[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-31925: The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nu... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
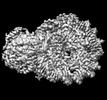
| Title | The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nucleosome complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nucleosome complex | |||||||||
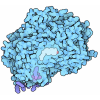
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / bBAF complex / npBAF complex /  nBAF complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / neural retina development / GBAF complex / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Tat protein binding ...positive regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / bBAF complex / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / neural retina development / GBAF complex / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Tat protein binding ...positive regulation of glucose mediated signaling pathway / bBAF complex / npBAF complex /  nBAF complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / neural retina development / GBAF complex / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Tat protein binding / EGR2 and SOX10-mediated initiation of Schwann cell myelination / nucleosome disassembly / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation by host of viral transcription / nBAF complex / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway / neural retina development / GBAF complex / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Tat protein binding / EGR2 and SOX10-mediated initiation of Schwann cell myelination / nucleosome disassembly / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / positive regulation by host of viral transcription /  SWI/SNF complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / nuclear androgen receptor binding / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / Chromatin modifying enzymes / SWI/SNF complex / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / nuclear androgen receptor binding / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / Chromatin modifying enzymes /  DNA polymerase binding / transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling / Interleukin-7 signaling / DNA polymerase binding / transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling / Interleukin-7 signaling /  helicase activity / helicase activity /  transcription coregulator binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / transcription coregulator binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / lysine-acetylated histone binding / negative regulation of cell growth / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / lysine-acetylated histone binding / negative regulation of cell growth /  kinetochore / kinetochore /  fibrillar center / RMTs methylate histone arginines / fibrillar center / RMTs methylate histone arginines /  nuclear matrix / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / nuclear matrix / positive regulation of miRNA transcription / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity /  nucleosome / nucleosome /  p53 binding / p53 binding /  nervous system development / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / nervous system development / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis /  transcription coactivator activity / transcription coactivator activity /  hydrolase activity / hydrolase activity /  chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of cell population proliferation /  chromatin / chromatin /  nucleolus / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / nucleolus / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  extracellular space / extracellular space /  RNA binding / RNA binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / membrane /  nucleus nucleusSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / synthetic construct (others) Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen ZC / Chen KJ / Yuan JJ | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structure of human chromatin-remodelling PBAF complex bound to a nucleosome. Authors: Junjie Yuan / Kangjing Chen / Wenbo Zhang / Zhucheng Chen /  Abstract: DNA wraps around the histone octamer to form nucleosomes, the repeating unit of chromatin, which create barriers for accessing genetic information. Snf2-like chromatin remodellers couple the energy ...DNA wraps around the histone octamer to form nucleosomes, the repeating unit of chromatin, which create barriers for accessing genetic information. Snf2-like chromatin remodellers couple the energy of ATP binding and hydrolysis to reposition and recompose the nucleosome, and have vital roles in various chromatin-based transactions. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the 12-subunit human chromatin-remodelling polybromo-associated BRG1-associated factor (PBAF) complex bound to the nucleosome. The motor subunit SMARCA4 engages the nucleosome in the active conformation, which reveals clustering of multiple disease-associated mutations at the interfaces that are essential for chromatin-remodelling activity. SMARCA4 recognizes the H2A-H2B acidic pocket of the nucleosome through three arginine anchors of the Snf2 ATP coupling (SnAc) domain. PBAF shows notable functional modularity, and most of the auxiliary subunits are interwoven into three lobe-like submodules for nucleosome recognition. The PBAF-specific auxiliary subunit ARID2 acts as the structural core for assembly of the DNA-binding lobe, whereas PBRM1, PHF10 and BRD7 are collectively incorporated into the lobe for histone tail binding. Together, our findings provide mechanistic insights into nucleosome recognition by PBAF and a structural basis for understanding SMARCA4-related human diseases. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_31925.map.gz emd_31925.map.gz | 9.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-31925-v30.xml emd-31925-v30.xml emd-31925.xml emd-31925.xml | 18.8 KB 18.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_31925.png emd_31925.png | 111 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31925 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31925 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31925 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vdtMC 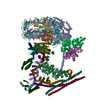 7vdvC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_31925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_31925.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nucleosome complex | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nu...
+Supramolecule #1: The motor-nucleosome module of human chromatin remodeling PBAF-nu...
+Macromolecule #1: Isoform 2 of Transcription activator BRG1
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B 1.1
+Macromolecule #5: Histone H3
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (207-MER)
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (207-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
+Macromolecule #9: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #10: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 208905 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller