+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 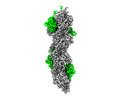 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
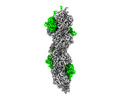
| Title | F-actin decorated by SipA426-685 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Salmonella invasion / CELL INVASION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationStriated Muscle Contraction / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle fiber development /  stress fiber / stress fiber /  actin filament / actin filament /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement /  actin binding / actin binding /  hydrolase activity / extracellular region / hydrolase activity / extracellular region /  ATP binding ATP bindingSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Salmonella (bacteria) / Salmonella (bacteria) /   Gallus gallus (chicken) Gallus gallus (chicken) | |||||||||
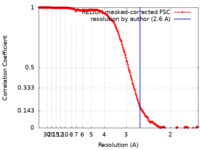
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yuan B / Wald J / Marlovits TC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for subversion of host cell actin cytoskeleton during infection. Authors: Biao Yuan / Jonas Scholz / Jiri Wald / Roland Thuenauer / Rory Hennell James / Irina Ellenberg / Sabine Windhorst / Jan Faix / Thomas C Marlovits /  Abstract: Secreted bacterial type III secretion system (T3SS) proteins are essential for successful infection by many human pathogens. Both T3SS translocator SipC and effector SipA are critical for infection ...Secreted bacterial type III secretion system (T3SS) proteins are essential for successful infection by many human pathogens. Both T3SS translocator SipC and effector SipA are critical for infection by subversion of the host cell cytoskeleton, but the precise molecular interplay between them remains unknown. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy, we show that SipA binds along the F-actin grooves with a unique binding pattern. SipA stabilizes F-actin through charged interface residues and appears to prevent inorganic phosphate release through closure of the "back door" of adenosine 5'-triphosphate pocket. We also show that SipC enhances the binding of SipA to F-actin, thus demonstrating that a sequential presence of T3SS proteins in host cells is associated with a sequence of infection events-starting with actin nucleation, filament growth, and stabilization. Together, our data explain the coordinated interplay of a precisely tuned and highly effective mechanism during infection and provide a blueprint for interfering with effectors acting on actin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16425.map.gz emd_16425.map.gz | 38.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16425-v30.xml emd-16425-v30.xml emd-16425.xml emd-16425.xml | 17.9 KB 17.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16425_fsc.xml emd_16425_fsc.xml | 18.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_16425.png emd_16425.png | 56.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16425.cif.gz emd-16425.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16425_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16425_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16425_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16425_half_map_2.map.gz | 410.6 MB 409.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16425 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16425 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16425 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16425 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 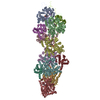 8c4eMC 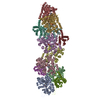 8c4cC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16425.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16425.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_16425_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_16425_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : F-actin polymerized by SipA497-669 under low-salt conditions
| Entire | Name: F-actin polymerized by SipA497-669 under low-salt conditions |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: F-actin polymerized by SipA497-669 under low-salt conditions
| Supramolecule | Name: F-actin polymerized by SipA497-669 under low-salt conditions type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: actin binding domain SipA-C
| Supramolecule | Name: actin binding domain SipA-C / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 / Details: SipA426-685 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Salmonella (bacteria) / Strain: LT2 Salmonella (bacteria) / Strain: LT2 |
-Supramolecule #3: F-actin
| Supramolecule | Name: F-actin / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Gallus gallus (chicken) Gallus gallus (chicken) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number:  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Gallus gallus (chicken) Gallus gallus (chicken) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.109973 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIE(HIC)G IIT NWDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLD SG DGVTHNVPIY ...String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIE(HIC)G IIT NWDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLD SG DGVTHNVPIY EGYALPHAIM RLDLAGRDLT DYLMKILTER GYSFVTTAER EIVRDIKEKL CYVALDFENE MATAASSS S LEKSYELPDG QVITIGNERF RCPETLFQPS FIGMESAGIH ETTYNSIMKC DIDIRKDLYA NNVMSGGTTM YPGIADRMQ KEITALAPST MKIKIIAPPE RKYSVWIGGS ILASLSTFQQ MWITKQEYDE AGPSIVHRKC F UniProtKB:  Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Cell invasion protein SipA
| Macromolecule | Name: Cell invasion protein SipA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Salmonella (bacteria) Salmonella (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.413857 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: TGETTSFDEV DGVTSKSIIG KPVQATVHGV DDNKQQSQTA EIVNVKPLAS QLAGVENVKT DTLQSDTTVI TGNKAGTTDN DNSQTDKTG PFSGLKFKQN SFLSTVPSVT NMHSMHFDAR ETFLGVIRKA LEPDTSTPFP VRRAFDGLRA EILPNDTIKS A ALKAQCSD ...String: TGETTSFDEV DGVTSKSIIG KPVQATVHGV DDNKQQSQTA EIVNVKPLAS QLAGVENVKT DTLQSDTTVI TGNKAGTTDN DNSQTDKTG PFSGLKFKQN SFLSTVPSVT NMHSMHFDAR ETFLGVIRKA LEPDTSTPFP VRRAFDGLRA EILPNDTIKS A ALKAQCSD IDKHPELKAK METLKEVITH HPQKEKLAEI ALQFAREAGL TRLKGETDYV LSNVLDGLIG DGSWRAGPAY ES YLNKPGV DRVITTVDGL HMQR UniProtKB: Cell invasion protein SipA |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Details: 5 mM Tris buffer, pH 7.5, 0.1 mM DTT, 0.2 mM ATP, 0.2 mM EGTA and 0.05 mM MgCl2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 3.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8c4e: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z
Z Y
Y X
X