+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Integrin alpha-v beta-8 in complex with minibinder B8_BP_dsulf | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Complex / Complex /  heterodimer / heterodimer /  signaling / signaling /  TGF-Beta / TGF-Beta /  DE NOVO PROTEIN DE NOVO PROTEIN | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / hard palate development / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / : /  opsonin binding ...ganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / hard palate development / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / : / opsonin binding ...ganglioside metabolic process / Langerhans cell differentiation / integrin alphav-beta6 complex / integrin alphav-beta8 complex / hard palate development / transforming growth factor beta production / negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell / integrin alphav-beta5 complex / : /  opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) / opsonin binding / integrin alphav-beta1 complex / Cross-presentation of particulate exogenous antigens (phagosomes) /  extracellular matrix protein binding / Laminin interactions / placenta blood vessel development / integrin alphav-beta3 complex / negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process / entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole / alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / negative regulation of lipid transport / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity / Elastic fibre formation / extracellular matrix protein binding / Laminin interactions / placenta blood vessel development / integrin alphav-beta3 complex / negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process / entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole / alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / negative regulation of lipid transport / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity / Elastic fibre formation /  regulation of phagocytosis / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex / regulation of phagocytosis / alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex /  transforming growth factor beta binding / filopodium membrane / positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction / transforming growth factor beta binding / filopodium membrane / positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction /  extracellular matrix binding / apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway / extracellular matrix binding / apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway /  wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / apoptotic cell clearance / cartilage development / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion / wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / apoptotic cell clearance / cartilage development / heterotypic cell-cell adhesion /  integrin complex / Molecules associated with elastic fibres / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / microvillus membrane / Syndecan interactions / negative chemotaxis / cell-substrate adhesion / endodermal cell differentiation / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / PECAM1 interactions / lamellipodium membrane / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage / integrin complex / Molecules associated with elastic fibres / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / microvillus membrane / Syndecan interactions / negative chemotaxis / cell-substrate adhesion / endodermal cell differentiation / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / TGF-beta receptor signaling activates SMADs / PECAM1 interactions / lamellipodium membrane / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / negative regulation of lipid storage /  fibronectin binding / positive regulation of cell adhesion / ECM proteoglycans / fibronectin binding / positive regulation of cell adhesion / ECM proteoglycans /  voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity /  vasculogenesis / Integrin cell surface interactions / specific granule membrane / vasculogenesis / Integrin cell surface interactions / specific granule membrane /  coreceptor activity / phagocytic vesicle / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / cell-matrix adhesion / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / coreceptor activity / phagocytic vesicle / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / cell-matrix adhesion / transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway /  protein kinase C binding / Signal transduction by L1 / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / calcium ion transmembrane transport / response to virus / protein kinase C binding / Signal transduction by L1 / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / calcium ion transmembrane transport / response to virus /  cell-cell adhesion / ruffle membrane / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / positive regulation of angiogenesis / cell-cell adhesion / ruffle membrane / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / positive regulation of angiogenesis /  cell migration / cell migration /  integrin binding / virus receptor activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / integrin binding / virus receptor activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration /  angiogenesis / angiogenesis /  protease binding / protease binding /  cell adhesion / positive regulation of cell migration / cell adhesion / positive regulation of cell migration /  immune response / symbiont entry into host cell / external side of plasma membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / immune response / symbiont entry into host cell / external side of plasma membrane / negative regulation of gene expression /  focal adhesion / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / positive regulation of gene expression / focal adhesion / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / positive regulation of gene expression /  cell surface / extracellular exosome / cell surface / extracellular exosome /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Campbell MG / Fernandez A / Roy A / Kraft J / Baker D | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: De novo design of highly selective miniprotein inhibitors of integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8. Authors: Anindya Roy / Lei Shi / Ashley Chang / Xianchi Dong / Andres Fernandez / John C Kraft / Jing Li / Viet Q Le / Rebecca Viazzo Winegar / Gerald Maxwell Cherf / Dean Slocum / P Daniel Poulson / ...Authors: Anindya Roy / Lei Shi / Ashley Chang / Xianchi Dong / Andres Fernandez / John C Kraft / Jing Li / Viet Q Le / Rebecca Viazzo Winegar / Gerald Maxwell Cherf / Dean Slocum / P Daniel Poulson / Garrett E Casper / Mary L Vallecillo-Zúniga / Jonard Corpuz Valdoz / Marcos C Miranda / Hua Bai / Yakov Kipnis / Audrey Olshefsky / Tanu Priya / Lauren Carter / Rashmi Ravichandran / Cameron M Chow / Max R Johnson / Suna Cheng / McKaela Smith / Catherine Overed-Sayer / Donna K Finch / David Lowe / Asim K Bera / Gustavo Matute-Bello / Timothy P Birkland / Frank DiMaio / Ganesh Raghu / Jennifer R Cochran / Lance J Stewart / Melody G Campbell / Pam M Van Ry / Timothy Springer / David Baker /     Abstract: The RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp)-binding integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8 are clinically validated cancer and fibrosis targets of considerable therapeutic importance. Compounds that can discriminate between ...The RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp)-binding integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8 are clinically validated cancer and fibrosis targets of considerable therapeutic importance. Compounds that can discriminate between homologous αvβ6 and αvβ8 and other RGD integrins, stabilize specific conformational states, and have high thermal stability could have considerable therapeutic utility. Existing small molecule and antibody inhibitors do not have all these properties, and hence new approaches are needed. Here we describe a generalized method for computationally designing RGD-containing miniproteins selective for a single RGD integrin heterodimer and conformational state. We design hyperstable, selective αvβ6 and αvβ8 inhibitors that bind with picomolar affinity. CryoEM structures of the designed inhibitor-integrin complexes are very close to the computational design models, and show that the inhibitors stabilize specific conformational states of the αvβ6 and the αvβ8 integrins. In a lung fibrosis mouse model, the αvβ6 inhibitor potently reduced fibrotic burden and improved overall lung mechanics, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of de novo designed integrin binding proteins with high selectivity. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41153.map.gz emd_41153.map.gz | 86 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41153-v30.xml emd-41153-v30.xml emd-41153.xml emd-41153.xml | 24.2 KB 24.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_41153.png emd_41153.png | 82.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41153_additional_1.map.gz emd_41153_additional_1.map.gz emd_41153_additional_2.map.gz emd_41153_additional_2.map.gz emd_41153_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41153_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41153_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41153_half_map_2.map.gz | 84 MB 84 MB 154.5 MB 154.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41153 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41153 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41153 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 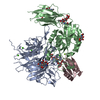 8tcfMC  7lmvC  7lmxC 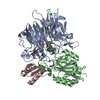 8tcgC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41153.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41153.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.122 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #2
| File | emd_41153_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_41153_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_41153_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_41153_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of integrin heterodimer (alpha-v beta-8) and the ...
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of integrin heterodimer (alpha-v beta-8) and the de novo minibinder protein B8_BP_dslf |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of integrin heterodimer (alpha-v beta-8) and the ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of integrin heterodimer (alpha-v beta-8) and the de novo minibinder protein B8_BP_dslf type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 Details: Integrin expressed in expiCHO cells, minibinder expressed in e. coli |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Integrin alpha-V heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin alpha-V heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.31052 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) |
| Sequence | String: FNLDVDSPAE YSGPEGSYFG FAVDFFVPSA SSRMFLLVGA PKANTTQPGI VEGGQVLKCD WSSTRRCQPI EFDATGNRDY AKDDPLEFK SHQWFGASVR SKQDKILACA PLYHWRTEMK QEREPVGTCF LQDGTKTVEY APCRSQDIDA DGQGFCQGGF S IDFTKADR ...String: FNLDVDSPAE YSGPEGSYFG FAVDFFVPSA SSRMFLLVGA PKANTTQPGI VEGGQVLKCD WSSTRRCQPI EFDATGNRDY AKDDPLEFK SHQWFGASVR SKQDKILACA PLYHWRTEMK QEREPVGTCF LQDGTKTVEY APCRSQDIDA DGQGFCQGGF S IDFTKADR VLLGGPGSFY WQGQLISDQV AEIVSKYDPN VYSIKYNNQL ATRTAQAIFD DSYLGYSVAV GDFNGDGIDD FV SGVPRAA RTLGMVYIYD GKNMSSLYNF TGEQMAAYFG FSVAATDING DDYADVFIGA PLFMDRGSDG KLQEVGQVSV SLQ RASGDF QTTKLNGFEV FARFGSAIAP LGDLDQDGFN DIAIAAPYGG EDKKGIVYIF NGRSTGLNAV PSQILEGQWA ARSG CPPSF GYSMKGATDI DKNGYPDLIV GAFGVDRAIL YRARPVITV UniProtKB:  Integrin alpha-V Integrin alpha-V |
-Macromolecule #2: Integrin beta-8
| Macromolecule | Name: Integrin beta-8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.267992 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) |
| Sequence | String: VHVIIPTENE INTQVTPGEV SIQLRPGAEA NFMLKVHPLK KYPVDLYYLV DVSASMHNNI EKLNSVGNDL SRKMAFFSRD FRLGFGSYV DKTVSPYISI HPERIHNQCS DYNLDCMPPH GYIHVLSLTE NITEFEKAVH RQKISGNIDT PEGGFDAMLQ A AVCESHIG ...String: VHVIIPTENE INTQVTPGEV SIQLRPGAEA NFMLKVHPLK KYPVDLYYLV DVSASMHNNI EKLNSVGNDL SRKMAFFSRD FRLGFGSYV DKTVSPYISI HPERIHNQCS DYNLDCMPPH GYIHVLSLTE NITEFEKAVH RQKISGNIDT PEGGFDAMLQ A AVCESHIG WRKEAKRLLL VMTDQTSHLA LDSKLAGIVC PNDGNCHLKN NVYVKSTTME HPSLGQLSEK LIDNNINVIF AV QGKQFHW YKDLLPLLPG TIAGEIESKA ANLNNLVVEA YQKLISEVKV QVENQVQGIY FNITAICPDG SRKPGMEGCR NVT SNDEVL FNVTVTMKKC DNYAIIKPIG FNETAKIHIH RNC UniProtKB: Integrin beta-8 |
-Macromolecule #3: Minibinder B8_BP_dslf
| Macromolecule | Name: Minibinder B8_BP_dslf / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.582782 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: TKCVVRFNFR GDMAVYALKA VKDHLKKEGP HWNITTHNDD EVYLVVRGIH ESDAKRIAKW VESTIPGISV ETQCD |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #8: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 116587 |
| Details | Movies were collected in super resolution and gain corrected |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z
Z Y
Y X
X

































