWP SYCSDSDATA VDKPTRPDVS VNRFYTLDTK LWEKSSKGWY WKFPDVLTET GVFGQNAQF HYLYRSGFCI HVQCNASKFH QGALLVAVLP EYVIGTVAGG TGTEDTHPPY KQTQPGADGF ELQHPYVLDA G IPISQLTV CPHQWINLRT NNCATIIVPY INALPFDSAL NHCNFGLLVV PISPLDYDQG ATPVIPITIT LAPMCSEFAG LR QAVTQ |
-Macromolecule #3: VP3
| Macromolecule | Name: VP3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Enterovirus A71 Enterovirus A71 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.468225 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) |
| Sequence | String: GFPTELKPGT NQFLTTDDGV SAPILPNFHP TPCIHIPGEV RNLLELCQVE TILEVNNVPT NATSLMERLR FPVSAQAGKG ELCAVFRAD PGRNGPWQST LLGQLCGYYT QWSGSLEVTF MFTGSFMATG KMLIAYTPPG GPLPKDRATA MLGTHVIWDF G LQSSVTLV ...String: GFPTELKPGT NQFLTTDDGV SAPILPNFHP TPCIHIPGEV RNLLELCQVE TILEVNNVPT NATSLMERLR FPVSAQAGKG ELCAVFRAD PGRNGPWQST LLGQLCGYYT QWSGSLEVTF MFTGSFMATG KMLIAYTPPG GPLPKDRATA MLGTHVIWDF G LQSSVTLV IPWISNTHYR AHARDGVFDY YTTGLVSIWY QTNYVVPIGA PNTAYIIALA AAQKNFTMKL CKDASDILQT GT IQ |
-Macromolecule #4: R10 ANTIBODY LIGHT CHAIN
| Macromolecule | Name: R10 ANTIBODY LIGHT CHAIN / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.283535 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
| Sequence | String: DIVLTQSPAI MSASPGEKVT MTCSASSSVS YIHWYQQKSG TSPKRWIYDT SRLAFGVPGR FSGSGSGTSY SLTISSMEAE DAATYYCQQ WSSNYTFGGG TNLEIKRADA APTVSIFPPS SEQLTSGGAS VVCFLNNFYP KDINVKWKID GSERQNGVLN S WTDQDSKD ...String: DIVLTQSPAI MSASPGEKVT MTCSASSSVS YIHWYQQKSG TSPKRWIYDT SRLAFGVPGR FSGSGSGTSY SLTISSMEAE DAATYYCQQ WSSNYTFGGG TNLEIKRADA APTVSIFPPS SEQLTSGGAS VVCFLNNFYP KDINVKWKID GSERQNGVLN S WTDQDSKD STYSMSSTLT LTKDEYERHN SYTCEATHKT STSPIVKSFN RNEC |
-Macromolecule #5: R10 ANTIBODY HEAVY CHAIN
| Macromolecule | Name: R10 ANTIBODY HEAVY CHAIN / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.67165 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) Mus musculoides (Temminck's mouse) |
| Sequence | String: EVKLVESGGG SVKPGGSLKL SCAASGFSFS TYGMSWVRQT PEKRLEWVAT ISGGGGYTYY PDSVKGRFTI SRDNARNILY LQMSSLRSG DTAMYYCARR VTTVAEYYFD YWGQGTTLTV SSPKTTPPSV YPLAPAAAQT NSMVTLGCLV KGYFPEPVTV T WNSGSLSS ...String: EVKLVESGGG SVKPGGSLKL SCAASGFSFS TYGMSWVRQT PEKRLEWVAT ISGGGGYTYY PDSVKGRFTI SRDNARNILY LQMSSLRSG DTAMYYCARR VTTVAEYYFD YWGQGTTLTV SSPKTTPPSV YPLAPAAAQT NSMVTLGCLV KGYFPEPVTV T WNSGSLSS GVHTFPAVLQ SDLYTLSSSV TVPSSTWPSE TVTCNVAHPA SSTKVDKKIV PR |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 6.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 1100 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller