[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-32002: Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 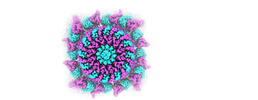 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by SPFH family proteins | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information regulation of peptidase activity / regulation of peptidase activity /  Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein catabolic process / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein catabolic process /  metalloendopeptidase activity / metalloendopeptidase activity /  peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 /  cell division / cell division /  ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding ... ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding ... regulation of peptidase activity / regulation of peptidase activity /  Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein catabolic process / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein catabolic process /  metalloendopeptidase activity / metalloendopeptidase activity /  peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 / peptidase activity / membrane => GO:0016020 /  cell division / cell division /  ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.27 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.27 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma CY / Wang CK / Luo DY / Yan L / Yang WX / Li NN / Gao N | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into the membrane microdomain organization by SPFH family proteins. Authors: Chengying Ma / Chengkun Wang / Dingyi Luo / Lu Yan / Wenxian Yang / Ningning Li / Ning Gao /  Abstract: The lateral segregation of membrane constituents into functional microdomains, conceptually known as lipid raft, is a universal organization principle for cellular membranes in both prokaryotes and ...The lateral segregation of membrane constituents into functional microdomains, conceptually known as lipid raft, is a universal organization principle for cellular membranes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The widespread Stomatin, Prohibitin, Flotillin, and HflK/C (SPFH) family proteins are enriched in functional membrane microdomains at various subcellular locations, and therefore were hypothesized to play a scaffolding role in microdomain formation. In addition, many SPFH proteins are also implicated in highly specific processes occurring on the membrane. However, none of these functions is understood at the molecular level. Here we report the structure of a supramolecular complex that is isolated from bacterial membrane microdomains and contains two SPFH proteins (HflK and HflC) and a membrane-anchored AAA+ protease FtsH. HflK and HflC form a circular 24-mer assembly, featuring a laterally segregated membrane microdomain (20 nm in diameter) bordered by transmembrane domains of HflK/C and a completely sealed periplasmic vault. Four FtsH hexamers are embedded inside this microdomain through interactions with the inner surface of the vault. These observations provide a mechanistic explanation for the role of HflK/C and their mitochondrial homologs prohibitins in regulating membrane-bound AAA+ proteases, and suggest a general model for the organization and functionalization of membrane microdomains by SPFH proteins. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32002.map.gz emd_32002.map.gz | 8.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32002-v30.xml emd-32002-v30.xml emd-32002.xml emd-32002.xml | 12.3 KB 12.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_32002.png emd_32002.png | 43.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32002 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32002 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32002 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32002 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vhpMC  7vhqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32002.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32002.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.057 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : KCF complex
| Entire | Name: KCF complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: KCF complex
| Supramolecule | Name: KCF complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease FtsH
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease FtsH / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 24 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number:  Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Metalloendopeptidases |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 70.797031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MAKNLILWLV IAVVLMSVFQ SFGPSESNGR KVDYSTFLQE VNNDQVREAR INGREINVTK KDSNRYTTYI PVQDPKLLDN LLTKNVKVV GEPPEEPSLL ASIFISWFPM LLLIGVWIFF MRQMQGGGGK GAMSFGKSKA RMLTEDQIKT TFADVAGCDE A KEEVAELV ...String: MAKNLILWLV IAVVLMSVFQ SFGPSESNGR KVDYSTFLQE VNNDQVREAR INGREINVTK KDSNRYTTYI PVQDPKLLDN LLTKNVKVV GEPPEEPSLL ASIFISWFPM LLLIGVWIFF MRQMQGGGGK GAMSFGKSKA RMLTEDQIKT TFADVAGCDE A KEEVAELV EYLREPSRFQ KLGGKIPKGV LMVGPPGTGK TLLAKAIAGE AKVPFFTISG SDFVEMFVGV GASRVRDMFE QA KKAAPCI IFIDEIDAVG RQRGAGLGGG HDEREQTLNQ MLVEMDGFEG NEGIIVIAAT NRPDVLDPAL LRPGRFDRQV VVG LPDVRG REQILKVHMR RVPLAPDIDA AIIARGTPGF SGADLANLVN EAALFAARGN KRVVSMVEFE KAKDKIMMGA ERRS MVMTE AQKESTAYHE AGHAIIGRLV PEHDPVHKVT IIPRGRALGV TFFLPEGDAI SASRQKLESQ ISTLYGGRLA EEIIY GPEH VSTGASNDIK VATNLARNMV TQWGFSEKLG PLLYAEEEGE VFLGRSVAKA KHMSDETARI IDQEVKALIE RNYNRA RQL LTDNMDILHA MKDALMKYET IDAPQIDDLM ARRDVRPPAG WEEPGASNNS GDNGSPKAPR PVDEPRTPNP GNTMSEQ LG DK |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein HflK
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein HflK / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.598793 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MAWNQPGNNG QDRDPWGSSK PGGNSEGNGN KGGRDQGPPD LDDIFRKLSK KLGGLGGGKG TGSGGGSSSQ GPRPQLGGRV VTIAAAAIV IIWAASGFYT IKEAERGVVT RFGKFSHLVE PGLNWKPTFI DEVKPVNVEA VRELAASGVM LTSDENVVRV E MNVQYRVT ...String: MAWNQPGNNG QDRDPWGSSK PGGNSEGNGN KGGRDQGPPD LDDIFRKLSK KLGGLGGGKG TGSGGGSSSQ GPRPQLGGRV VTIAAAAIV IIWAASGFYT IKEAERGVVT RFGKFSHLVE PGLNWKPTFI DEVKPVNVEA VRELAASGVM LTSDENVVRV E MNVQYRVT NPEKYLYSVT SPDDSLRQAT DSALRGVIGK YTMDRILTEG RTVIRSDTQR ELEETIRPYD MGITLLDVNF QA ARPPEEV KAAFDDAIAA RENEQQYIRE AEAYTNEVQP RANGQAQRIL EEARAYKAQT ILEAQGEVAR FAKLLPEYKA APE ITRERL YIETMEKVLG NTRKVLVNDK GGNLMVLPLD QMLKGGNAPA AKSDNGASNL LRLPPASSST TSGASNTSST SQGD IMDQR RANAQRNDYQ RQGE |
-Macromolecule #3: Modulator of FtsH protease HflC
| Macromolecule | Name: Modulator of FtsH protease HflC / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.703887 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MRKSVIAIII IVLVVLYMSV FVVKEGERGI TLRFGKVLRD DDNKPLVYEP GLHFKIPFIE TVKMLDARIQ TMDNQADRFV TKEKKDLIV DSYIKWRISD FSRYYLATGG GDISQAEVLL KRKFSDRLRS EIGRLDVKDI VTDSRGRLTL EVRDALNSGS A GTEDEVTT ...String: MRKSVIAIII IVLVVLYMSV FVVKEGERGI TLRFGKVLRD DDNKPLVYEP GLHFKIPFIE TVKMLDARIQ TMDNQADRFV TKEKKDLIV DSYIKWRISD FSRYYLATGG GDISQAEVLL KRKFSDRLRS EIGRLDVKDI VTDSRGRLTL EVRDALNSGS A GTEDEVTT PAADNAIAEA AERVTAETKG KVPVINPNSM AALGIEVVDV RIKQINLPTE VSEAIYNRMR AEREAVARRH RS QGQEEAE KLRATADYEV TRTLAEAERQ GRIMRGEGDA EAAKLFADAF SKDPDFYAFI RSLRAYENSF SGNQDVMVMS PDS DFFRYM KTPTSATR |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.27 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 84693 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








