[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-34594: Cryo-EM structure of the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12ac... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
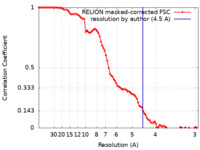
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12acK16ac nucleosome, class 4 (4.5 angstrom resolution) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Acetyl taransferase /  Complex / Complex /  Nucleosome / Nucleosome /  TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex TRANSFERASE / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbehavioral defense response / protein propionyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine propionylation / histone lactyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine crotonylation / peptidyl-lysine butyrylation / histone butyryltransferase activity / histone H3K122 acetyltransferase activity /  swimming / peptide butyryltransferase activity ...behavioral defense response / protein propionyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine propionylation / histone lactyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine crotonylation / peptidyl-lysine butyrylation / histone butyryltransferase activity / histone H3K122 acetyltransferase activity / swimming / peptide butyryltransferase activity ...behavioral defense response / protein propionyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine propionylation / histone lactyltransferase activity / peptidyl-lysine crotonylation / peptidyl-lysine butyrylation / histone butyryltransferase activity / histone H3K122 acetyltransferase activity /  swimming / peptide butyryltransferase activity / histone H2B acetyltransferase activity / swimming / peptide butyryltransferase activity / histone H2B acetyltransferase activity /  thigmotaxis / peptide 2-hydroxyisobutyryltransferase activity / histone crotonyltransferase activity / NOTCH2 intracellular domain regulates transcription / lysine N-acetyltransferase activity, acting on acetyl phosphate as donor / peptidyl-lysine acetylation / histone H4 acetyltransferase activity / histone H3 acetyltransferase activity / cellular response to L-leucine / internal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / NFE2L2 regulating ER-stress associated genes / peptide N-acetyltransferase activity / STAT3 nuclear events downstream of ALK signaling / acetylation-dependent protein binding / Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / NFE2L2 regulating inflammation associated genes / NGF-stimulated transcription / Polo-like kinase mediated events / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / NFE2L2 regulates pentose phosphate pathway genes / regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / NFE2L2 regulating MDR associated enzymes / positive regulation by host of viral transcription / regulation of mitochondrion organization / face morphogenesis / thigmotaxis / peptide 2-hydroxyisobutyryltransferase activity / histone crotonyltransferase activity / NOTCH2 intracellular domain regulates transcription / lysine N-acetyltransferase activity, acting on acetyl phosphate as donor / peptidyl-lysine acetylation / histone H4 acetyltransferase activity / histone H3 acetyltransferase activity / cellular response to L-leucine / internal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / NFE2L2 regulating ER-stress associated genes / peptide N-acetyltransferase activity / STAT3 nuclear events downstream of ALK signaling / acetylation-dependent protein binding / Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / NFE2L2 regulating inflammation associated genes / NGF-stimulated transcription / Polo-like kinase mediated events / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / NFE2L2 regulates pentose phosphate pathway genes / regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / NFE2L2 regulating MDR associated enzymes / positive regulation by host of viral transcription / regulation of mitochondrion organization / face morphogenesis /  Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Regulation of NFE2L2 gene expression / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / regulation of glycolytic process / platelet formation / nuclear androgen receptor binding / NFE2L2 regulating anti-oxidant/detoxification enzymes / megakaryocyte development / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / regulation of tubulin deacetylation / macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / peptide-lysine-N-acetyltransferase activity / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell death genes / NFE2L2 regulating tumorigenic genes / internal protein amino acid acetylation / STAT family protein binding / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Regulation of NFE2L2 gene expression / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / regulation of glycolytic process / platelet formation / nuclear androgen receptor binding / NFE2L2 regulating anti-oxidant/detoxification enzymes / megakaryocyte development / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / regulation of tubulin deacetylation / macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / peptide-lysine-N-acetyltransferase activity / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell death genes / NFE2L2 regulating tumorigenic genes / internal protein amino acid acetylation / STAT family protein binding /  acyltransferase activity / fat cell differentiation / acyltransferase activity / fat cell differentiation /  protein acetylation / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway / protein acetylation / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway /  acetyltransferase activity / cellular response to nutrient levels / RUNX3 regulates p14-ARF / acetyltransferase activity / cellular response to nutrient levels / RUNX3 regulates p14-ARF /  NF-kappaB binding / NF-kappaB binding /  histone acetyltransferase complex / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Attenuation phase / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / histone acetyltransferase complex / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Attenuation phase / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome /  somitogenesis / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / pre-mRNA intronic binding / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of cellular response to heat / skeletal muscle tissue development / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / somitogenesis / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / pre-mRNA intronic binding / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of cellular response to heat / skeletal muscle tissue development / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways /  histone acetyltransferase activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / histone acetyltransferase activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere /  histone acetyltransferase / histone acetyltransferase /  Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidineSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kikuchi M / Morita S / Wakamori M / Shin S / Uchikubo-Kamo T / Shirouzu M / Umehara T | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 1 items Japan, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Epigenetic mechanisms to propagate histone acetylation by p300/CBP. Authors: Masaki Kikuchi / Satoshi Morita / Masatoshi Wakamori / Shin Sato / Tomomi Uchikubo-Kamo / Takehiro Suzuki / Naoshi Dohmae / Mikako Shirouzu / Takashi Umehara /  Abstract: Histone acetylation is important for the activation of gene transcription but little is known about its direct read/write mechanisms. Here, we report cryogenic electron microscopy structures in which ...Histone acetylation is important for the activation of gene transcription but little is known about its direct read/write mechanisms. Here, we report cryogenic electron microscopy structures in which a p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) multidomain monomer recognizes histone H4 N-terminal tail (NT) acetylation (ac) in a nucleosome and acetylates non-H4 histone NTs within the same nucleosome. p300/CBP not only recognized H4NTac via the bromodomain pocket responsible for reading, but also interacted with the DNA minor grooves via the outside of that pocket. This directed the catalytic center of p300/CBP to one of the non-H4 histone NTs. The primary target that p300 writes by reading H4NTac was H2BNT, and H2BNTac promoted H2A-H2B dissociation from the nucleosome. We propose a model in which p300/CBP replicates histone N-terminal tail acetylation within the H3-H4 tetramer to inherit epigenetic storage, and transcribes it from the H3-H4 tetramer to the H2B-H2A dimers to activate context-dependent gene transcription through local nucleosome destabilization. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34594.map.gz emd_34594.map.gz | 55.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34594-v30.xml emd-34594-v30.xml emd-34594.xml emd-34594.xml | 20 KB 20 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
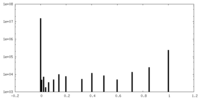
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_34594_fsc.xml emd_34594_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_34594.png emd_34594.png | 74.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_34594_msk_1.map emd_34594_msk_1.map | 59.6 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_34594_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34594_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34594_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34594_half_map_2.map.gz | 46.2 MB 46.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34594 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34594 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34594 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34594 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8hakMC  8hagC  8hahC  8haiC  8hajC  8halC  8hamC  8hanC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34594.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34594.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 59.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.47 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
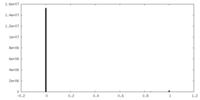
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_34594_msk_1.map emd_34594_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
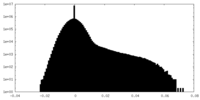
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_34594_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_34594_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12acK16ac nucleosome
| Entire | Name: the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12acK16ac nucleosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12acK16ac nucleosome
| Supramolecule | Name: the p300 catalytic core bound to the H4K12acK16ac nucleosome type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 / Details: p300 was expressed in insect cells. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.305969 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: ARTKQTARKS TGGKAPRKQL ATKAARKSAP ATGGVKKPHR YRPGTVALRE IRRYQKSTEL LIRKLPFQRL VREIAQDFKT DLRFQSSAV MALQEACEAY LVGLFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA UniProtKB:  Histone H3.1 Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.345289 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKGGKGL G(ALY)GGA(ALY)RHRK VLRDNIQGIT KPAIRRLARR GGVKRISGLI YEETRGVLKV FLENVIRDAV TY TEHAKRK TVTAMDVVYA LKRQGRTLYG FGG |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.034355 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKQGGKA RAKAKTRSSR AGLQFPVGRV HRLLRKGNYS ERVGAGAPVY LAAVLEYLTA EILELAGNAA RDNKKTRIIP RHLQLAIRN DEELNKLLGR VTIAQGGVLP NIQAVLLPKK TESHHKAKGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-J / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.804045 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: PEPAKSAPAP KKGSKKAVTK AQKKDGKKRK RSRKESYSIY VYKVLKQVHP DTGISSKAMG IMNSFVNDIF ERIAGEASRL AHYNKRSTI TSREIQTAVR LLLPGELAKH AVSEGTKAVT KYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-J |
-Macromolecule #6: Histone acetyltransferase p300
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone acetyltransferase p300 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  histone acetyltransferase histone acetyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 92.314391 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: GSSGSSGIFK PEELRQALMP TLEALYRQDP ESLPFRQPVD PQLLGIPDYF DIVKSPMDLS TIKRKLDTGQ YQEPWQYVDD IWLMFNNAW LYNRKTSRVY KYCSKLSEVF EQEIDPVMQS LGYCCGRKLE FSPQTLCCYG KQLCTIPRDA TYYSYQNRYH F CEKCFNEI ...String: GSSGSSGIFK PEELRQALMP TLEALYRQDP ESLPFRQPVD PQLLGIPDYF DIVKSPMDLS TIKRKLDTGQ YQEPWQYVDD IWLMFNNAW LYNRKTSRVY KYCSKLSEVF EQEIDPVMQS LGYCCGRKLE FSPQTLCCYG KQLCTIPRDA TYYSYQNRYH F CEKCFNEI QGESVSLGDD PSQPQTTINK EQFSKRKNDT LDPELFVECT ECGRKMHQIC VLHHEIIWPA GFVCDGCLKK SA RTRKENK FSAKRLPSTR LGTFLENRVN DFLRRQNHPE SGEVTVRVVH ASDKTVEVKP GMKARFVDSG EMAESFPYRT KAL FAFEEI DGVDLCFFGM HVQEYGSDCP PPNQRRVYIS YLDSVHFFRP KCLRTAVYHE ILIGYLEYVK KLGYTTGHIW ACPP SEGDD YIFHCHPPDQ KIPKPKRLQE WYKKMLDKAV SERIVHDYKD IFKQATEDRL TSAKELPYFE GDFWPNVLEE SIKEL EQEE EERKREENTS NESTDVTKGD SKNAKKKNNK KTSKNKSSLS RGNKKKPGMP NVSNDLSQKL YATMEKHKEV FFVIRL IAG PAANSLPPIV DPDPLIPCDL MDGRDAFLTL ARDKHLEFSS LRRAQWSTMC MLVELHTQSQ DRFVYTCNEC KHHVETR WH CTVCEDYDLC ITCYNTKNHD HKMEKLGLGL DDESNNQQAA ATQSPGDSRR LSIQRCIQSL VHACQCRNAN CSLPSCQK M KRVVQHTKGC KRKTNGGCPI CKQLIALCCY HAKHCQENKC PVPFCLNIKQ KLRQQQLQHR LQQAQMLRRR MASMQ UniProtKB: Histone acetyltransferase p300 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (180-mer)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (180-mer) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.560527 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DT) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DT) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DA)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DG)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DG)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







































 Z
Z Y
Y X
X