+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20967 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
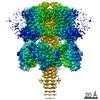
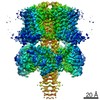
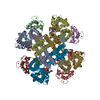
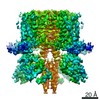
| Title | structure of human KCNQ1-KCNE3-CaM complex with PIP2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | KCNQ1-KCNE3-CaM complex with PIP2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  potassium channel / potassium channel /  KCNQ1 / CaM / KCNQ1 / CaM /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / negative regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / regulation of gastric acid secretion ...negative regulation of membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / negative regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane / gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / regulation of gastric acid secretion / stomach development / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / membrane repolarization during action potential / iodide transport / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / Phase 2 - plateau phase / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / renal sodium ion absorption / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / auditory receptor cell development / regulation of membrane repolarization /  protein phosphatase 1 binding / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / Voltage gated Potassium channels / potassium ion homeostasis / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / non-motile cilium assembly / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / protein phosphatase 1 binding / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / Voltage gated Potassium channels / potassium ion homeostasis / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / non-motile cilium assembly / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / outward rectifier potassium channel activity /  CaM pathway / intestinal absorption / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / CaM pathway / intestinal absorption / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers /  regulation of heart contraction / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / monoatomic ion channel complex / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / ciliary base / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / organelle localization by membrane tethering / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / autophagosome membrane docking / positive regulation of heart rate / neuronal cell body membrane / cochlea development / renal absorption / sodium ion transport / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart contraction / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / monoatomic ion channel complex / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / ciliary base / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / organelle localization by membrane tethering / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / autophagosome membrane docking / positive regulation of heart rate / neuronal cell body membrane / cochlea development / renal absorption / sodium ion transport / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation /  voltage-gated potassium channel activity / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding /  social behavior / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / inner ear development / social behavior / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / inner ear development /  Long-term potentiation / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Long-term potentiation / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT /  catalytic complex / DARPP-32 events / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / potassium channel regulator activity / Smooth Muscle Contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction catalytic complex / DARPP-32 events / detection of calcium ion / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / potassium channel regulator activity / Smooth Muscle Contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contractionSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mackinnon R / Sun J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Authors: Ji Sun / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: KCNQ1, also known as Kv7.1, is a voltage-dependent K channel that regulates gastric acid secretion, salt and glucose homeostasis, and heart rhythm. Its functional properties are regulated in a tissue- ...KCNQ1, also known as Kv7.1, is a voltage-dependent K channel that regulates gastric acid secretion, salt and glucose homeostasis, and heart rhythm. Its functional properties are regulated in a tissue-specific manner through co-assembly with beta subunits KCNE1-5. In non-excitable cells, KCNQ1 forms a complex with KCNE3, which suppresses channel closure at negative membrane voltages that otherwise would close it. Pore opening is regulated by the signaling lipid PIP2. Using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), we show that KCNE3 tucks its single-membrane-spanning helix against KCNQ1, at a location that appears to lock the voltage sensor in its depolarized conformation. Without PIP2, the pore remains closed. Upon addition, PIP2 occupies a site on KCNQ1 within the inner membrane leaflet, which triggers a large conformational change that leads to dilation of the pore's gate. It is likely that this mechanism of PIP2 activation is conserved among Kv7 channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20967.map.gz emd_20967.map.gz | 7.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20967-v30.xml emd-20967-v30.xml emd-20967.xml emd-20967.xml | 12.5 KB 12.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20967.png emd_20967.png | 152 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20967.cif.gz emd-20967.cif.gz | 5.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20967 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20967 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20967 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20967 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6v01MC  6uzzC  6v00C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20967.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20967.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | KCNQ1-KCNE3-CaM complex with PIP2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : KCNQ1-CaM complex
| Entire | Name: KCNQ1-CaM complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: KCNQ1-CaM complex
| Supramolecule | Name: KCNQ1-CaM complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB:  Calmodulin-1 Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 3
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.725399 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: METTNGTETW YESLHAVLKA LNATLHSNLL CRPGPGLGPD NQTEERRASL PGRDDNSYMY ILFVMFLFAV TVGSLILGYT RSRKVDKRS DPYHVYIKNR VSMI UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 3 |
-Macromolecule #3: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.258574 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MASDLGPRPP VSLDPRVSIY STRRPVLART HVQGRVYNFL ERPTGWKCFV YHFAVFLIVL VCLIFSVLST IEQYAALATG TLFWMEIVL VVFFGTEYVV RLWSAGCRSK YVGLWGRLRF ARKPISIIDL IVVVASMVVL CVGSKGQVFA TSAIRGIRFL Q ILRMLHVD ...String: MASDLGPRPP VSLDPRVSIY STRRPVLART HVQGRVYNFL ERPTGWKCFV YHFAVFLIVL VCLIFSVLST IEQYAALATG TLFWMEIVL VVFFGTEYVV RLWSAGCRSK YVGLWGRLRF ARKPISIIDL IVVVASMVVL CVGSKGQVFA TSAIRGIRFL Q ILRMLHVD RQGGTWRLLG SVVFIHRQEL ITTLYIGFLG LIFSSYFVYL AEKDAVNESG RVEFGSYADA LWWGVVTVTT IG YGDKVPQ TWVGKTIASC FSVFAISFFA LPAGILGSGF ALKVQQKQRQ KHFNRQIPAA ASLIQTAWRC YAAENPDSST WKI YIRKAP RSHTLLSPSP KPKKSVVVKK KKFKLDKDNG VTPGEKMLTV PHITCDPPEE RRLDHFSVDG YDSSVRKSPT LLEV SMPHF MRTNSFAEDL DLEGETLLTP ITHISQLREH HRATIKVIRR MQYFVAKKKF QQARKPYDVR DVIEQYSQGH LNLMV RIKE LQRRLDQSIG KPSLFISVSE KSKDRGSNTI GARLNRVEDK VTQLDQRLAL ITDMLHQLLS LHSNSLEVLF QGP UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phospho ryl]oxy-propan-2-yl] (8Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: PT5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.047088 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 94.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 73640 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6v01: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller