[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-22371: Cryo-EM structure of RIG-I:dsRNA filament in complex with RIPLET ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22371 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of RIG-I:dsRNA filament in complex with RIPLET PrySpry domain (trimer) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Innate immunity / Innate immunity /  E3 ligase / E3 ligase /  helicase / antiviral signaling / RLR / dsRNA sensor / HYDROLASE-TRANSFERASE-RNA complex helicase / antiviral signaling / RLR / dsRNA sensor / HYDROLASE-TRANSFERASE-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRIG-I binding / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / regulation of type III interferon production / RIG-I signaling pathway / positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production / OAS antiviral response / detection of virus / NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10 / positive regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production ...RIG-I binding / free ubiquitin chain polymerization / regulation of type III interferon production / RIG-I signaling pathway / positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production / OAS antiviral response / detection of virus / NF-kB activation through FADD/RIP-1 pathway mediated by caspase-8 and -10 / positive regulation of response to cytokine stimulus / positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production /  pattern recognition receptor activity / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / pattern recognition receptor activity / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation /  regulation of innate immune response / cellular response to exogenous dsRNA / response to exogenous dsRNA / cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / antiviral innate immune response / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / bicellular tight junction / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / regulation of innate immune response / cellular response to exogenous dsRNA / response to exogenous dsRNA / cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / antiviral innate immune response / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / bicellular tight junction / ribonucleoprotein complex binding /  regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / response to virus / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / protein homooligomerization / ISG15 antiviral mechanism / ruffle membrane / cytoplasmic stress granule / protein polyubiquitination / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / SARS-CoV-1 activates/modulates innate immune responses / regulation of cell migration / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / Negative regulators of DDX58/IFIH1 signaling / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / response to virus / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / DDX58/IFIH1-mediated induction of interferon-alpha/beta / protein homooligomerization / ISG15 antiviral mechanism / ruffle membrane / cytoplasmic stress granule / protein polyubiquitination / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / SARS-CoV-1 activates/modulates innate immune responses /  ubiquitin protein ligase activity / positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity / Ovarian tumor domain proteases /  actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / actin cytoskeleton / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production /  double-stranded RNA binding / double-stranded RNA binding /  gene expression / TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway / gene expression / TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway /  double-stranded DNA binding / defense response to virus / double-stranded DNA binding / defense response to virus /  RNA helicase activity / RNA helicase activity /  single-stranded RNA binding / protein ubiquitination / Ub-specific processing proteases / single-stranded RNA binding / protein ubiquitination / Ub-specific processing proteases /  RNA helicase / RNA helicase /  ribonucleoprotein complex / ribonucleoprotein complex /  innate immune response / innate immune response /  ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / GTP binding / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / GTP binding / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses /  ATP hydrolysis activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / zinc ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / zinc ion binding /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kato K / Ahmad S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural analysis of RIG-I-like receptors reveals ancient rules of engagement between diverse RNA helicases and TRIM ubiquitin ligases. Authors: Kazuki Kato / Sadeem Ahmad / Zixiang Zhu / Janet M Young / Xin Mu / Sehoon Park / Harmit S Malik / Sun Hur /   Abstract: RNA helicases and E3 ubiquitin ligases mediate many critical functions in cells, but their actions have largely been studied in distinct biological contexts. Here, we uncover evolutionarily conserved ...RNA helicases and E3 ubiquitin ligases mediate many critical functions in cells, but their actions have largely been studied in distinct biological contexts. Here, we uncover evolutionarily conserved rules of engagement between RNA helicases and tripartite motif (TRIM) E3 ligases that lead to their functional coordination in vertebrate innate immunity. Using cryoelectron microscopy and biochemistry, we show that RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), viral RNA receptors with helicase domains, interact with their cognate TRIM/TRIM-like E3 ligases through similar epitopes in the helicase domains. Their interactions are avidity driven, restricting the actions of TRIM/TRIM-like proteins and consequent immune activation to RLR multimers. Mass spectrometry and phylogeny-guided biochemical analyses further reveal that similar rules of engagement may apply to diverse RNA helicases and TRIM/TRIM-like proteins. Our analyses suggest not only conserved substrates for TRIM proteins but also, unexpectedly, deep evolutionary connections between TRIM proteins and RNA helicases, linking ubiquitin and RNA biology throughout animal evolution. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22371.map.gz emd_22371.map.gz | 8.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22371-v30.xml emd-22371-v30.xml emd-22371.xml emd-22371.xml | 14.8 KB 14.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22371.png emd_22371.png | 220.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22371.cif.gz emd-22371.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22371 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22371 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22371 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22371 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7jl3MC  7jl0C  7jl1C  7jl2C  7jl4C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22371.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 115.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22371.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 115.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04203 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of dsRNA-bound RIG-I filament with RIPLET PrySpry...
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of dsRNA-bound RIG-I filament with RIPLET PrySpry domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of dsRNA-bound RIG-I filament with RIPLET PrySpry...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of dsRNA-bound RIG-I filament with RIPLET PrySpry domain type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Antiviral innate immune response receptor RIG-I
| Macromolecule | Name: Antiviral innate immune response receptor RIG-I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number:  RNA helicase RNA helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 82.72407 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: METSDIQIFY QEDPECQNLS ENSCPPSEVS DTNLYSPFKP RNYQLELALP AMKGKNTIIC APTGCGKTFV SLLICEHHLK KFPQGQKGK VVFFANQIPV YEQQKSVFSK YFERHGYRVT GISGATAENV PVEQIVENND IIILTPQILV NNLKKGTIPS L SIFTLMIF ...String: METSDIQIFY QEDPECQNLS ENSCPPSEVS DTNLYSPFKP RNYQLELALP AMKGKNTIIC APTGCGKTFV SLLICEHHLK KFPQGQKGK VVFFANQIPV YEQQKSVFSK YFERHGYRVT GISGATAENV PVEQIVENND IIILTPQILV NNLKKGTIPS L SIFTLMIF DECHNTSKQH PYNMIMFNYL DQKLGGSSGP LPQVIGLTAS VGVGDAKNTD EALDYICKLC ASLDASVIAT VK HNLEELE QVVYKPQKFF RKVESRISDK FKYIIAQLMR DTESLAKRIC KDLENLSQIQ NREFGTQKYE QWIVTVQKAC MVF QMPDKD EESRICKALF LYTSHLRKYN DALIISEHAR MKDALDYLKD FFSNVRAAGF DEIEQDLTQR FEEKLQELES VSRD PSNEN PKLEDLCFIL QEEYHLNPET ITILFVKTRA LVDALKNWIE GNPKLSFLKP GILTGRGKTN QNTGMTLPAQ KCILD AFKA SGDHNILIAT SVADEGIDIA QCNLVILYEY VGNVIKMIQT RGRGRARGSK CFLLTSNAGV IEKEQINMYK EKMMND SIL RLQTWDEAVF REKILHIQTH EKFIRDSQEK PKPVPDKENK KLLCRKCKAL ACYTADVRVI EECHYTVLGD AFKECFV SR PHPKPKQFSS FEKRAKIFCA RQNCSHDWGI HVKYKTFEIP VIKIESFVVE DIATGVQTLY SKWKDFHFEK IPFDPAEM S K UniProtKB: Antiviral innate immune response receptor RIG-I |
-Macromolecule #2: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF135
| Macromolecule | Name: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF135 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 21.021904 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: RRASRFAQWA IHPTFNLKSL SCSLEVSKDS RTVTVSHRPQ PYRWSCERFS TSQVLCSQAL SSGKHYWEVD TRNCSHWAVG VASWEMSRD QVLGRTMDSC CVEWKGTSQL SAWHMVKETV LGSDRPGVVG IWLNLEEGKL AFYSVDNQEK LLYECTISAS S PLYPAFWL YGLHPGNYLI IKQVKV UniProtKB: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF135 |
-Macromolecule #3: dsRNA strand1
| Macromolecule | Name: dsRNA strand1 / type: rna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.550107 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GACUGACUGA CUGAGACUGA CUGACUGAGA CUGACUGACU GA |
-Macromolecule #4: dsRNA strand 2
| Macromolecule | Name: dsRNA strand 2 / type: rna / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.360916 KDa |
| Sequence | String: UCAGUCAGUC AGUCUCAGUC AGUCAGUCUC AGUCAGUCAG UC |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #6: TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ALF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 102.975 Da |
| Chemical component information | 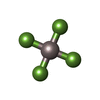 ChemComp-ALF: |
-Macromolecule #7: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 19.424 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Featureless cylinder |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 46.2706 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 76.1005 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 39718 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller